Question: Problem 1: Define a function with the following signature: def upperRightTriangleSum(L): The argument L represents an nn matrix, specified as nested lists. More precisely, L
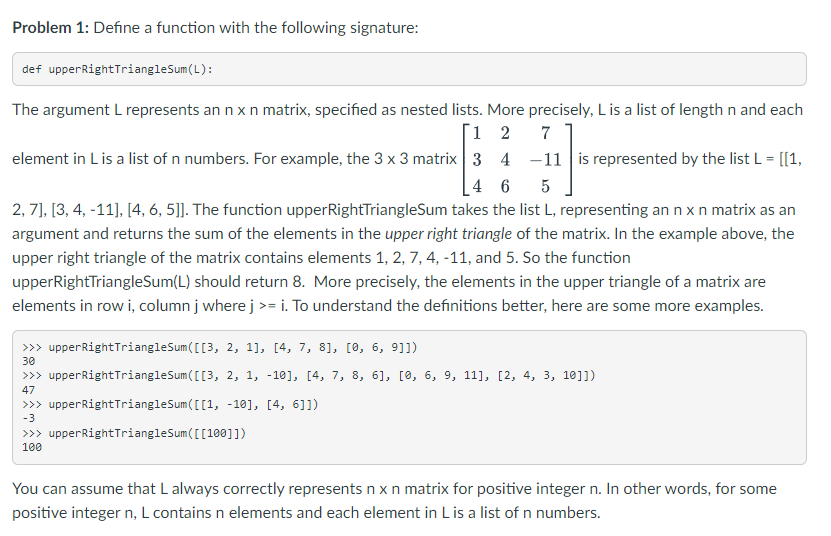
Problem 1: Define a function with the following signature: def upperRightTriangleSum(L): The argument L represents an nn matrix, specified as nested lists. More precisely, L is a list of length n and each element in L is a list of n numbers. For example, the 33 matrix 1342467115 is represented by the list L=[[1, 2,7],[3,4,11],[4,6,5]]. The function upperRightTriangleSum takes the list L, representing an nn matrix as an argument and returns the sum of the elements in the upper right triangle of the matrix. In the example above, the upper right triangle of the matrix contains elements 1,2,7,4,11, and 5 . So the function upperRightTriangleSum(L) should return 8. More precisely, the elements in the upper triangle of a matrix are elements in row i, column j where j>=i. To understand the definitions better, here are some more examples. > upperRightTriangleSum ([[3,2,1],[4,7,8],[0,6,9]]) 30 > upperRightTriangleSum( [[3,2,1,10],[4,7,8,6],[0,6,9,11],[2,4,3,10]]) 47 upperRightTriangleSum ([[1,10],[4,6]]) 3 upperRightTriangleSum ([[100]]) 100 You can assume that L always correctly represents nn matrix for positive integer n. In other words, for some positive integer n,L contains n elements and each element in L is a list of n numbers
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


