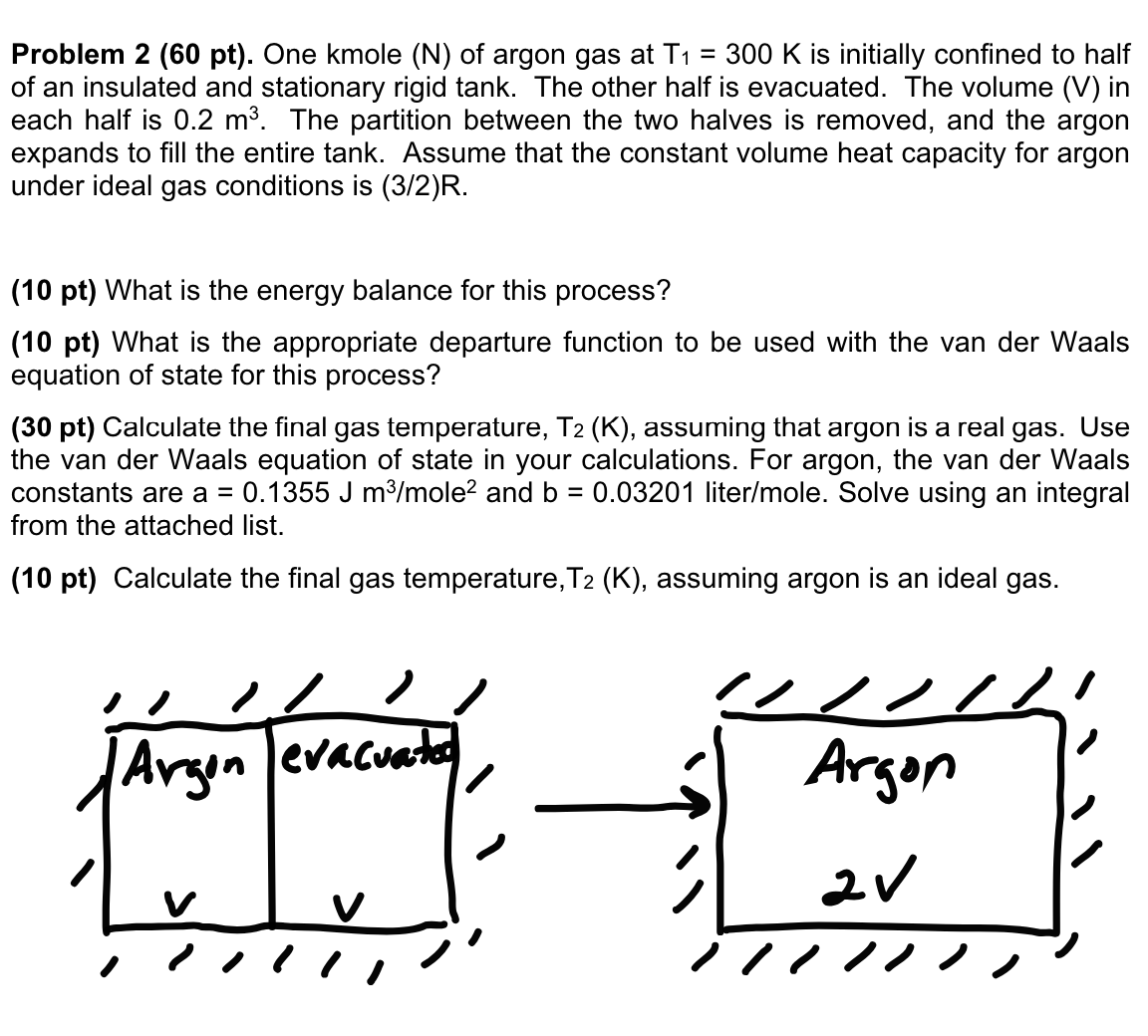
Question: Problem 2 ( 6 0 pt ) . One kmole ( N ) of argon gas at T 1 = 3 0 0 K is
Problem pt One kmole of argon gas at is initially confined to half
of an insulated and stationary rigid tank. The other half is evacuated. The volume V in
each half is The partition between the two halves is removed, and the argon
expands to fill the entire tank. Assume that the constant volume heat capacity for argon
under ideal gas conditions is
pt What is the energy balance for this process?
pt What is the appropriate departure function to be used with the van der Waals
equation of state for this process?
pt Calculate the final gas temperature, assuming that argon is a real gas. Use
the van der Waals equation of state in your calculations. For argon, the van der Waals
constants are and litermole Solve using an integral
from the attached list.
pt Calculate the final gas temperature, assuming argon is an ideal gas.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


