Question: Problem 1. Lawson's Department Store faces a buying decision for a seasonal product for which demand can be high, medium or low. The purchaser for
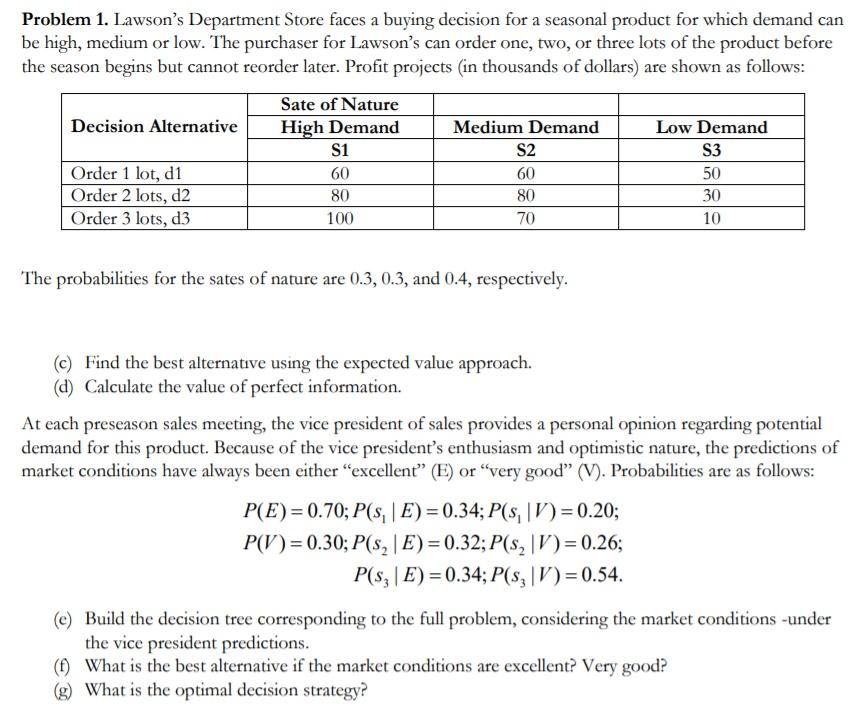
Problem 1. Lawson's Department Store faces a buying decision for a seasonal product for which demand can be high, medium or low. The purchaser for Lawson's can order one, two, or three lots of the product before the season begins but cannot reorder later. Profit projects (in thousands of dollars) are shown as follows: Sate of Nature Decision Alternative High Demand Medium Demand Low Demand S1 S2 S3 Order 1 lot, d1 60 50 Order 2 lots, d2 80 80 30 Order 3 lots, d3 100 70 10 60 The probabilities for the sates of nature are 0.3, 0.3, and 0.4, respectively. (c) Find the best alternative using the expected value approach. (d) Calculate the value of perfect information. At each preseason sales meeting, the vice president of sales provides a personal opinion regarding potential demand for this product. Because of the vice president's enthusiasm and optimistic nature, the predictions of market conditions have always been either "excellent (E) or very good (V). Probabilities are as follows: P(E)= 0.70; P(s, | E)= 0.34;P(s|V=0.20; P(V)= 0.30; P(s| E)=0.32; P(s2 |V)= 0.26; P(sz | E)= 0.34; P(SzIV)=0.54. (e) Build the decision tree corresponding to the full problem, considering the market conditions -under the vice president predictions. (1) What is the best alternative if the market conditions are excellent? Very good? (g) What is the optimal decision strategy? Problem 1. Lawson's Department Store faces a buying decision for a seasonal product for which demand can be high, medium or low. The purchaser for Lawson's can order one, two, or three lots of the product before the season begins but cannot reorder later. Profit projects (in thousands of dollars) are shown as follows: Sate of Nature Decision Alternative High Demand Medium Demand Low Demand S1 S2 S3 Order 1 lot, d1 60 50 Order 2 lots, d2 80 80 30 Order 3 lots, d3 100 70 10 60 The probabilities for the sates of nature are 0.3, 0.3, and 0.4, respectively. (c) Find the best alternative using the expected value approach. (d) Calculate the value of perfect information. At each preseason sales meeting, the vice president of sales provides a personal opinion regarding potential demand for this product. Because of the vice president's enthusiasm and optimistic nature, the predictions of market conditions have always been either "excellent (E) or very good (V). Probabilities are as follows: P(E)= 0.70; P(s, | E)= 0.34;P(s|V=0.20; P(V)= 0.30; P(s| E)=0.32; P(s2 |V)= 0.26; P(sz | E)= 0.34; P(SzIV)=0.54. (e) Build the decision tree corresponding to the full problem, considering the market conditions -under the vice president predictions. (1) What is the best alternative if the market conditions are excellent? Very good? (g) What is the optimal decision strategy





