Question: Problem 3. (1 point) - Decimal approximations are not allowed for this problem. - Enter your answer in exact form. - Use sqrt( ) to
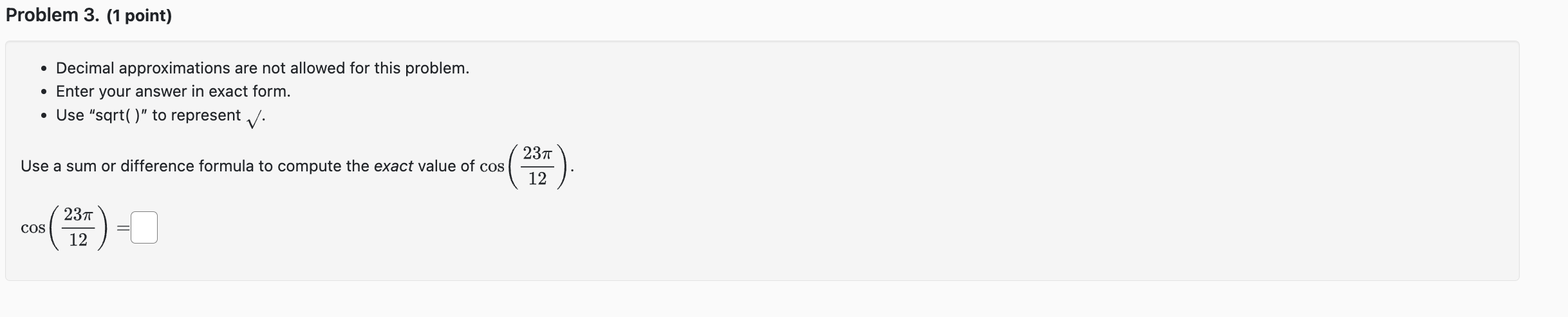
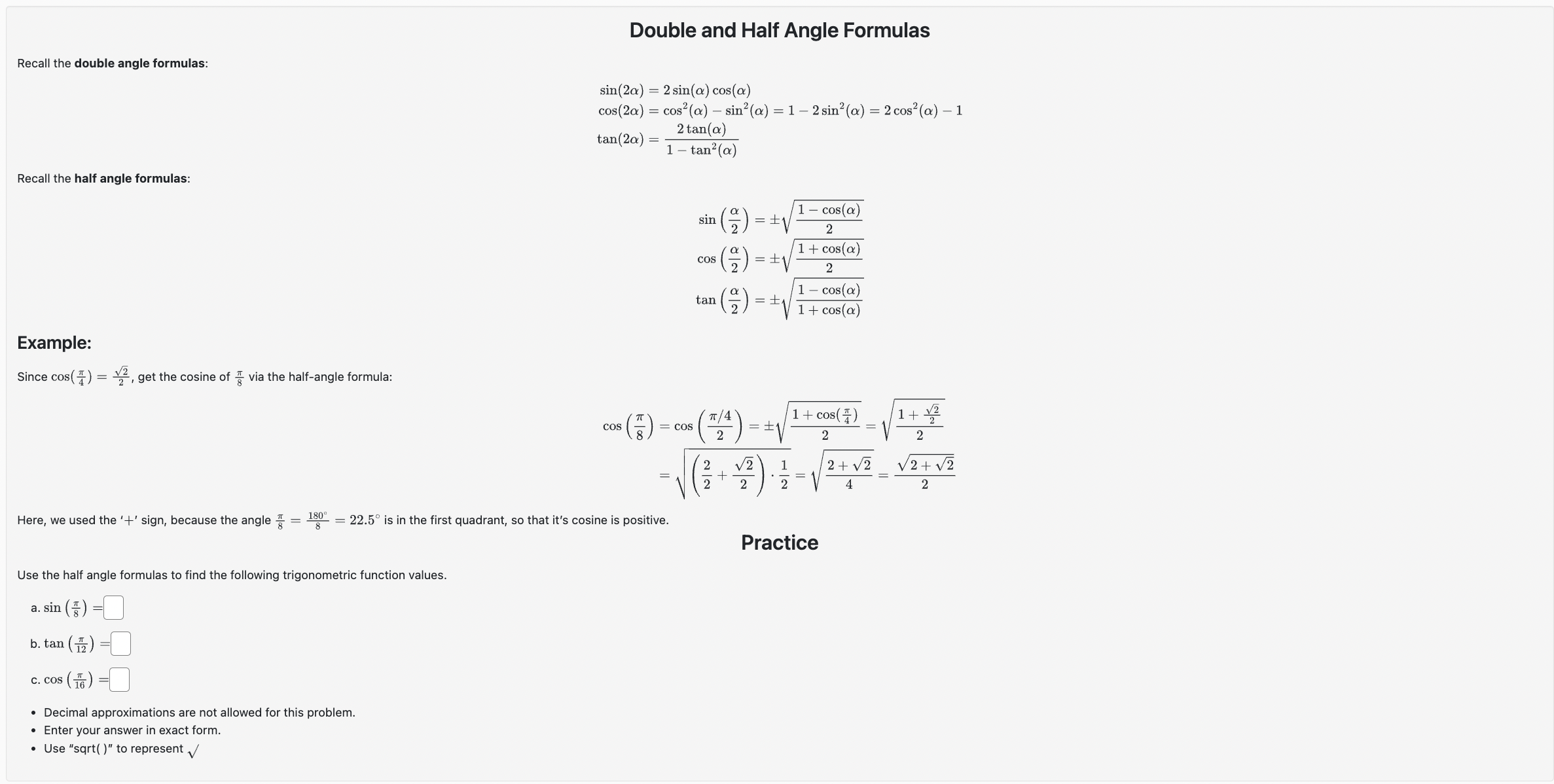
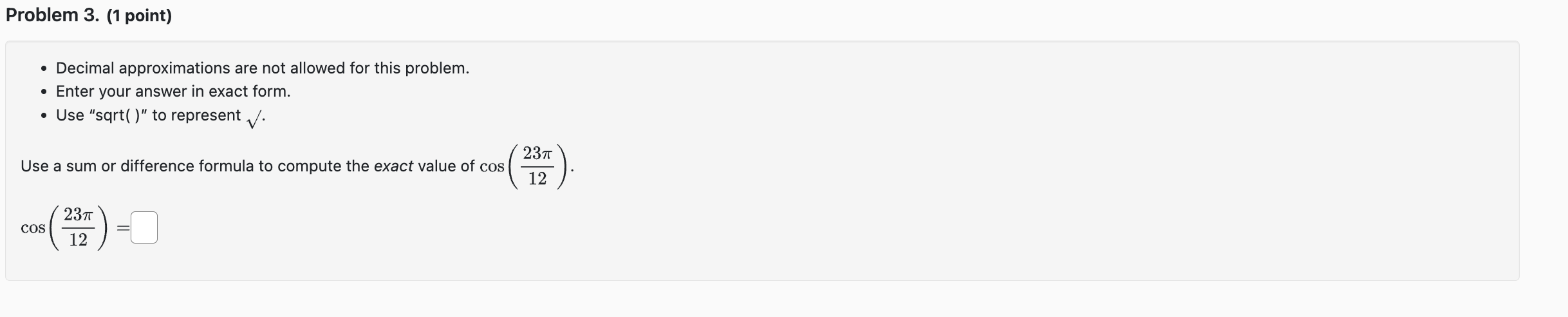
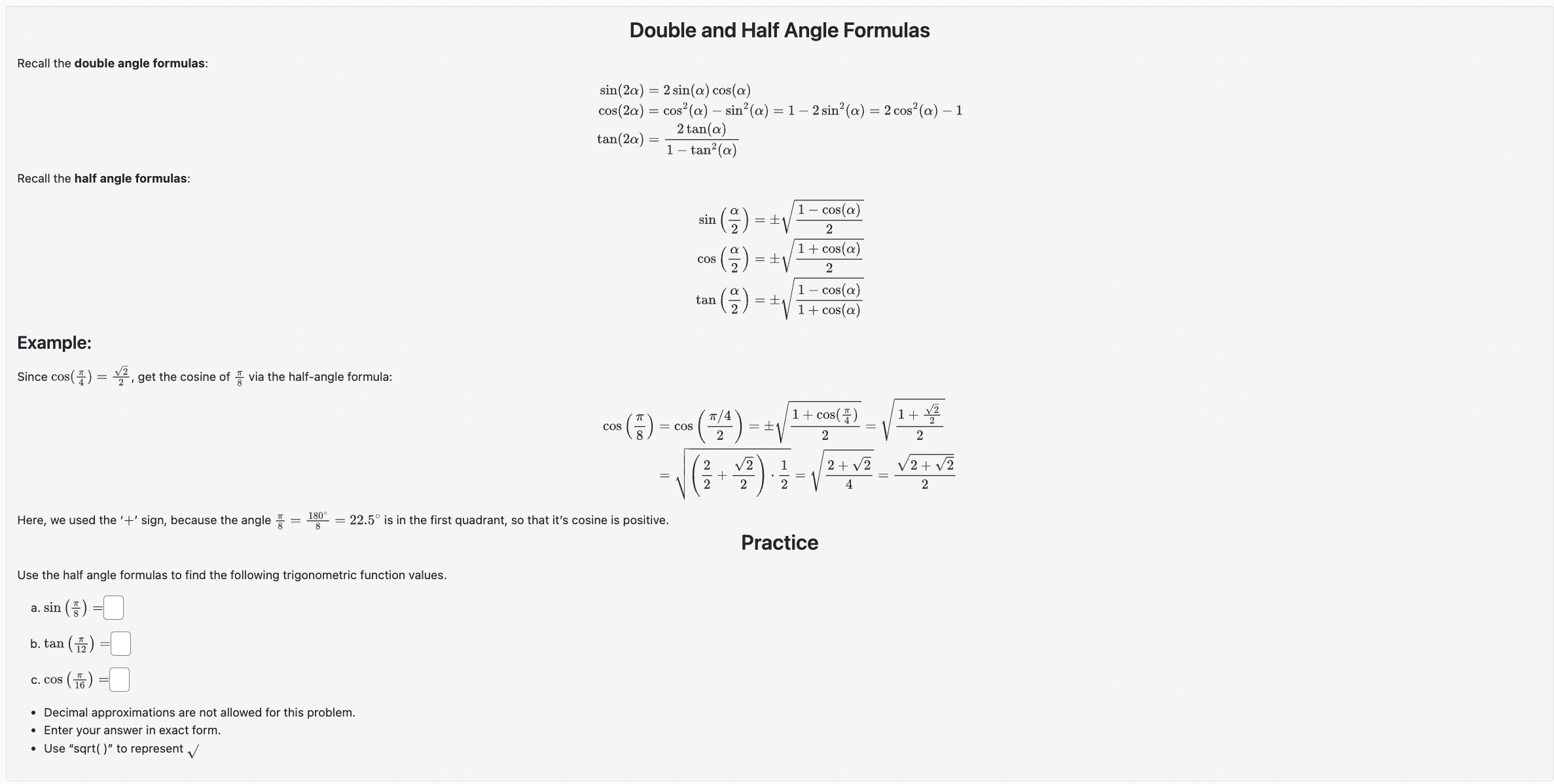
Problem 3. (1 point) - Decimal approximations are not allowed for this problem. - Enter your answer in exact form. - Use "sqrt( )\" to represent \\/. 237r Use a sum or difference formula to compute the exact value of cos ( ). 12 2311' i' (F) :L' Double and Half Angle Formulas Recall the double angle formulas: sin(20) = 2 sin(a) cos(a) cos(2a) = cos"(a) - sin?(a) = 1 - 2 sin?(a) = 2 cos?(a) - 1 tan(20) = - 2 tan(a) 1 - tan?(a) Recall the half angle formulas: sin (2) = $1 1 - cos() 2 cos () = + 1 + cos(a) 2 tan (2) = +1 1 - cos(a) 1 + cos(a) Example: Since cos( $) = 2-, get the cosine of # via the half-angle formula: 1 + cos( 1+ 12 cos = Cos IT /4 2 2 V2 1 2 + V2 V2+ v2 2 2 Here, we used the '+' sign, because the angle
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


