Question: ***** printf(%s, prime_vector(3)[0]); should equal 4 ******* In C (30 points) Implement a function unsigned char *prime_vector(unsigned long num) that accepts a number num and
![***** printf("%s", prime_vector(3)[0]); should equal 4 ******* In C (30 points)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f53a7dc8bed_32566f53a7d49b00.jpg)
***** printf("%s", prime_vector(3)[0]); should equal 4 *******
In C
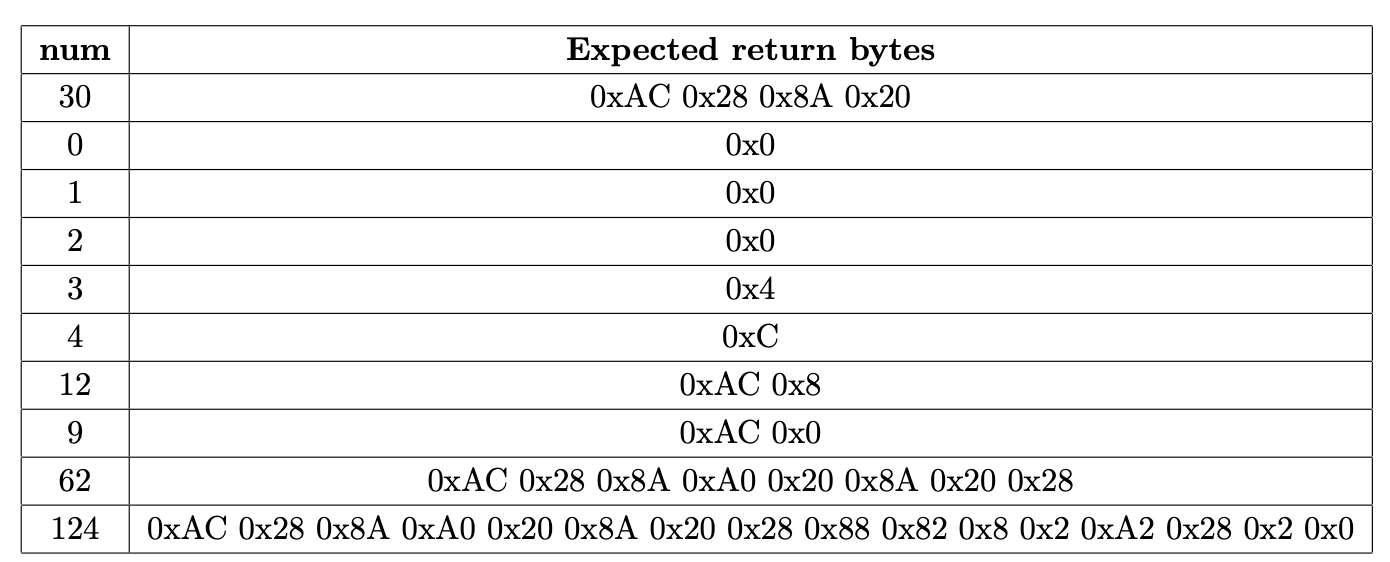
(30 points) Implement a function unsigned char *prime_vector(unsigned long num) that accepts a number num and returns a bit vector that indicates all the prime numbers less than number num. You must allocate the appropriate amount of memory. For example, if num is 12, then the return character array must have 2 bytes with the following bit configuration: 15 14 12 11 10 9 8 Bit number Value in Binary Value in Hex 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 0 1 1 OxAC 1 0 0 0 13 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0x8 Notice that all the bits in the last byte that correspond to num or above is set to 0 even though there may be a prime within (e.g., 13). Here is another example if num is 30. 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 OxAC 0x28 23 22 21 18 17 16 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 31 0 1 0 20 19 0 1 0x8A 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 Ox20 You are encouraged to implement helper functions (e.g., is-prime, set_bit). num 30 0 1 2 3 4 Expected return bytes OxAC 0x28 0x8A 0x20 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x4 OxC OxAC 0x8 OxAC Ox0 OxAC 0x28 0x8A OxAO Ox20 0x8A 0x20 Ox28 OxAC 0x28 0x8A OxAO Ox20 0x8A 0x20 Ox28 0x88 0x82 0x8 0x2 OxA2 0x28 0x2 0x0 12 9 62 124
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


