Question: Problem 1: A baseball catcher is performing a stunt for a television commercial. He will catch a baseball with mass mm = I .73 g,

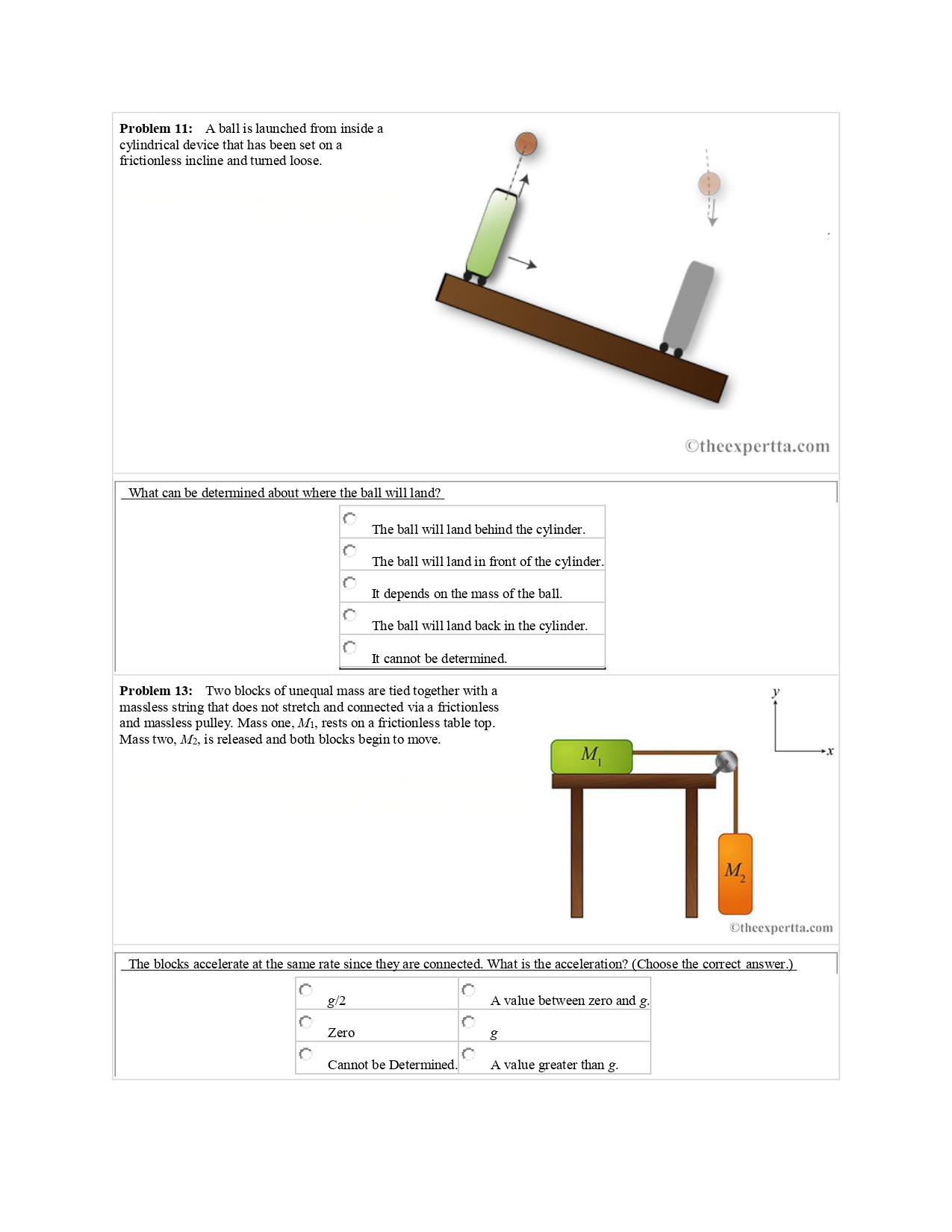



Problem 1: A baseball catcher is performing a stunt for a television commercial. He will catch a baseball with mass mm = I .73 g, dropped from rest at a height yy = 24'. 6 m above his glove. The glove brings the ball to a complete stop in time tgiavet glove = 0. 065 seconds after the ball hits the glove. Part (:1) Use your understanding of kinematic equations to write a formula for the time that the ball is falling before it hits the glove tighttlght. Use variables from the problem statement alongside gg for the acceleration due to gravity to write your equation. Part (1)) What is the amount of time tighttlght in seconds the ball takes to hit the glove after it is dropped? Part (c) Write an equation for the speed of the ball nggjust before it hits the glove. Use gg for the acceleration due to gravity and tighttight for the time it takes for the ball to hit the glove after it is dropped. Part ((1) Find the speed of the ball ngg in meters per second at the moment it first touches the glove. Part (e) Considering the amount of time tgiovet glove it took for the glove to stop the ball nd the magnitude of the net force on the ball in newtons while it is in the glove. Problem 2: A boxer's st and glove have a mass of m = 0. '6 kg. The boxer's st can obtain a speed ofv = 725 mfs in a time off: 0,275. 'Part (:1) Find the magnitude of the average acceleration mg. in meters per square second. of the boxer's st. Part (1)) How much force did the boxer apply to his fistfglove. in newtons? lProblem 3: Consider the quantities weight and mass. 'Which of the following statements is true? r" An object has the same weight on the Moon and the Earth. f" Both weight and mass can be considered vector quantities. F Weight and mass are different names for the same quantity. r An object has the same mass on the Moon and the Earth. f. Weight and mass have the same units. Problem 11: A ball is launched from inside a cylindrical device that has been set on a frictionless incline and turned loose. Otheexpertta.com What can be determined about where the ball will land? The ball will land behind the cylinder. O The ball will land in front of the cylinder. It depends on the mass of the ball. The ball will land back in the cylinder. It cannot be determined Problem 13: Two blocks of unequal mass are tied together with a massless string that does not stretch and connected via a frictionless and massless pulley. Mass one, Mi, rests on a frictionless table top. Mass two, M2, is released and both blocks begin to move. M, -x M, Otheexpertta.com The blocks accelerate at the same rate since they are connected. What is the acceleration? (Choose the correct answer.) C 8/2 A value between zero and g. O Zero g O Cannot be Determined. A value greater than g.P1'oblem4: Jennifer is a gymnast with a mass of m=m:45. 3 kg. She jumps on a trampoline which provides and upward force of magnitude FtF t. Her resulting acceleration is upward with magnitude a=a=6. 01 n1/sszs2. Part (a) Write an expression for the magnitude of the net force Jennifer experiences using variables from the problem statement and gg (the acceleration of gravity near Earth's surface). Part 11)] What is the magnitude of the force, FtFt in newtons? l Problem 5: A car and a dump truck are involved in an accident and crash into each other. Assuming the only force acting is the force of collision. which one experiences the most force I during the crash - the car or the dump truck? l'" It depends on which one is moving faster. The dump truck. The car. It depends on the angle of their collision. "11'3\"? They experience the same size force. FnetFI] Problem 6: Suppose two children push horizontally, but in exactly opposite directions. on a third child in a sled. The first child exerts a force of 78 N. the second a force of 91 N. kinetic friction is 5.5 N, and the mass of the third child plus sled is 22.5 kg. Using a coordinate system where the second child is pushing in the positive direction, calculate the acceleration in mfsg. Problem 7: Two children pull a third child backwards on a snow-saucer sled exerting forces F1 = 13.5 Nand F2 = 7.5 N, as shown in the gure. Note that the direction ofthe iction force, f : 5. 7N, is unspecied; it will be opposite in direction to the sum of the other two forces. f.' .' I thccx its: a.- R I Part (3) Find the magnitude. in meters per squared second. of the acceleration of the 48 kg sled and child system. a: ............ m/SZ Part (D) Let east be towards the right of the sketch, and let north be towards the top of the sketch. Assuming the sled starts at rest, nd the direction of the velocity in degrees north of east. Problem 8: A 38 kg dolphin moving in the positive direction decelerates om 13 to 9.5 m/s in 2.45 s to join another dolphin in play. What average force, in newtons, was exerted to slow him if he was moving horizontally? (The gravitational force is balanced by the buoyant force of the water.)_ Problem 9: A basketball player jumps straight up for a ball. To do this, he lowers his body 0.315 m and then accelerates through this distance by forcefully straightening his legs. This player leaves the floor with a vertical velocity sufficient to carry him 0.89 m above the floor. For this problem, use a coordinate system where up is positive. Part (a) Calculate his velocity when he leaves the floor in m/s. vo = b) Calculate his acceleration, in m/'s2, while he is straightening his legs. He goes from zero to the velocity found in part a) in a distance of 0.315 m. a = Part (c) Calculate the magnitude of the force he exerts on the floor to do this, in newtons, given that his mass is 112 kg. F= Problem 10: Given Newton's First Law of Motion, what do we reasonably expect an object to do given the following scenarios?Part (a) An object sits at rest with no unbalanced forces acting upon it. What do we expect this object to do? O The object will begin to move with a changing velocity . None of these answers. The object will remain at rest. The object will begin to move at a constant velocity. Part (b) An object is traveling with a constant velocity with no unbalanced forces acting upon it. What do we expect this object to do? The object will begin to spin as it slows down. The object will remain at the same speed but change direction. The object will slow down and eventually come to rest. None of these answers. The object will remain at the same speed, traveling in the same direction. The object will speed up. Part (c) An object sits at rest with an unbalanced force acting upon it. What should we not expect this object to do? Asking another way, which of the following choices could not be an outcome? The object will begin to move with a changing velocity. None of these answers. The object will remain at rest. O The object will begin to move and then move with a constant velocity
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


