Question: Problem 2. (70 points) You have $10 thousand saved up to invest for a year, and are considering stocks and/or short-term Treasury bills. The returns
Problem 2. (70 points) You have $10 thousand saved up to invest for a year, and are considering stocks and/or short-term Treasury bills. The returns (in %) from both sources are judged uncertain, of course, as the following joint probability Table 1 indicates:
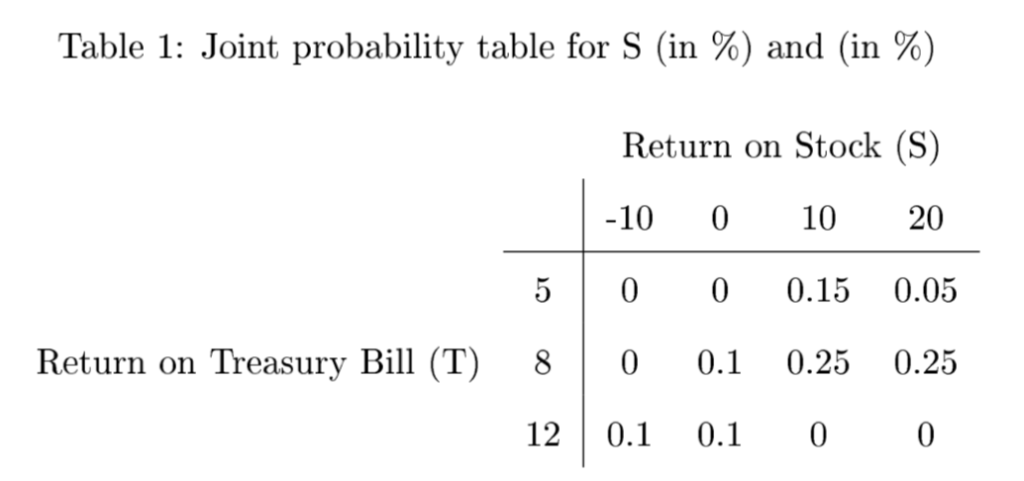
1. (5 points) Calculate the expected returns from stock and treasury bill, i.e., E(S) =? and E(T ) =?
1.b) Which strategy leads to a higher expected return, investing in stock or investing in treasury bill?
2. (5 points) Calculate the variances of both returns, i.e., Var(S) =? and Var(T ) =?
2.b) Which strategy is more risky, investing in stock or investing in treasury bill?
3. (5 points) Calculate the co-variance between the two returns (both are in unit of %), i.e.,
Cov(S,T) =?
4. (5 points) What is the correlation coecient between Stock return S and T-bill return T, i.e.,
ST =?
Now both returns are expressed in decimals, not in percentage anymore. The joint probability
distribution table becomes the following Table 2:
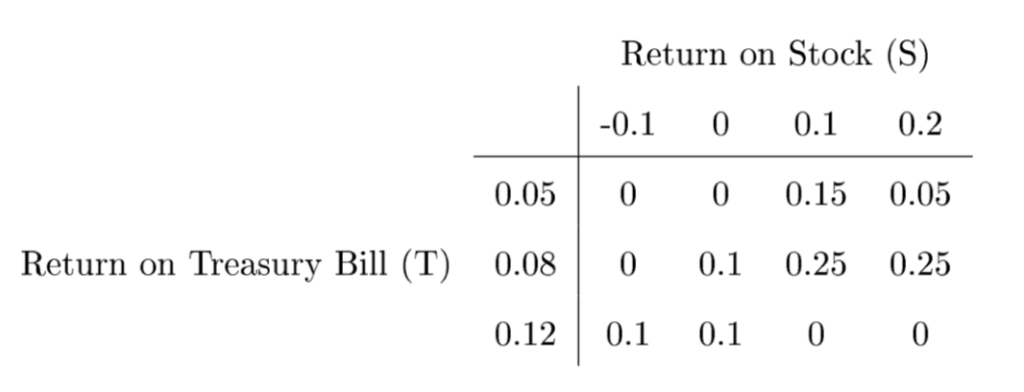
5. (5 points) Use Table 2 to calculate the expected returns from stock and treasury bill, i.e., E(S) =? and E(T) =?
5.b) How are the two expected returns related to the two expected returns you found in part 1.
6. (5 points) Use Table 2 to calculate the variances of both returns, i.e., V ar(S) =? and V ar(T ) =?
6.b) How are the two variances related to the two variances you found in part 2.
7. (5 points) Use Table 2 to calculate the co-variance between the two returns , i.e., Cov(S,T) =?
7.b) How is the co-variance related to the co-variance you found in part 3.
8. (5 points) Use Table 2 to find the correlation coefficient between Stock return S and T-bill return T, i.e., ST =?
8.b) Are the two correlation coefficients (in part 4 and part 8), identical?
Use Table 2 to answer following questions:
9. (5 points) If you invested your $10 thousand entirely in stocks, what would be the expected value of your return? What is the variance?
- In other words, find out E[10 (1 + S)] and Var[10 (1 + S)], respectively.
10. (5 points) If you invested your $10 thousand entirely in treasury bills, what would be the expected value of your return? What is the variance?
- In other words, find out E[10 (1 + T )] and Var[10 (1 + T )] respectively.
11. (5 points) If you split your investment 50-50, invest $5 thousand in stocks and the other $5 thousand in treasury bills. What would be the return you expect? What is the variance?
- In other words, find out E[5(1+S)+5(1+T)] and Var[5(1+S)+5(1+T)], respectively.
12. (5 points) If you split your investment 80-20, i.e. investing $8 thousand in stocks and the rest $2 thousand in treasury bills. What are the expected return and its variance, respectively?
- In other words, find out E[8(1+S)+2(1+T)] and Var[8(1+S)+2(1+T)], respectively.
13. (5 points) If you split your investment w-(1 w), invest w 10 thousand in stock and other (1 w) 10 in treasury bills, where w is a fraction between 0 and 1. The return on your investment is:
R = w 10 (1 + S) + (1 w) 10 (1 + T) = 10 + w 10 S + (1 w) 10 T
What would be the return you expect? What is the variance?
- In other words, find out E[10 + w 10 S + (1 w) 10 T ] and Var[10 + w 10 S + (1 w) 10 T ], respectively.
14. (5 points) What is the value of w that minimizes the variance Var[w10(1+S)+(1w) 10 (1 + T )]?
(Hint: you can solve this by algebra, or calculus, or plot Var over w in Excel.)
Table 1: Joint probability table for S (in %) and (in %) Return on Stock (S) -10 0 10 20 5 0 00.15 0.05 Return on Treasury Bill (T) 80 0.1 0.25 0.25 12 0.1 0.1 00 Return on Stock (S) 0.1 0 0.1 0.2 0.05 0 00.15 0.05 Return on Treasury Bill (T) 0.08 0.1 0.25 0.25 0.120.1 0.1 00
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


