Question: Problem 2 (4 pts): HashMap class Implement a HashMap class with the following methods. Note: most of the credit for this section is given to


Problem 2 (4 pts): HashMap class Implement a HashMap class with the following methods. Note: most of the credit for this section is given to the modifications required over the book version. Please do not simply copy the book version and submit.
class HashMap:
def __init__(self): Creates a new empty hashtable, with the following attributes: size - the hash table size (a prime number larger than the number of items (x2)) Table size should have a load factor in the range 0.5 - 0.75. keys - hashtable slot numbers (hashed from original keys) values - data corresponding to keys count - counter for the number of key-value in the hashtable (exluding None). def getNumItems(self): returns the number of key-value pairs stored in the hashtable def getTableSize(self): returns the table size def getKeys(self): returns a list with the slot numbers of the key-value pairs stored in the hashmap. def getValues(self): returns a list with the values of the key-value pairs stored in the hashmap. def __getitem__(self, key): return self.get(key) def get(self, key): Given a key, return the value stored in the hashtable, or None otherwise. def __setitem__(self, key, data): return self.put(key, data) def put(self, key, data): Adds a new key-value pair in the hashtable. Raise OverflowError if the table is full. def hashFunction(self, key): Maps keys to a slot number (integer) in the hashtable. returns that integer. Do not use the hash function implement in the textbook. Instead implement the universal hashing function, h(k)= ((a*k+b) % p) % m, where a and b are random numbers between 0 and p-1, and where p is a big prime number bigger than the size of the table. def rehash(self, oldHash): In case of collision, calculate and return a new slot number. Do not use the rehash function implement in the textbook. Instead use double hushing to resolve collisions, with h2(x) = x mod p + 1, and p is a small prime number. def __str__(self): returns a string for printing the hashtable. Each key-value will be printed, with a single space between them, in a new line. Note: both the original keys (could be a string), and the integers that are the slot numbers in the hashtable, are sometime called keys. To avoid confusion, I will refer to the hashed values of the keys as slots. Problem 3 (2 pts): HashMap class Application and Testing Using the HashMap class from problem 2, solve the exercises from Problem 1 and compare the results. Note that the HashMaps in problems 1a and 1b are different. If your implementation takes too much time, break after 1000 lines, and compare your results for that case.

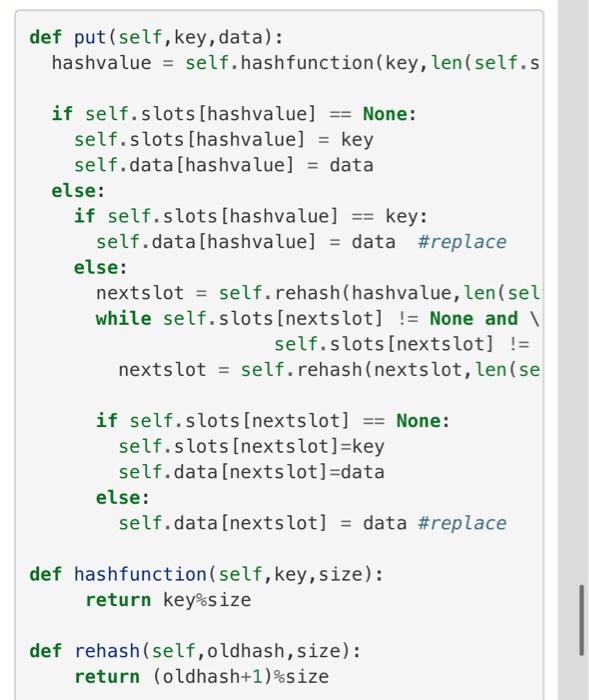
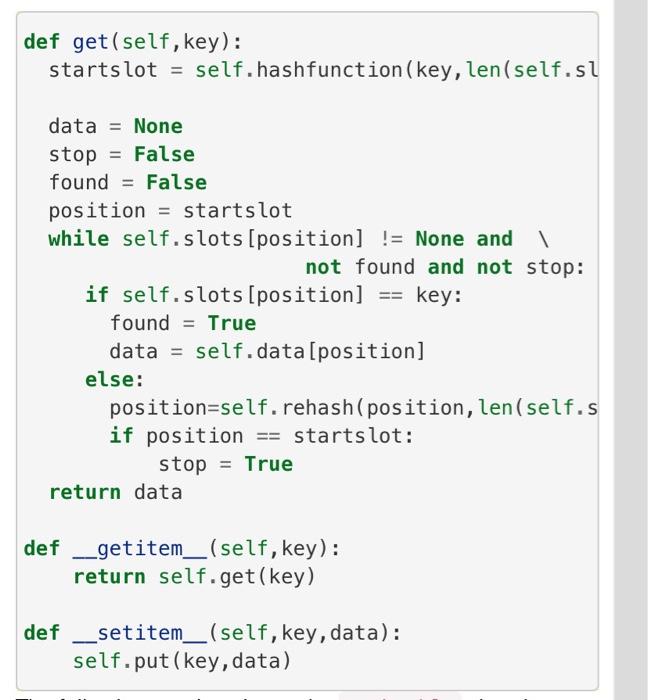
Problem 2 (4 pts): HashMap class Implement a HashMap class with the following methods. Note: most of the credit for this section is given to the modifications required over the book version. Please do not simply copy the book version and submit. class HashMap: def__init__(self): Creates a new empty hashtable, with the following attributes: size - the hash table size (a prime number larger than the number of items (x2)) Table size should have a load factor in the range 0.50.75. keys - hashtable slot numbers (hashed from original keys) values - data corresponding to keys count - counter for the number of key-value in the hashtable (exluding None). def getNumitems(self): returns the number of key-value pairs stored in the hashtable def getTableSize(self): returns the table size def getKeys(self): returns a list with the slot numbers of the key-value pairs stored in the hashmap. def getValues(self): returns a list with the values of the key-value pairs stored in the hashmap. def__getitem_(self, key): def __setitem__(self, key, data): return self.put(key, data) def put(self, key, data): Adds a new key-value pair in the hashtable. Raise OverflowError if the table is full. def hashFunction(self, key): Maps keys to a slot number (integer) in the hashtable. returns that integer. - Do not use the hash function implement in the textbook. Instead implement the universal hashing function, h(k)=((ak+b)%p)%m, where a and b are random numbers between 0 and p1, and where p is a big prime number bigger than the size of the table. def rehash(self, old Hash): In case of collision, calculate and return a new slot number. Do not use the rahash function implement in the textbook. Instead use double hushing to resolve collisions, with h2(x)=x mod p+1, and p is a small prime number. def ______(self): returns a string for printing the hashtable. Each key-value will be printed, with a single space between them, in a new line. Note: both the original keys (could be a string), and the integers that are the slot numbers in the hashtable, are sometime called "keys". To avoid confusion, I will refer to the hashed values of the keys as "slots w. Problem 3 (2 pts): HashMap class Application and Testing Using the HashMap class from problem 2, solve the exercises from Problem 1 and compare the results. Note that the HashMaps in problems 1 a and 1b are different. If your implementation takes too much time, break after 1000 lines, and compare your results for that case. def hash(astring, tablesize): sum =0 for pos in range(len(astring)): sum = sum + ord(astring[pos]) return sum\%tablesize
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


