Question: Problem 1. The Black-Scholes model is not only useful for pricing individual European options, it is also useful for pricing trading strategies that are combinations
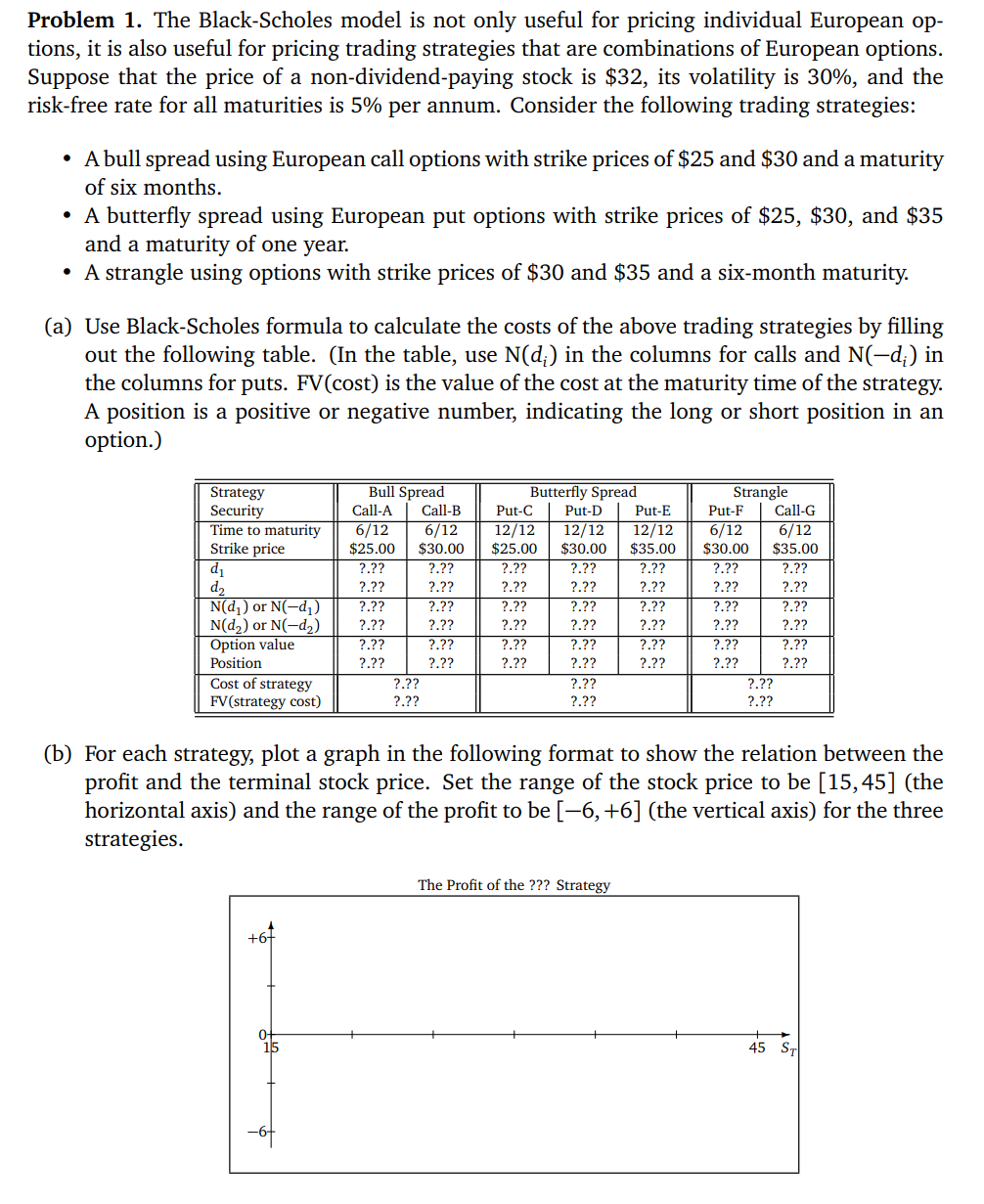
Problem 1. The Black-Scholes model is not only useful for pricing individual European options, it is also useful for pricing trading strategies that are combinations of European options. Suppose that the price of a non-dividend-paying stock is $32, its volatility is 30%, and the risk-free rate for all maturities is 5% per annum. Consider the following trading strategies: - A bull spread using European call options with strike prices of $25 and \$30 and a maturity of six months. - A butterfly spread using European put options with strike prices of $25,$30, and $35 and a maturity of one year. - A strangle using options with strike prices of \$30 and \$35 and a six-month maturity. (a) Use Black-Scholes formula to calculate the costs of the above trading strategies by filling out the following table. (In the table, use N(di) in the columns for calls and N(di) in the columns for puts. FV(cost) is the value of the cost at the maturity time of the strategy. A position is a positive or negative number, indicating the long or short position in an option.) (b) For each strategy, plot a graph in the following format to show the relation between the profit and the terminal stock price. Set the range of the stock price to be [15,45] (the horizontal axis) and the range of the profit to be [6,+6] (the vertical axis) for the three strategies
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


