Question: Problem 2. (30 points total, 2a to 2e) The coronavirus pandemic has greatly increased the demand for disinfectants, with ethanol emerging as one of the


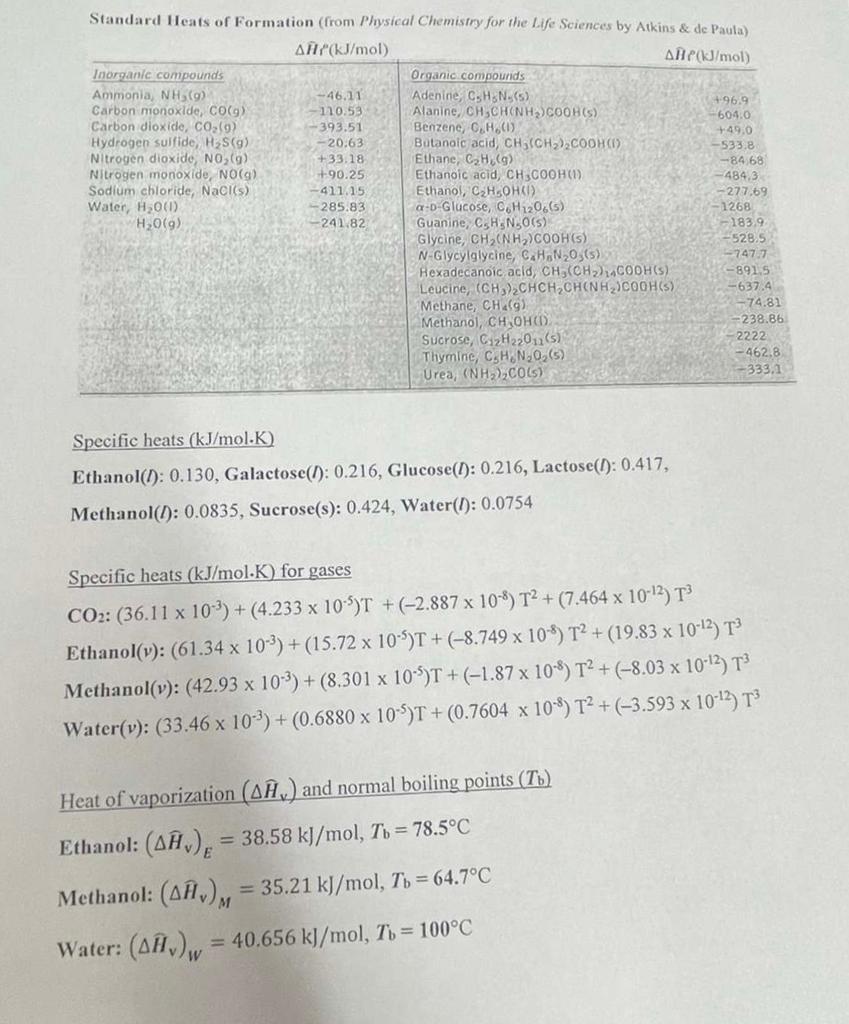
Problem 2. (30 points total, 2a to 2e) The coronavirus pandemic has greatly increased the demand for disinfectants, with ethanol emerging as one of the most used. Ethanol (C2H5OH) is usually manufactured by using yeasts cultured in bioreactors to convert sucrose (C12H22011) to ethanol. The overall equation for the reaction may be represented by C12H22011 () + H2O 4 C2H5OH (1) +4 CO2 (a) (1) Assume ideal gas behavior when answering the following, 2a. What is the standard heat of reaction of the above equation, in kJ/mole sucrose? 2b. A yeast that can grow and convert sucrose to ethanol more efficiently at 45C is to be used in the bioreactor. We want to calculate the heat of reaction of the above equation at 45C (in kJ) from the standard heat of reaction. Propose a hypothetical process path that can be used for this. Give the heat of reaction from the changes in enthalpy (AH) in each step of this path. (Hint: recall Hess's Law) ( Just show how you get the heat of reaction at 45C, from the Att's in the path, no values.). 2c. Find one of the unknown changes in enthalpy (Al) in your path (2b), in kJ/mol sucione, (Yes, only one of the unknown changes in enthalpy.) Standard Heats of Formation (from Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences by Atkins & de Paula) AH(kJ/mol ANPJ/mol Inorganic compounds Organic compounds Ammonia, NH (9) -46.11 Adenine, CHN (5) +96.9 Carbon monoxide, COO) 110.53 Alanine, CH SCHONHYCOOH(S) -6040 Carbon dioxide, CO (9) -393.51 Benzene, C.H.(1) +49.0 Hydrogen sulfide, H3S(9) -- 20.63 Butanoic acid, CH(CH3)2COOHC) -533.8 Nitrogen dioxide, NO (6) +33.18 Ethane, CH (9) -84.68 Nitrogen monoxide, NO(g) +90.25 Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH(1) ana Sodium chloride, Naciis) Ethanol, C,HSOHO Water, H2001) -285. 5.83 a-b Glucose, CH 120.65) -1268 H2O(9) -241.82 - 183.9 Glycine, CH (NH)COOH(s) -528.5 N-Glycylglycine, C.H.N203(5) -747.7 Hexadecanoic acid, CH,(CH) CODH(S) -891.5 Leucine, (CH)CHCH,CHINH)COOH(S) -637.4 Methane, CH.) - 74.81 Methanol, CH OHOD -238.86 Sucrose, C2H22011 (5) Thymine, C.H.N.O.(5) - 462,8 Urea, (NH) COL) -333.1 -411.15 -4843 -277.69 anne, C.H.N.O(S) -2222 Specific heats (kJ/mol.K) Ethanol(1): 0.130, Galactose(l): 0.216, Glucose(l): 0.216, Lactose(): 0.417, Methanol(1): 0.0835, Sucrose(s): 0.424, Water(I): 0.0754 Specific heats (kJ/mol.K) for gases CO2: (36.11 x 10-3) +(4.233 x 10-5)T + (-2.887 x 10-9) T2 + (7.464 x 10-12) T3 Ethanol(y): (61.34 x 10-3) + (15.72 x 10-4)T + (-8.749 x 108) T2 + (19.83 x 10-42) T Methanol(v): (42.93 x 10-3) +(8.301 x 10-5)T + (-1.87 x 10-8) T2 + (-8.03 x 10-12) T3 Water(v): (33.46 x 10-2) + (0.6880 x 10-5)T + (0.7604 x 10-4) T2 + (-3.593 x 10-13) T3 Heat of vaporization (Aw) and normal boiling points (T6) Ethanol: (), = 38.58 kJ/mol, To = 78.5C Methanol: (AA), = 35.21 kJ/mol, Tu = 64.7C Water: (18.), = 40.656 kJ/mol, Tu = 100C Problem 2. (30 points total, 2a to 2e) The coronavirus pandemic has greatly increased the demand for disinfectants, with ethanol emerging as one of the most used. Ethanol (C2H5OH) is usually manufactured by using yeasts cultured in bioreactors to convert sucrose (C12H22011) to ethanol. The overall equation for the reaction may be represented by C12H22011 () + H2O 4 C2H5OH (1) +4 CO2 (a) (1) Assume ideal gas behavior when answering the following, 2a. What is the standard heat of reaction of the above equation, in kJ/mole sucrose? 2b. A yeast that can grow and convert sucrose to ethanol more efficiently at 45C is to be used in the bioreactor. We want to calculate the heat of reaction of the above equation at 45C (in kJ) from the standard heat of reaction. Propose a hypothetical process path that can be used for this. Give the heat of reaction from the changes in enthalpy (AH) in each step of this path. (Hint: recall Hess's Law) ( Just show how you get the heat of reaction at 45C, from the Att's in the path, no values.). 2c. Find one of the unknown changes in enthalpy (Al) in your path (2b), in kJ/mol sucione, (Yes, only one of the unknown changes in enthalpy.) Standard Heats of Formation (from Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences by Atkins & de Paula) AH(kJ/mol ANPJ/mol Inorganic compounds Organic compounds Ammonia, NH (9) -46.11 Adenine, CHN (5) +96.9 Carbon monoxide, COO) 110.53 Alanine, CH SCHONHYCOOH(S) -6040 Carbon dioxide, CO (9) -393.51 Benzene, C.H.(1) +49.0 Hydrogen sulfide, H3S(9) -- 20.63 Butanoic acid, CH(CH3)2COOHC) -533.8 Nitrogen dioxide, NO (6) +33.18 Ethane, CH (9) -84.68 Nitrogen monoxide, NO(g) +90.25 Ethanoic acid, CH3COOH(1) ana Sodium chloride, Naciis) Ethanol, C,HSOHO Water, H2001) -285. 5.83 a-b Glucose, CH 120.65) -1268 H2O(9) -241.82 - 183.9 Glycine, CH (NH)COOH(s) -528.5 N-Glycylglycine, C.H.N203(5) -747.7 Hexadecanoic acid, CH,(CH) CODH(S) -891.5 Leucine, (CH)CHCH,CHINH)COOH(S) -637.4 Methane, CH.) - 74.81 Methanol, CH OHOD -238.86 Sucrose, C2H22011 (5) Thymine, C.H.N.O.(5) - 462,8 Urea, (NH) COL) -333.1 -411.15 -4843 -277.69 anne, C.H.N.O(S) -2222 Specific heats (kJ/mol.K) Ethanol(1): 0.130, Galactose(l): 0.216, Glucose(l): 0.216, Lactose(): 0.417, Methanol(1): 0.0835, Sucrose(s): 0.424, Water(I): 0.0754 Specific heats (kJ/mol.K) for gases CO2: (36.11 x 10-3) +(4.233 x 10-5)T + (-2.887 x 10-9) T2 + (7.464 x 10-12) T3 Ethanol(y): (61.34 x 10-3) + (15.72 x 10-4)T + (-8.749 x 108) T2 + (19.83 x 10-42) T Methanol(v): (42.93 x 10-3) +(8.301 x 10-5)T + (-1.87 x 10-8) T2 + (-8.03 x 10-12) T3 Water(v): (33.46 x 10-2) + (0.6880 x 10-5)T + (0.7604 x 10-4) T2 + (-3.593 x 10-13) T3 Heat of vaporization (Aw) and normal boiling points (T6) Ethanol: (), = 38.58 kJ/mol, To = 78.5C Methanol: (AA), = 35.21 kJ/mol, Tu = 64.7C Water: (18.), = 40.656 kJ/mol, Tu = 100C
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


