Question: Problem 2 Consider two gases: methane CH4 (Orot =7.54 K (3-fold degenerate); Ovib,i =4170 K, 2180 K (2-fold degenerate), 4320 K (3-fold degenerate), and 1870
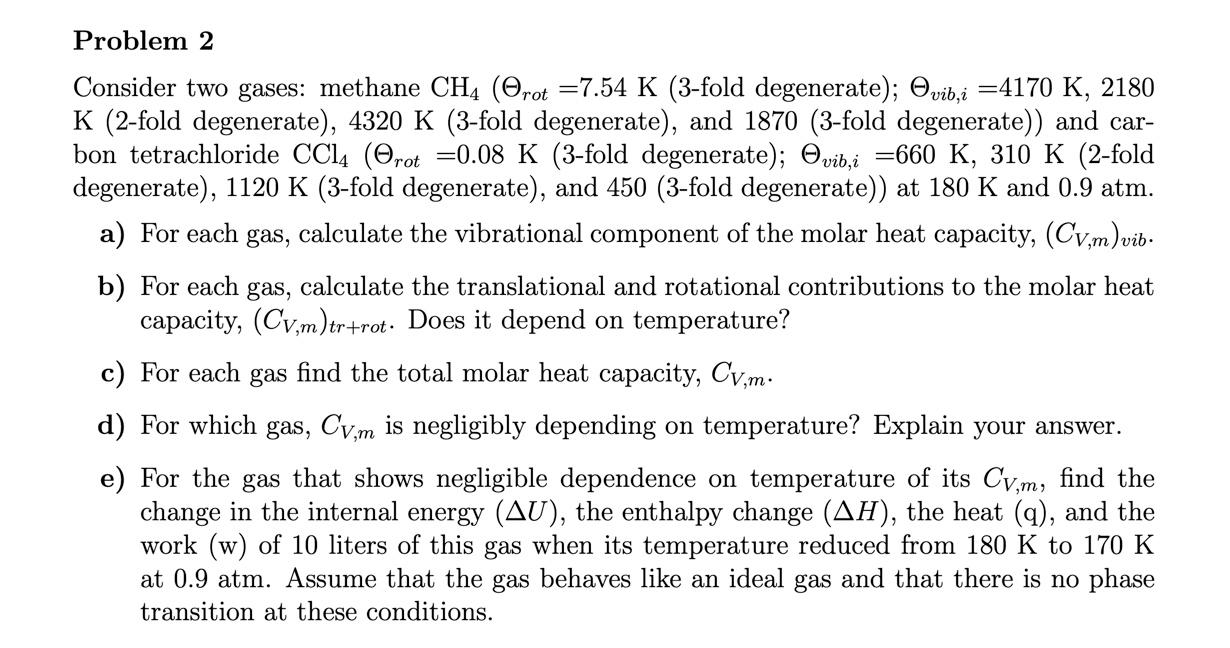
Problem 2 Consider two gases: methane CH4 (Orot =7.54 K (3-fold degenerate); Ovib,i =4170 K, 2180 K (2-fold degenerate), 4320 K (3-fold degenerate), and 1870 (3-fold degenerate)) and car- bon tetrachloride CCl4 (Orot =0.08 K (3-fold degenerate); Ovib,i =660 K, 310 K (2-fold degenerate), 1120 K (3-fold degenerate), and 450 (3-fold degenerate)) at 180 K and 0.9 atm. a) For each gas, calculate the vibrational component of the molar heat capacity, (Cv,m)vib. b) For each gas, calculate the translational and rotational contributions to the molar heat capacity, (Cv,m)tr+rot. Does it depend on temperature? c) For each gas find the total molar heat capacity, Cv,m. d) For which gas, CV,m is negligibly depending on temperature? Explain your answer. e) For the gas that shows negligible dependence on temperature of its CV,m, find the change in the internal energy (AU), the enthalpy change (AH), the heat (q), and the work (w) of 10 liters of this gas when its temperature reduced from 180 K to 170 K at 0.9 atm. Assume that the gas behaves like an ideal gas and that there is no phase transition at these conditions. Problem 2 Consider two gases: methane CH4 (Orot =7.54 K (3-fold degenerate); Ovib,i =4170 K, 2180 K (2-fold degenerate), 4320 K (3-fold degenerate), and 1870 (3-fold degenerate)) and car- bon tetrachloride CCl4 (Orot =0.08 K (3-fold degenerate); Ovib,i =660 K, 310 K (2-fold degenerate), 1120 K (3-fold degenerate), and 450 (3-fold degenerate)) at 180 K and 0.9 atm. a) For each gas, calculate the vibrational component of the molar heat capacity, (Cv,m)vib. b) For each gas, calculate the translational and rotational contributions to the molar heat capacity, (Cv,m)tr+rot. Does it depend on temperature? c) For each gas find the total molar heat capacity, Cv,m. d) For which gas, CV,m is negligibly depending on temperature? Explain your answer. e) For the gas that shows negligible dependence on temperature of its CV,m, find the change in the internal energy (AU), the enthalpy change (AH), the heat (q), and the work (w) of 10 liters of this gas when its temperature reduced from 180 K to 170 K at 0.9 atm. Assume that the gas behaves like an ideal gas and that there is no phase transition at these conditions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


