Question: Problem 2 Work problem 4 . 1 9 from the reference text by Rowell and Wormley. This problem relies on problem 4 . 1 8
Problem
Work problem from the reference text by Rowell and Wormley. This problem relies on problem ; both are included below for your convenience.
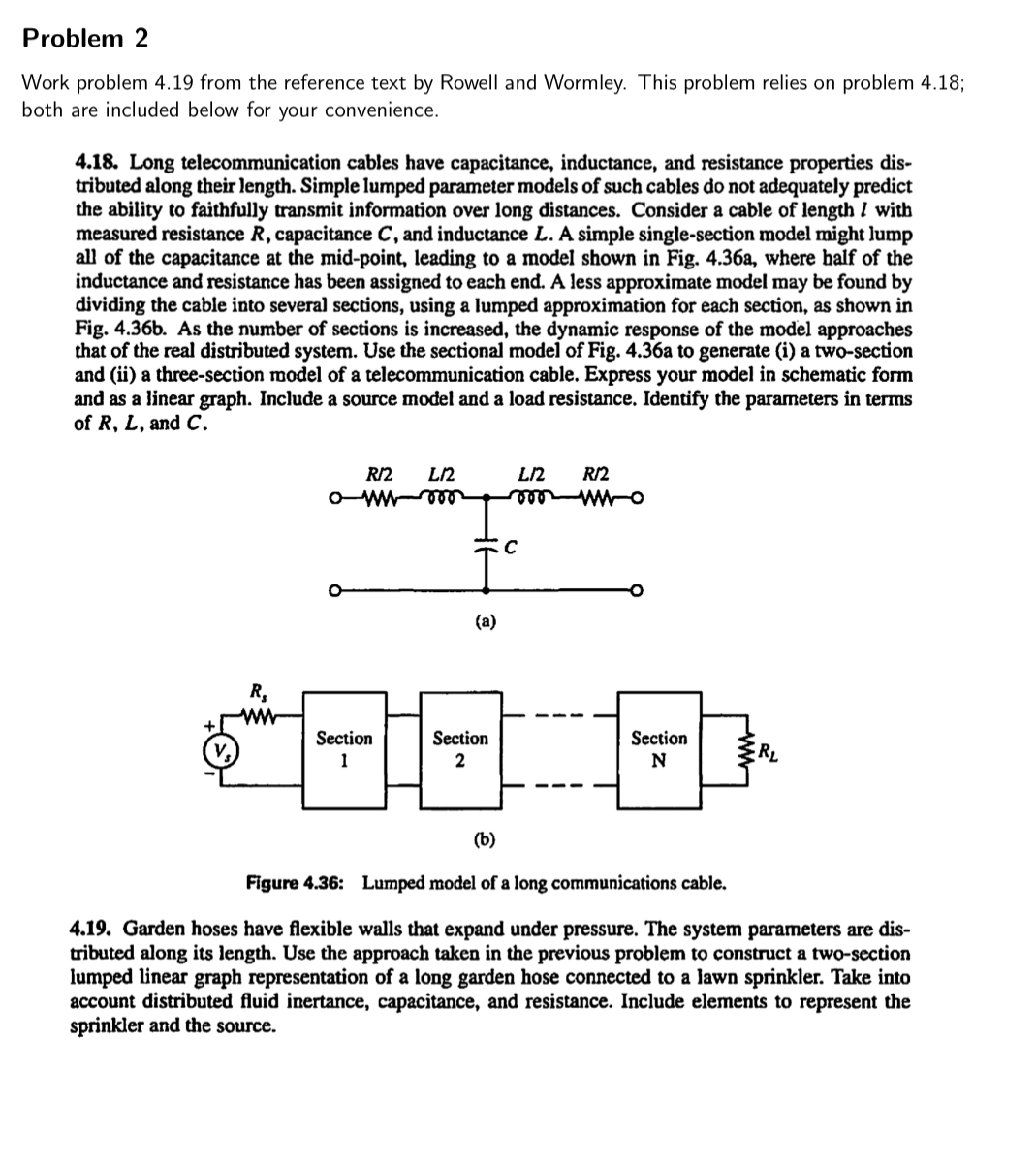
Long telecommunication cables have capacitance, inductance, and resistance properties distributed along their length. Simple lumped parameter models of such cables do not adequately predict the ability to faithfully transmit information over long distances. Consider a cable of length l with measured resistance R capacitance C and inductance L A simple singlesection model might lump all of the capacitance at the midpoint, leading to a model shown in Fig. a where half of the inductance and resistance has been assigned to each end. A less approximate model may be found by dividing the cable into several sections, using a lumped approximation for each section, as shown in Fig. b As the number of sections is increased, the dynamic response of the model approaches that of the real distributed system. Use the sectional model of Fig. a to generate i a twosection and ii a threesection model of a telecommunication cable. Express your model in schematic form and as a linear graph. Include a source model and a load resistance. Identify the parameters in terms of R L and C
Garden hoses have flexible walls that expand under pressure. The system parameters are distributed along its length. Use the approach taken in the previous problem to construct a twosection lumped linear graph representation of a long garden hose connected to a lawn sprinkler. Take into account distributed fluid inertance, capacitance, and resistance. Include elements to represent the sprinkler and the source.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


