Question: Problem 4. (Heat equation at interface: parallel circuit case) Typically, satellites contain electronic devices which often operate at cryogenic temperatures to reduce the signal to

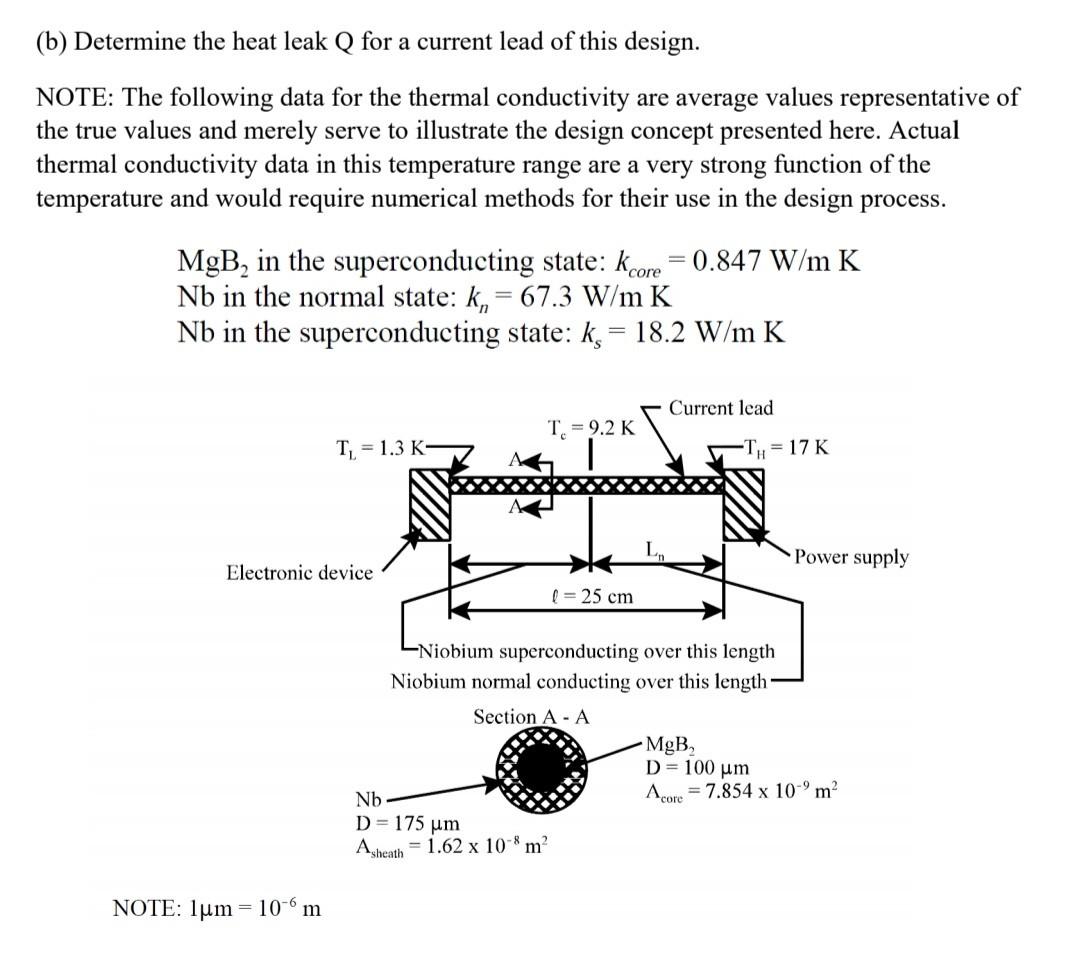
Problem 4. (Heat equation at interface: parallel circuit case) Typically, satellites contain electronic devices which often operate at cryogenic temperatures to reduce the signal to noise ratio. In order to operate, these devices require electrical power delivered to the cooled electronic device through an electrical conductor connected to the device at one end while the other end is connected to the source of electricity at ambient temperature at the other end. Unfortunately, normal conductors, such as copper, transport to the cold end of the conductor not only the desired electrons from the power source, but also unwanted energy and entropy. Thus, the electrical current lead becomes a heat leak, and the greater the heat leak, the faster the coolant (cryogen) is consumed. In addition, the conductor has an electrical resistance; consequently, the moving electrons also generate entropy via Joule heating (IR dissipation) in the conductor which is also ultimately transported to the coolant. Since coolant is not considered part of the satellite payload and since a limited supply of coolant is available, it is desirable to reduce these sources of entropy. One possible solution is to employ superconducting current leads. When materials undergo a transition from the normal state to the superconducting state, both their electrical resistivity and their thermal conductivity are reduced substantially. As a consequence, Joule heating, as well as energy and entropy transfer through the conductor into the cryogenic region of a satellite, can be significantly reduced by employing superconducting current leads for electronic devices. If properly designed, this reduced heat leak can extend the lifetime of the cryogen and/or decrease the amount of cryogen needed for a mission by a substantial amount. Unfortunately, metallic superconductors undergo the superconducting phase transition at very low temperatures, typically T.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


