Question: A capacitor is built of two non-parallel, rectangular metallic plates. In a cross-sectional view the capacitor is composed of two right-angled triangles with differently
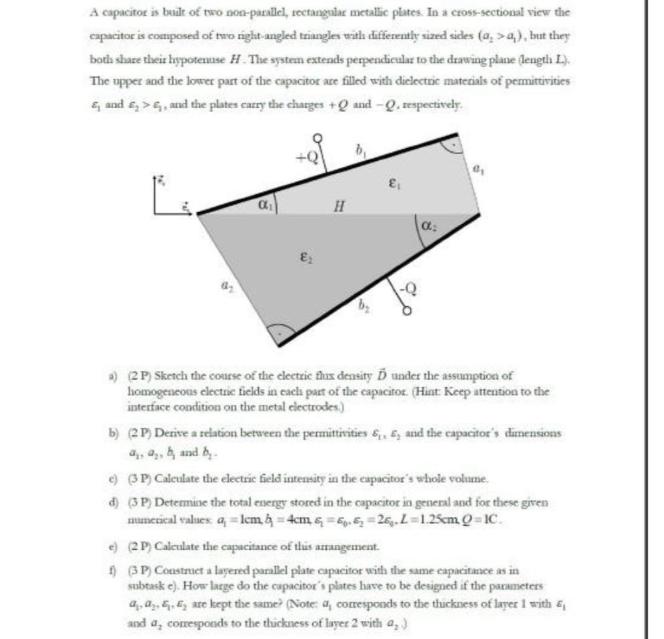
A capacitor is built of two non-parallel, rectangular metallic plates. In a cross-sectional view the capacitor is composed of two right-angled triangles with differently sized sides (a,>a,), but they both share their hypotenuse H. The system extends perpendicular to the drawing plane (length L.). The upper and the lower part of the capacitor are filled with dielectric materials of permittivities & and >, and the plates carry the charges +Q and -Q, respectively. E: H b a) (2P) Sketch the course of the electric flux density D under the assumption of homogeneous electric fields in each part of the capacitor. (Hint: Keep attention to the interface condition on the metal electrodes.) b) (2P) Derive a relation between the permittivities 6, 5, and the capacitor's dimensions a, a, b, and by e) (3P) Calculate the electric field intensity in the capacitor's whole volume. d) (3P) Determine the total energy stored in the capacitor in general and for these given mumerical values alem &=4cm & = 6. & = 26. L=1.25cm 0=IC. e) (2P) Calculate the capacitance of this arrangement. f) (3P) Construct a layered parallel plate capacitor with the same capacitance as in subtask e). How large do the capacitor's plates have to be designed if the parameters a. a... are kept the same? (Note: a, corresponds to the thickness of layer 1 with and a, corresponds to the thickness of layer 2 with 4,)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Electric Flux Density For a dielectric material the relationship between electric field E electric ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


