Question: Problem 1 ( 2 5 points ) Let we are analyzing a non zero - sum game. The tree of this game is shown in
Problem points
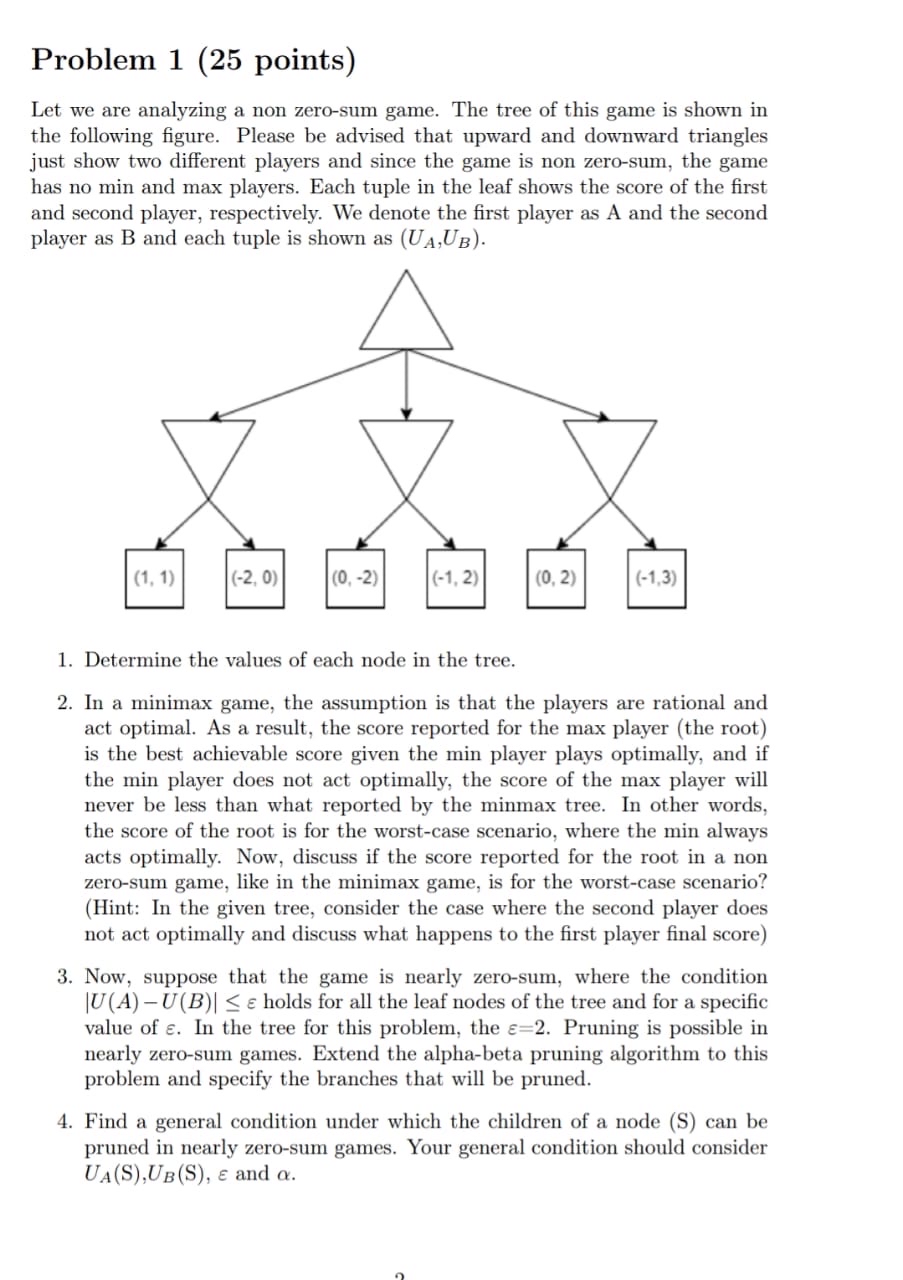
Let we are analyzing a non zerosum game. The tree of this game is shown in the following figure. Please be advised that upward and downward triangles just show two different players and since the game is non zerosum, the game has no min and max players. Each tuple in the leaf shows the score of the first and second player, respectively. We denote the first player as A and the second player as B and each tuple is shown as
Determine the values of each node in the tree.
In a minimax game, the assumption is that the players are rational and act optimal. As a result, the score reported for the max player the root is the best achievable score given the min player plays optimally, and if the min player does not act optimally, the score of the max player will never be less than what reported by the minmax tree. In other words, the score of the root is for the worstcase scenario, where the min always acts optimally. Now, discuss if the score reported for the root in a non zerosum game, like in the minimax game, is for the worstcase scenario? Hint: In the given tree, consider the case where the second player does not act optimally and discuss what happens to the first player final score
Now, suppose that the game is nearly zerosum, where the condition holds for all the leaf nodes of the tree and for a specific value of In the tree for this problem, the Pruning is possible in nearly zerosum games. Extend the alphabeta pruning algorithm to this problem and specify the branches that will be pruned.
Find a general condition under which the children of a node S can be pruned in nearly zerosum games. Your general condition should consider and
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


