Question: Problem 2 : An electro - thermo - mechanical actuator ( 3 0 points ) Thermal actuators are widely used MEMS components. Here we will
Problem : An electrothermomechanical actuator points
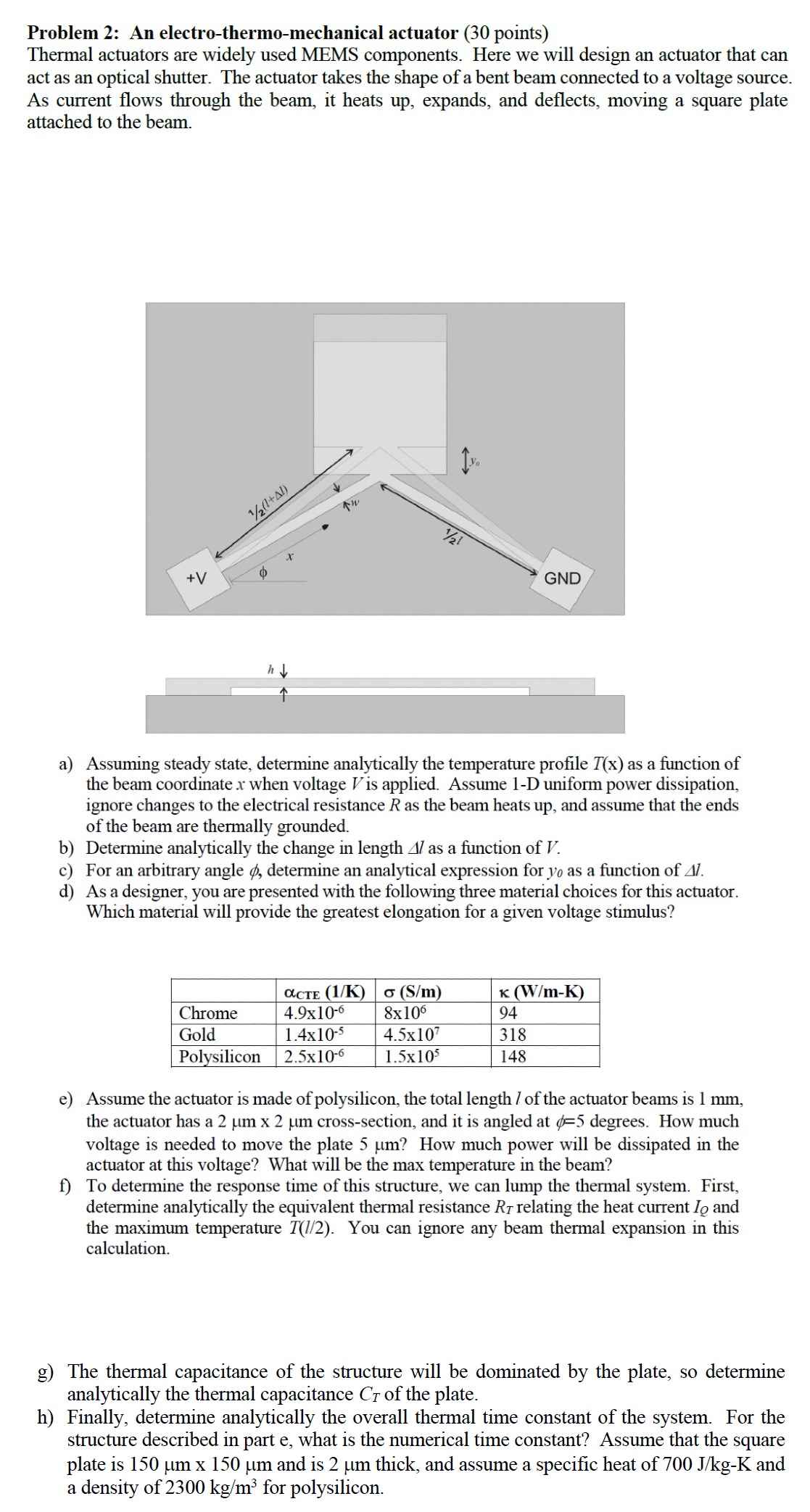
Thermal actuators are widely used MEMS components. Here we will design an actuator that can act as an optical shutter. The actuator takes the shape of a bent beam connected to a voltage source. As current flows through the beam, it heats up expands, and deflects, moving a square plate attached to the beam.
a Assuming steady state, determine analytically the temperature profile Tmathrmx as a function of the beam coordinate x when voltage V is applied. Assume D uniform power dissipation, ignore changes to the electrical resistance R as the beam heats up and assume that the ends of the beam are thermally grounded.
b Determine analytically the change in length Delta l as a function of V
c For an arbitrary angle phi determine an analytical expression for y as a function of Delta l
d As a designer, you are presented with the following three material choices for this actuator. Which material will provide the greatest elongation for a given voltage stimulus?
e Assume the actuator is made of polysilicon, the total length l of the actuator beams is mm the actuator has a mu mathrm~mtimes mu mathrm~m crosssection, and it is angled at phi degrees. How much voltage is needed to move the plate mu mathrm~m How much power will be dissipated in the actuator at this voltage? What will be the max temperature in the beam?
f To determine the response time of this structure, we can lump the thermal system. First, determine analytically the equivalent thermal resistance RT relating the heat current IQ and the maximum temperature Tl You can ignore any beam thermal expansion in this calculation.
g The thermal capacitance of the structure will be dominated by the plate, so determine analytically the thermal capacitance CT of the plate.
h Finally, determine analytically the overall thermal time constant of the system. For the structure described in part e what is the numerical time constant? Assume that the square plate is mu mathrm~mtimes mu mathrm~m and is mu mathrm~m thick, and assume a specific heat of mathrm~JmathrmkgmathrmK and a density of mathrm~kgmathrmm for polysilicon. Problem : An electrothermomechanical actuator points
Thermal actuators are widely used MEMS components. Here we will design an actuator that can act as an optical shutter. The actuator takes the shape of a bent beam connected to a voltage source. As current flows through the beam, it heats up expands, and deflects, moving a square plate attached to the beam.
a Assuming steady state, determine analytically the temperature profile Tmathrmx as a function of the beam coordinate x when voltage V is applied. Assume D uniform power dissipation, ignore changes to the electrical resistance R as the beam heats up and assume that the ends of the beam are thermally grounded.
b Determine analytically the change in length Delta l as a function of V
c For an arbitrary angle phi determine an analytical expression for y as a function of Delta l
d As a designer, you are presented with the following three material choices for this actuator. Which material will provide the greatest elongation for a given voltage stimulus?
e Assume the actuator is made of polysilicon, the total length l of the actuator beams is mm the actuator has a mu mathrm~mtimes mu mathrm~m crosssection, and it is angled at phi degrees. How much voltage is needed to move the plate mu mathrm~m How much power will be dissipated in the actuator at this voltage? What will be the max temperature in the beam?
f To determine the response time of this structure, we can lump the thermal system. First, determine analytically the equivalent thermal resistance RT relating the heat current IQ and the maximum temperature Tl You can ignore any beam thermal expansion in this calculation.
g The thermal capacitance of the structure will be dominated by the plate, so determine analytically the thermal capacitance CT of the plate.
h Finally, determine analytically the overall thermal time constant of the system. For the structure described in part e what is the numerical time constant? Assume that the square plate is mu mathrm~mtimes mu mathrm~m and is mu mathrm~m thick, and assume a specific heat of mathrm~JmathrmkgmathrmK and a density of mathrm~kgmathrmm for polysilicon.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


