Question: Problem 1: Options Basics (5 points) Imagine AAPL stock closed at $520 on November 15th. At that time, the following options were traded for AAPL
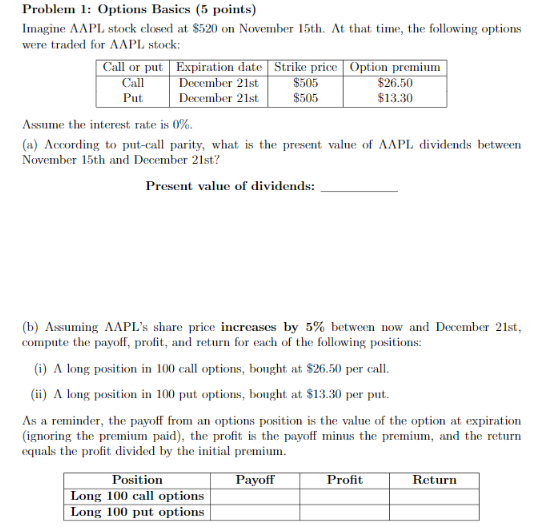
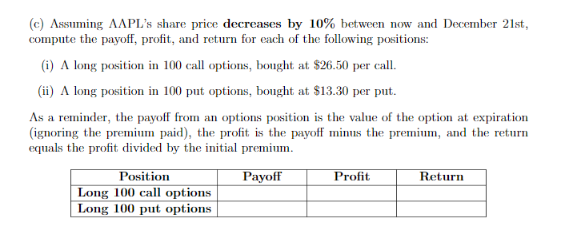
Problem 1: Options Basics (5 points) Imagine AAPL stock closed at $520 on November 15th. At that time, the following options were traded for AAPL stock: Call or put Expiration dateStrike price Option premium Call Put December 21st December 21st 505 $505 26.50 $13.30 Assume the interest rate is 0% (a) According to put-c parity, what is the present value of AAPL dividends between November 15th and December 21st? Present value of dividends: (b) Assuming AAPL's share price increases by 5% between now and December 21st compute the payoff, profit, and return for each of the following positions: (i) A long position in 100 call options, bought at $26.50 per call (ii) A long position in 100 put options, bought at $13.30 per put. As a reminder, the payoff from an options position is the value of the option at expiration (ignoring the premium paid), the profit is the payoff minus the premim, and the return equals the profit divided by the initial premium. Position Payoff Profit Return ng 100 call options Long 100 put options Problem 1: Options Basics (5 points) Imagine AAPL stock closed at $520 on November 15th. At that time, the following options were traded for AAPL stock: Call or put Expiration dateStrike price Option premium Call Put December 21st December 21st 505 $505 26.50 $13.30 Assume the interest rate is 0% (a) According to put-c parity, what is the present value of AAPL dividends between November 15th and December 21st? Present value of dividends: (b) Assuming AAPL's share price increases by 5% between now and December 21st compute the payoff, profit, and return for each of the following positions: (i) A long position in 100 call options, bought at $26.50 per call (ii) A long position in 100 put options, bought at $13.30 per put. As a reminder, the payoff from an options position is the value of the option at expiration (ignoring the premium paid), the profit is the payoff minus the premim, and the return equals the profit divided by the initial premium. Position Payoff Profit Return ng 100 call options Long 100 put options
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


