Question: Problem 4 (30 points) Consider the following two 9-bit floating-point representations based on the IEEE floating-point format 1. Format A * There is 1 sign
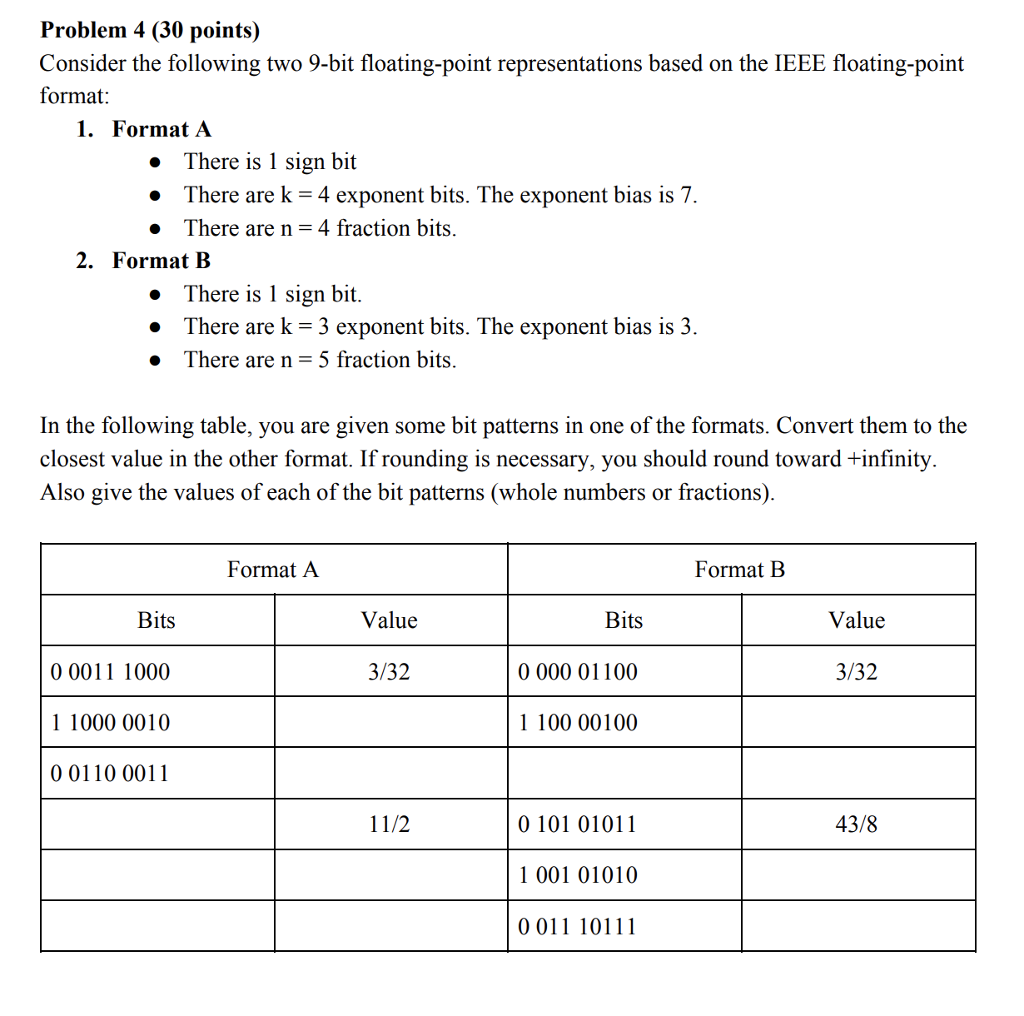

Problem 4 (30 points) Consider the following two 9-bit floating-point representations based on the IEEE floating-point format 1. Format A * There is 1 sign bit There are k- 4 exponent bits. The exponent bias is 7. There are n- 4 fraction bits 2. Format B There is 1 sign bit. There are k- 3 exponent bits. The exponent bias is 3. There are n-5 fraction bits In the following table, you are given some bit patterns in one of the formats. Convert them to the closest value in the other format. If rounding is necessary, you should round toward +infinity. Also give the values of each of the bit patterns (whole numbers or fractions) Format A Format B Value Bits 0 0011 1000 11000 0010 0 0110 0011 Bits 0 000 01100 1 100 00100 Value 3/32 3/32 0 101 01011 1 001 01010 0011 10111 11/2 43/8 Problem 4 (30 points) Consider the following two 9-bit floating-point representations based on the IEEE floating-point format 1. Format A * There is 1 sign bit There are k- 4 exponent bits. The exponent bias is 7. There are n- 4 fraction bits 2. Format B There is 1 sign bit. There are k- 3 exponent bits. The exponent bias is 3. There are n-5 fraction bits In the following table, you are given some bit patterns in one of the formats. Convert them to the closest value in the other format. If rounding is necessary, you should round toward +infinity. Also give the values of each of the bit patterns (whole numbers or fractions) Format A Format B Value Bits 0 0011 1000 11000 0010 0 0110 0011 Bits 0 000 01100 1 100 00100 Value 3/32 3/32 0 101 01011 1 001 01010 0011 10111 11/2 43/8
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


