Question: Problem 1. (Chapter 3 Aggregate Planning) Skycell, a major European cell phone manufacturer, is making production plans for the coming year. Skycell has worked with
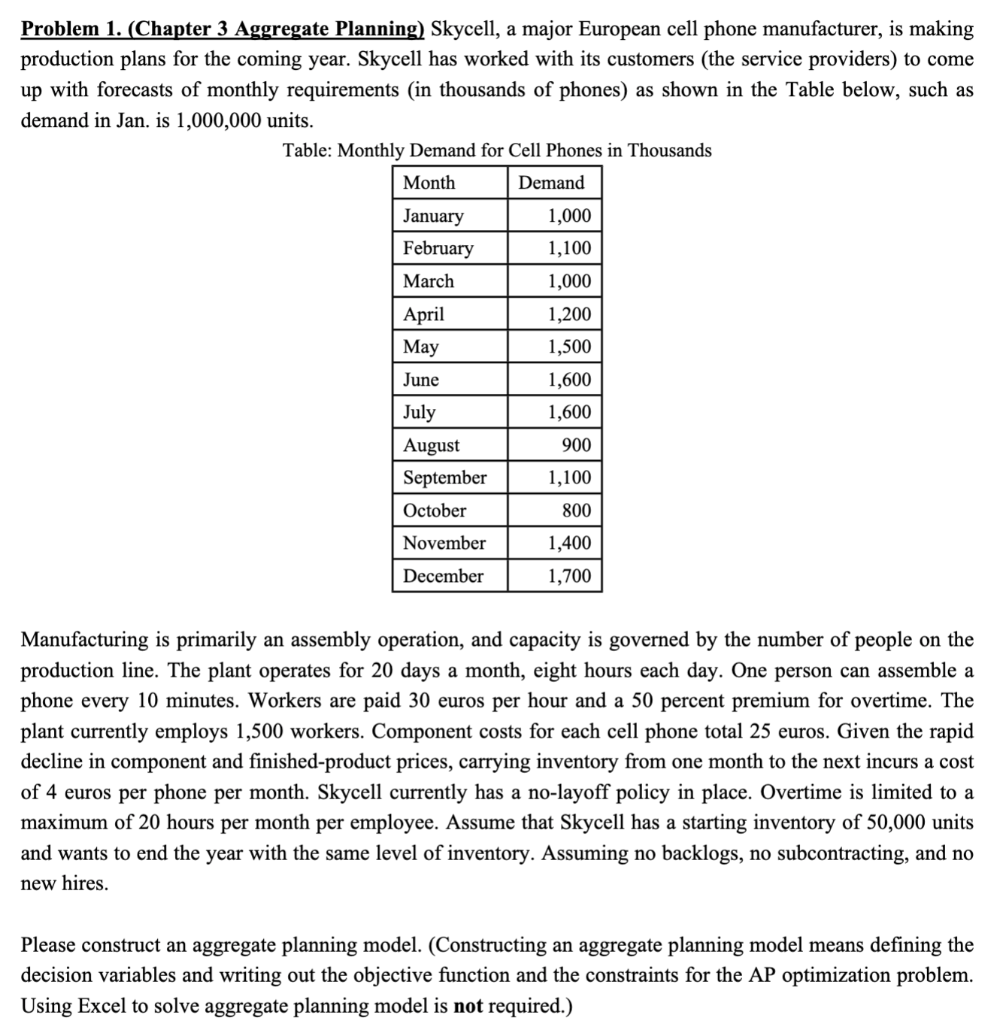
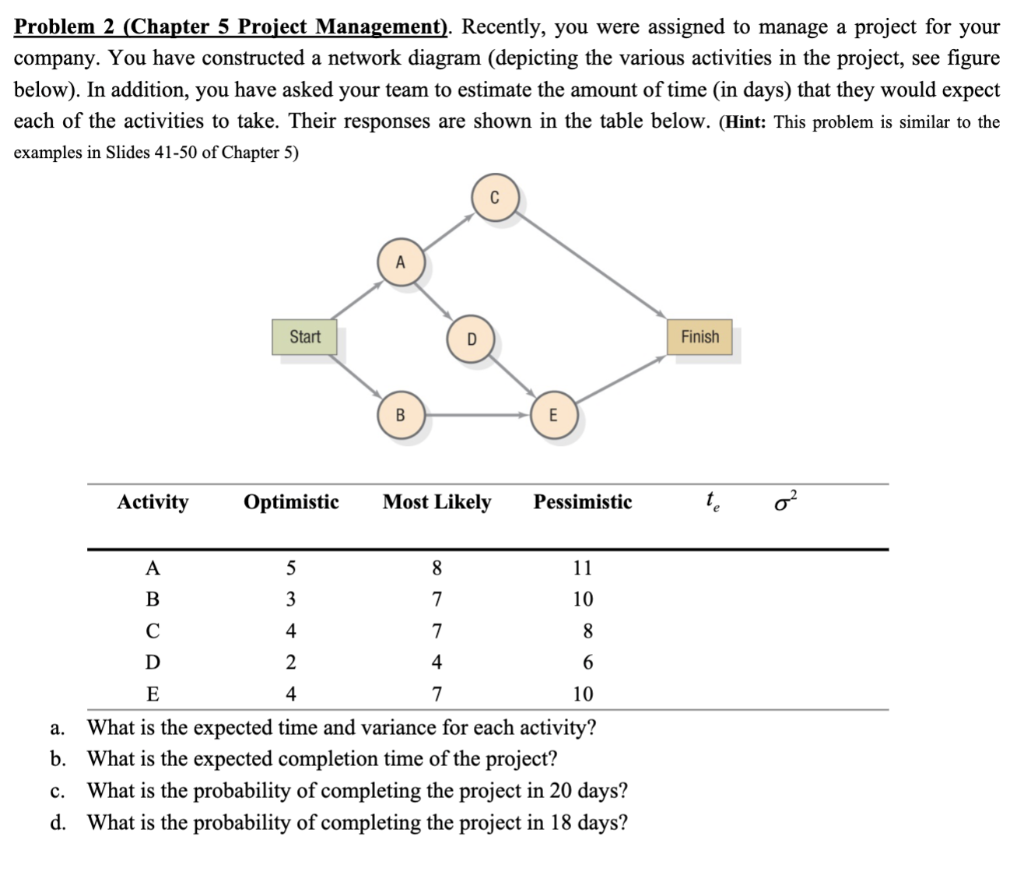
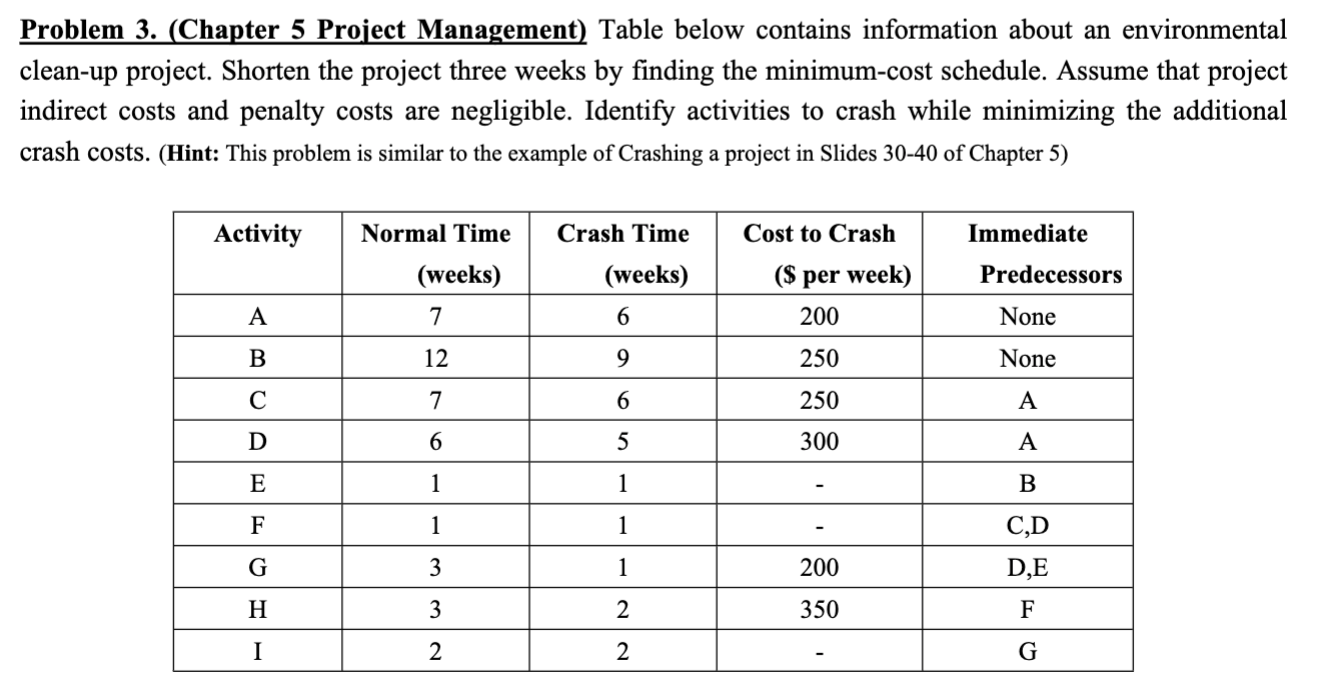
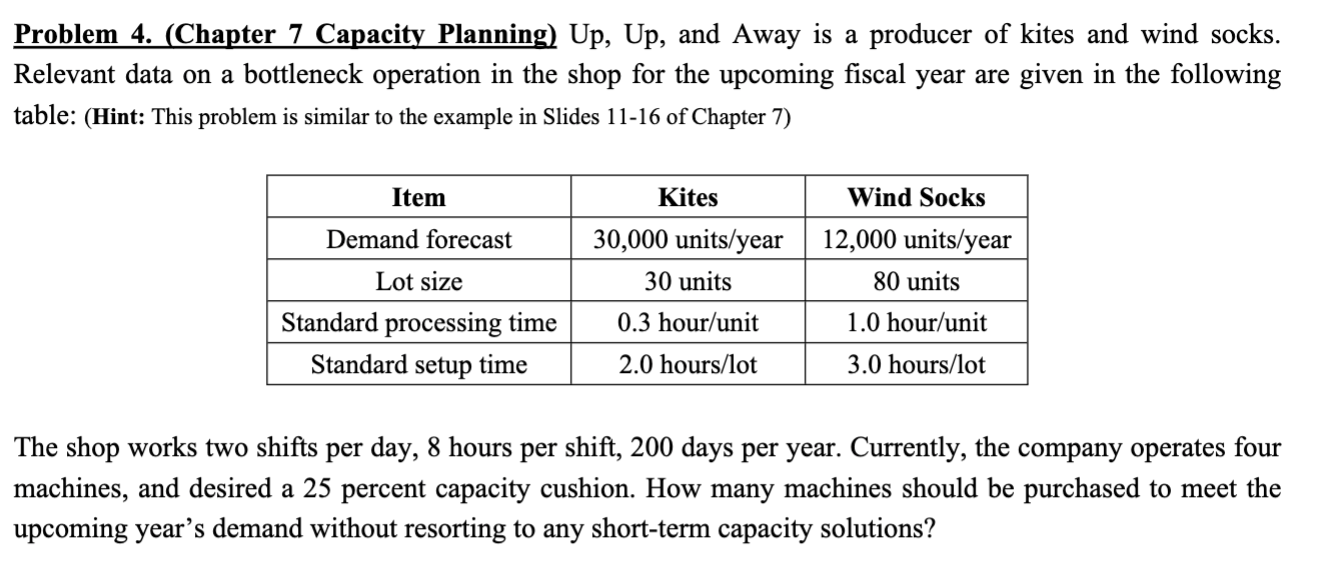
Problem 1. (Chapter 3 Aggregate Planning) Skycell, a major European cell phone manufacturer, is making production plans for the coming year. Skycell has worked with its customers (the service providers) to come up with forecasts of monthly requirements (in thousands of phones) as shown in the Table below, such as demand in Jan. is 1,000,000 units. Table: Monthly Demand for Cell Phones in Thousands Manufacturing is primarily an assembly operation, and capacity is governed by the number of people on the production line. The plant operates for 20 days a month, eight hours each day. One person can assemble a phone every 10 minutes. Workers are paid 30 euros per hour and a 50 percent premium for overtime. The plant currently employs 1,500 workers. Component costs for each cell phone total 25 euros. Given the rapid decline in component and finished-product prices, carrying inventory from one month to the next incurs a cost of 4 euros per phone per month. Skycell currently has a no-layoff policy in place. Overtime is limited to a maximum of 20 hours per month per employee. Assume that Skycell has a starting inventory of 50,000 units and wants to end the year with the same level of inventory. Assuming no backlogs, no subcontracting, and no new hires. Please construct an aggregate planning model. (Constructing an aggregate planning model means defining the decision variables and writing out the objective function and the constraints for the AP optimization problem. Using Excel to solve aggregate planning model is not required.) Problem 2 (Chapter 5 Project Management). Recently, you were assigned to manage a project for your company. You have constructed a network diagram (depicting the various activities in the project, see figure below). In addition, you have asked your team to estimate the amount of time (in days) that they would expect each of the activities to take. Their responses are shown in the table below. (Hint: This problem is similar to the examples in Slides 41-50 of Chapter 5) a. What is the expected time and variance for each activity? b. What is the expected completion time of the project? c. What is the probability of completing the project in 20 days? d. What is the probability of completing the project in 18 days? Problem 3. (Chapter 5 Project Management) Table below contains information about an environmental clean-up project. Shorten the project three weeks by finding the minimum-cost schedule. Assume that project indirect costs and penalty costs are negligible. Identify activities to crash while minimizing the additional crash costs. (Hint: This problem is similar to the example of Crashing a project in Slides 3040 of Chapter 5) Problem 4. (Chapter 7 Capacity Planning) Up, Up, and Away is a producer of kites and wind socks. Relevant data on a bottleneck operation in the shop for the upcoming fiscal year are given in the following table: (Hint: This problem is similar to the example in Slides 11-16 of Chapter 7) The shop works two shifts per day, 8 hours per shift, 200 days per year. Currently, the company operates four machines, and desired a 25 percent capacity cushion. How many machines should be purchased to meet the upcoming year's demand without resorting to any short-term capacity solutions? Problem 1. (Chapter 3 Aggregate Planning) Skycell, a major European cell phone manufacturer, is making production plans for the coming year. Skycell has worked with its customers (the service providers) to come up with forecasts of monthly requirements (in thousands of phones) as shown in the Table below, such as demand in Jan. is 1,000,000 units. Table: Monthly Demand for Cell Phones in Thousands Manufacturing is primarily an assembly operation, and capacity is governed by the number of people on the production line. The plant operates for 20 days a month, eight hours each day. One person can assemble a phone every 10 minutes. Workers are paid 30 euros per hour and a 50 percent premium for overtime. The plant currently employs 1,500 workers. Component costs for each cell phone total 25 euros. Given the rapid decline in component and finished-product prices, carrying inventory from one month to the next incurs a cost of 4 euros per phone per month. Skycell currently has a no-layoff policy in place. Overtime is limited to a maximum of 20 hours per month per employee. Assume that Skycell has a starting inventory of 50,000 units and wants to end the year with the same level of inventory. Assuming no backlogs, no subcontracting, and no new hires. Please construct an aggregate planning model. (Constructing an aggregate planning model means defining the decision variables and writing out the objective function and the constraints for the AP optimization problem. Using Excel to solve aggregate planning model is not required.) Problem 2 (Chapter 5 Project Management). Recently, you were assigned to manage a project for your company. You have constructed a network diagram (depicting the various activities in the project, see figure below). In addition, you have asked your team to estimate the amount of time (in days) that they would expect each of the activities to take. Their responses are shown in the table below. (Hint: This problem is similar to the examples in Slides 41-50 of Chapter 5) a. What is the expected time and variance for each activity? b. What is the expected completion time of the project? c. What is the probability of completing the project in 20 days? d. What is the probability of completing the project in 18 days? Problem 3. (Chapter 5 Project Management) Table below contains information about an environmental clean-up project. Shorten the project three weeks by finding the minimum-cost schedule. Assume that project indirect costs and penalty costs are negligible. Identify activities to crash while minimizing the additional crash costs. (Hint: This problem is similar to the example of Crashing a project in Slides 3040 of Chapter 5) Problem 4. (Chapter 7 Capacity Planning) Up, Up, and Away is a producer of kites and wind socks. Relevant data on a bottleneck operation in the shop for the upcoming fiscal year are given in the following table: (Hint: This problem is similar to the example in Slides 11-16 of Chapter 7) The shop works two shifts per day, 8 hours per shift, 200 days per year. Currently, the company operates four machines, and desired a 25 percent capacity cushion. How many machines should be purchased to meet the upcoming year's demand without resorting to any short-term capacity solutions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Lets tackle each problem one by one Problem 1 Aggregate Planning for Skycell Step 1 Define Decision Variables Pt Number of phones produced in month t ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


