Question: Problem 3: Two-lens system Two lenses are placed 1 m = 100 cm apart from each other. The left (L) lens is a converging lens
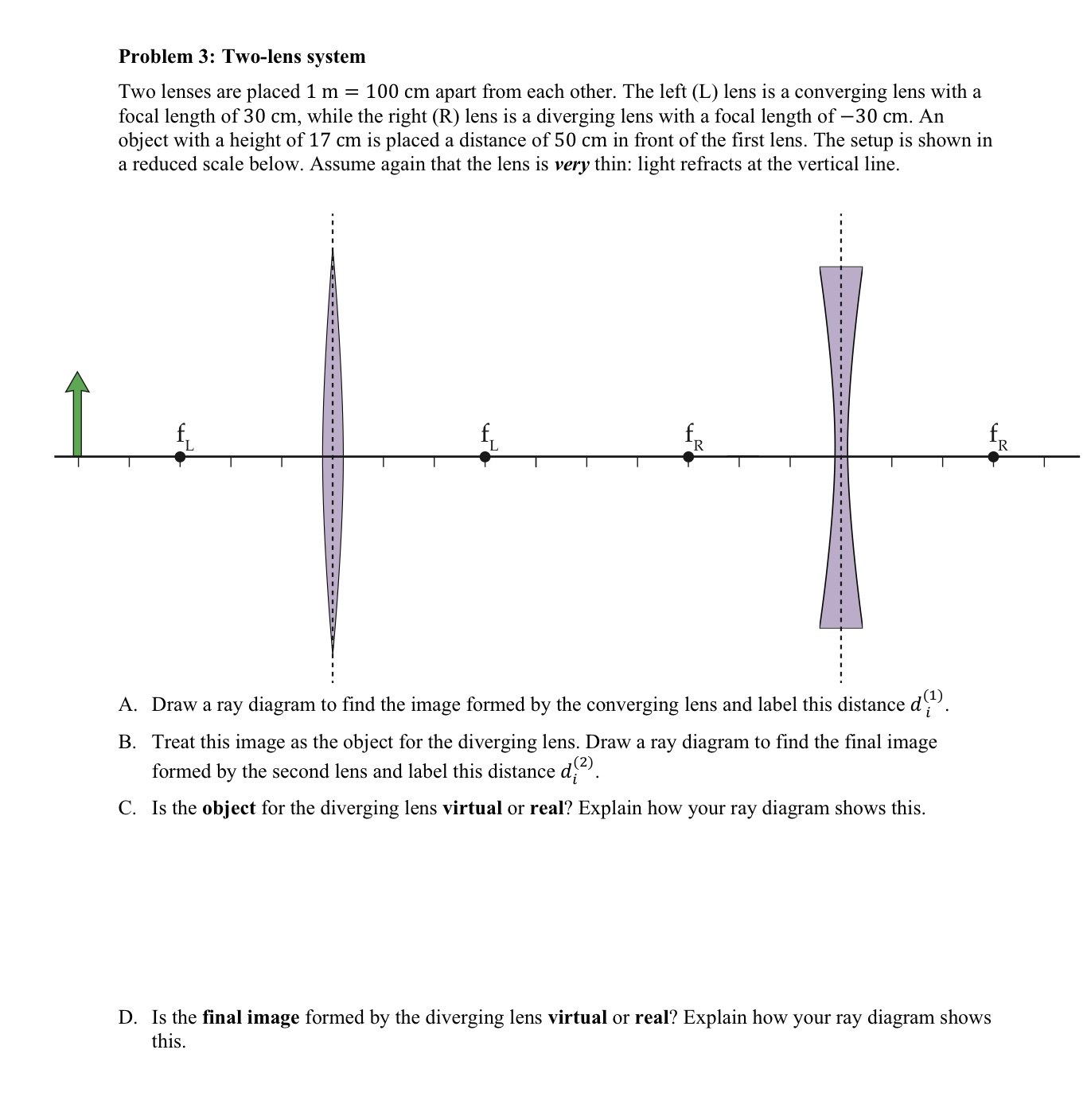

Problem 3: Two-lens system Two lenses are placed 1 m = 100 cm apart from each other. The left (L) lens is a converging lens with a focal length of 30 cm, while the right (R) lens is a diverging lens with a focal length of 30 cm. An object with a height of 17 cm is placed a distance of 50 cm in front of the rst lens. The setup is shown in a reduced scale below. Assume again that the lens is very thin: light refracts at the vertical line. A. Draw a ray diagram to nd the image formed by the converging lens and label this distance (121). B. Treat this image as the object for the diverging lens. Draw a ray diagram to nd the final image formed by the second lens and label this distance dim. C. ls the object for the diverging lens virtual or real? Explain how your ray diagram shows this. D. Is the nal image formed by the diverging lens virtual or real? Explain how your ray diagram shows this. E. To find the location of the final image using the thin lens equation proceed as follows: 1. Use the thin lens equation to find the distance d." of the image formed by the first lens. 2. Recall that this value is the distance away from the first lens. Since this image will be the object for the second lens, calculate the object distance do measured from the second lens. 3. Use this object distance d.' to find the location of the final image. According to your answer, is it real or virtual. 4. This final image has been magnified twice: once by the first lens and then again by the second lens. Calculate each of the magnifications: m, due to the first lens and m2 due to the second lens. Use them to calculate the final magnification (Hint: think about the meaning of magnification then answer, should you add or multiply the individual magnifications?)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


