Question: Problem 4 : Derivatives of Data with Errors [ 1 pt ] Aside from unequal spacing, another problem related to differentiating empirical data is that
Problem : Derivatives of Data with Errors pt
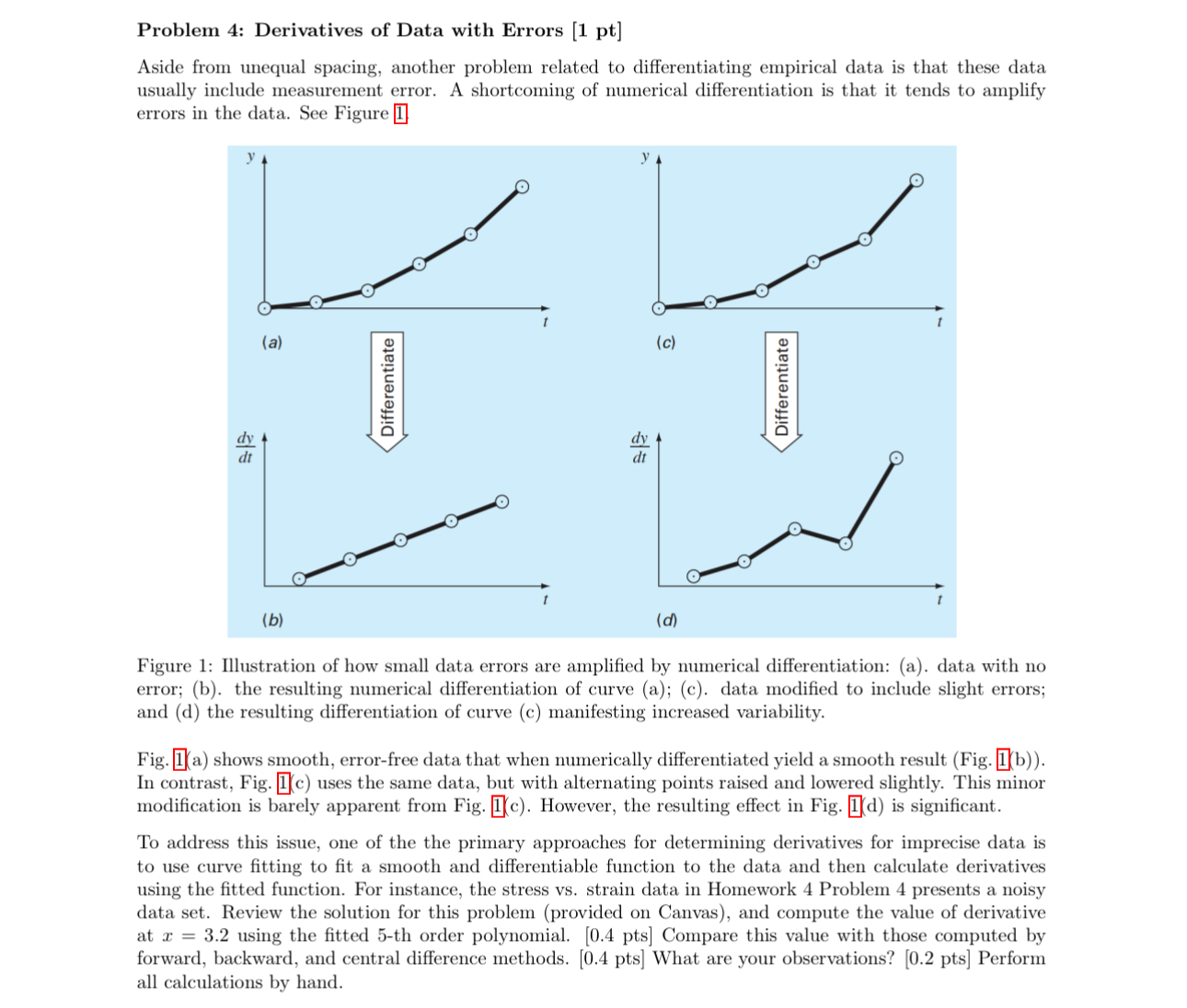
Aside from unequal spacing, another problem related to differentiating empirical data is that these data usually include measurement error. A shortcoming of numerical differentiation is that it tends to amplify errors in the data. See Figure
Figure : Illustration of how small data errors are amplified by numerical differentiation: a data with no error; b the resulting numerical differentiation of curve a; c data modified to include slight errors; and d the resulting differentiation of curve c manifesting increased variability.
Fig. a shows smooth, errorfree data that when numerically differentiated yield a smooth result Figb In contrast, Fig. c uses the same data, but with alternating points raised and lowered slightly. This minor modification is barely apparent from Fig. c However, the resulting effect in Fig. d is significant.
To address this issue, one of the the primary approaches for determining derivatives for imprecise data is to use curve fitting to fit a smooth and differentiable function to the data and then calculate derivatives using the fitted function. For instance, the stress vs strain data in Homework Problem presents a noisy data set. Review the solution for this problem provided on Canvas and compute the value of derivative at using the fitted th order polynomial. pts
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


