Question: Problem 10.3. The graph below shows the daily demand for labor at Leisure Lawn, a small landscape maintenance company. The graph also includes the corresponding
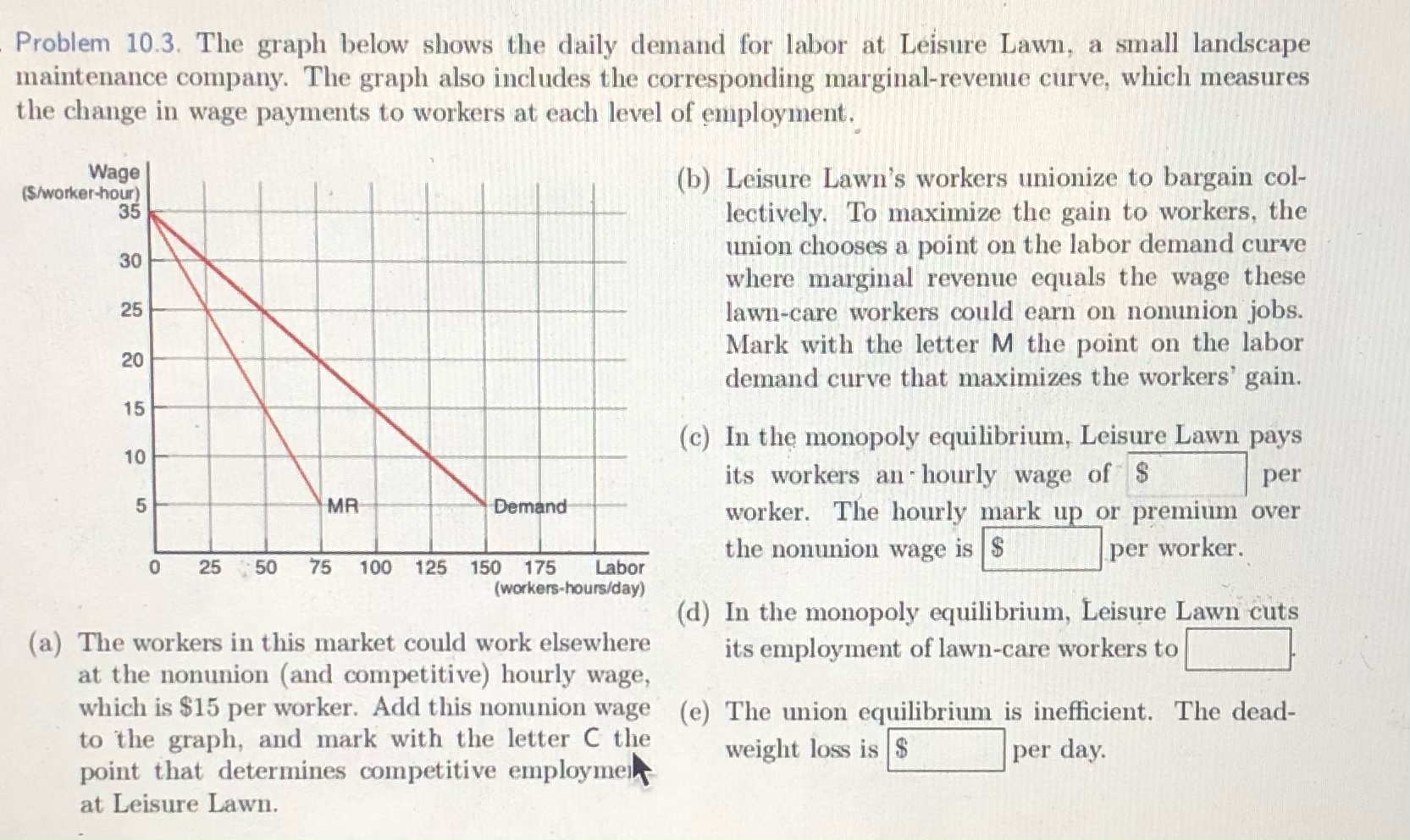
Problem 10.3. The graph below shows the daily demand for labor at Leisure Lawn, a small landscape maintenance company. The graph also includes the corresponding marginal-revenue curve, which measures the change in wage payments to workers at each level of employment. Wage ($/worker-hour) (b) Leisure Lawn's workers unionize to bargain col- 35 lectively. To maximize the gain to workers, the 30 union chooses a point on the labor demand curve where marginal revenue equals the wage these 25 lawn-care workers could earn on nonunion jobs. 20 Mark with the letter M the point on the labor demand curve that maximizes the workers' gain. 15 10 (c) In the monopoly equilibrium, Leisure Lawn pays its workers an hourly wage of $ per 5 MR Demand worker. The hourly mark up or premium over 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 Labor the nonunion wage is $ per worker. (workers-hours/day) (a) The workers in this market could work elsewhere (d) In the monopoly equilibrium, Leisure Lawn cuts at the nonunion (and competitive) hourly wage, its employment of lawn-care workers to which is $15 per worker. Add this nonunion wage to the graph, and mark with the letter C the (e) The union equilibrium is inefficient. The dead- point that determines competitive employment weight loss is $ per day. at Leisure Lawn
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


