Question: Problem 2. (1 point) Assume F() is a continuous differentiable function such that F(0) = 3 and F(1) = 5. Let f(x) be the derivative
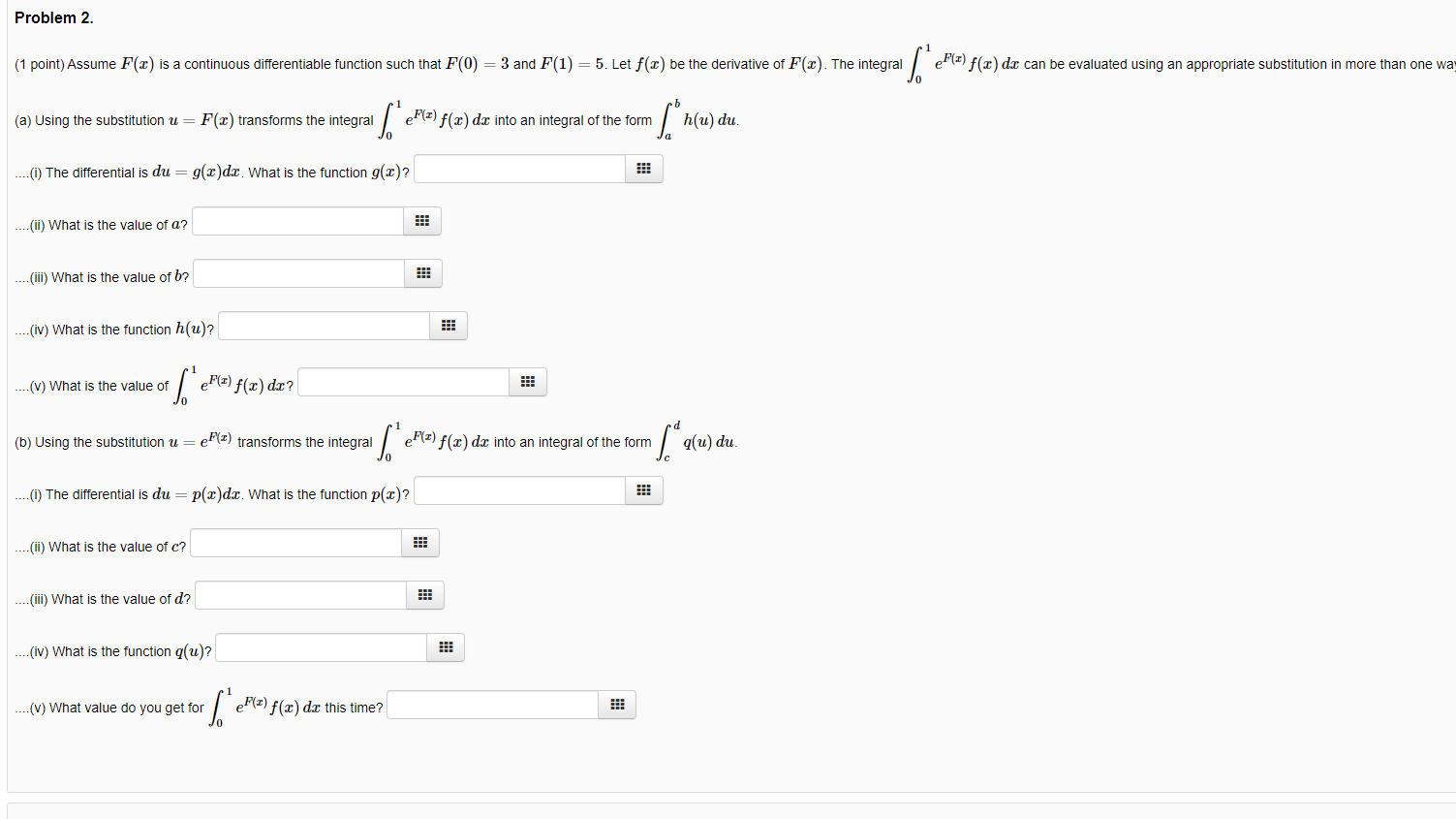
Problem 2. (1 point) Assume F() is a continuous differentiable function such that F(0) = 3 and F(1) = 5. Let f(x) be the derivative of F(x). The integral / e"(T) f(x) dax can be evaluated using an appropriate substitution in more than one wa (a) Using the substitution u = F(x) transforms the integral / e"() f(x) dax into an integral of the form / h(u) du. ....(1) The differential is du = g(x)dx. What is the function g(x)? ....(ii) What is the value of a? ..(iii) What is the value of b? ..(iv) What is the function h(u)? ...(V) What is the value of / eF(:) f(x) dx? (b) Using the substitution u = e"() transforms the integral / eF(x) f(x) da into an integral of the form / q(u) du. ....(i) The differential is du = p(x)dx. What is the function p(I)? .(ii) What is the value of c? ...(ili) What is the value of d? ....(iv) What is the function q(u)? ....(V) What value do you get for / eF(x) f(x) dx this time
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


