Question: Problem 1: Error of least squares approximation (concept question) Recall that the least squares problem minimizes the overall error of approximation; i.e, it determines fo(x)

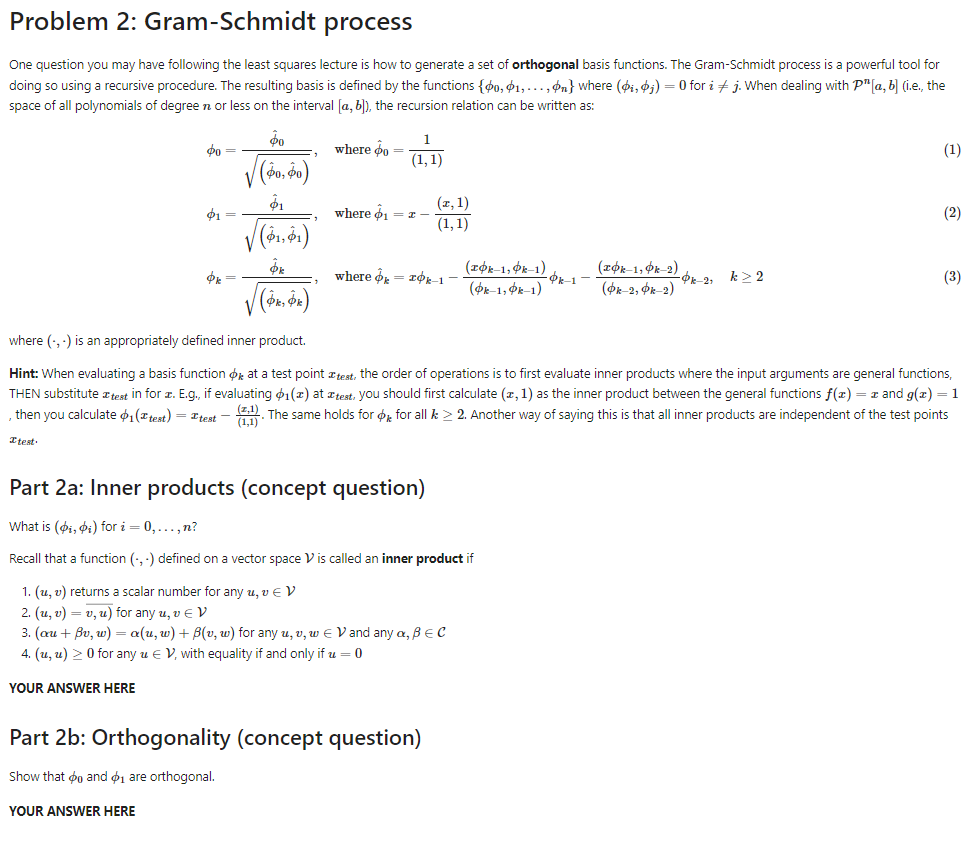

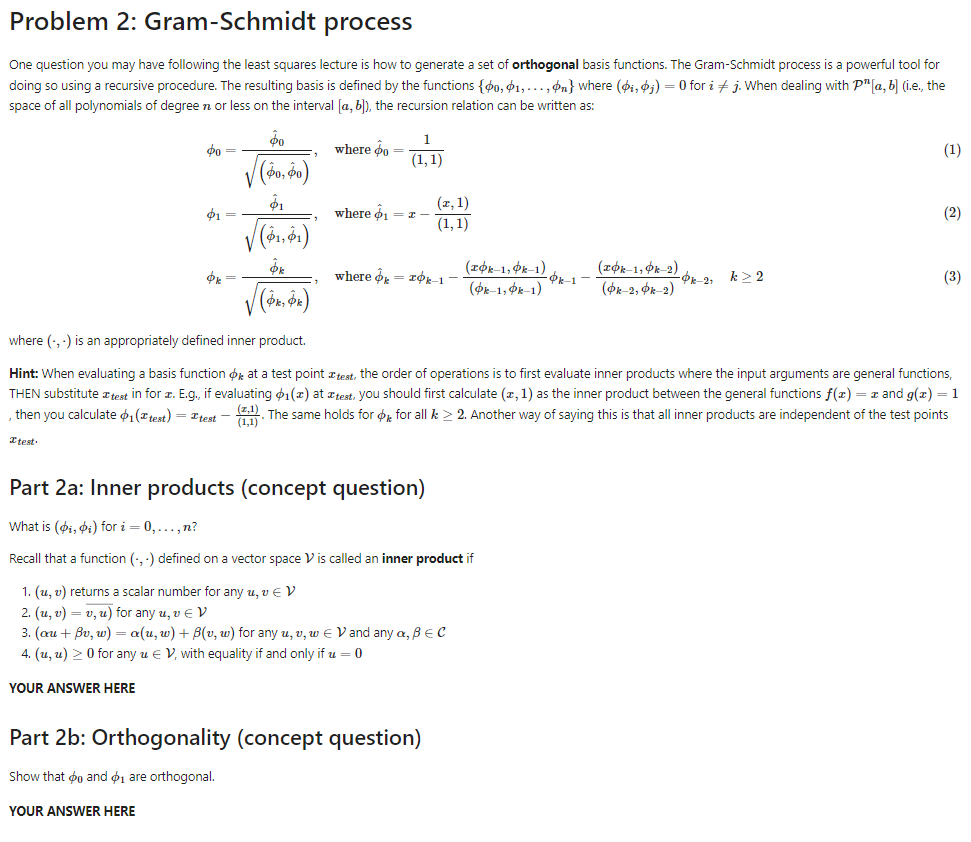
Problem 1: Error of least squares approximation (concept question) Recall that the least squares problem minimizes the overall error of approximation; i.e, it determines fo(x) such that the square of the norm of the error, lle|12 = 1If - fall2 is minimized. Prove that (f - fa, bi) = 0 for di E {bo, . .., $n). Use: . domain [a, b] . basis functions symbolically written as {do, . .., da} . the inner product definition, (u, v) = fru(x)v(x)dx Hint: At the minimum of a function g(a, b, c), = 0Problem 2: Gram-Schmidt process One question you may have following the least squares lecture is how to generate a set of orthogonal basis functions. The Gram-Schmidt process is a powerful tool for doing so using a recursive procedure. The resulting basis is defined by the functions {rumh .. . 1%} where ($55951) = l] forz' a j. when dealing with 'P"[a._l 1:] (Le... the space of all polynomials of degree n. or less on the interval [o. b]], the recursion relation can be written as: le .
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


