Question: Problem 5. Consider the spinning disk that is attached to an arm, which is, in turn, attached to a rotating shaft, as visualized in
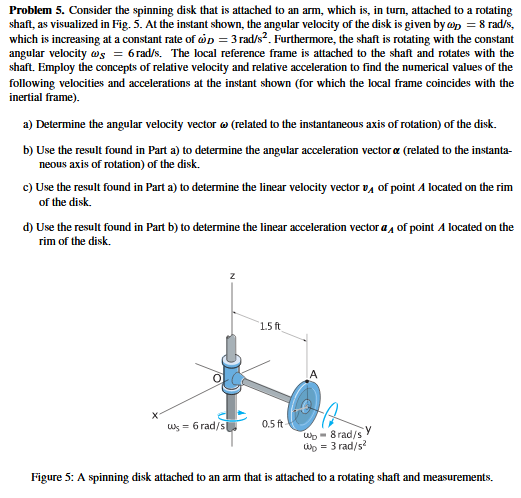
Problem 5. Consider the spinning disk that is attached to an arm, which is, in turn, attached to a rotating shaft, as visualized in Fig. 5. At the instant shown, the angular velocity of the disk is given by @p = 8 rad/s, which is increasing at a constant rate of p = 3 rad/s. Furthermore, the shaft is rotating with the constant angular velocity ws = 6 rad/s. The local reference frame is attached to the shaft and rotates with the shaft. Employ the concepts of relative velocity and relative acceleration to find the numerical values of the following velocities and accelerations at the instant shown (for which the local frame coincides with the inertial frame). a) Determine the angular velocity vector (related to the instantaneous axis of rotation) of the disk. b) Use the result found in Part a) to determine the angular acceleration vector & (related to the instanta- neous axis of rotation) of the disk. c) Use the result found in Part a) to determine the linear velocity vector v of point A located on the rim of the disk. d) Use the result found in Part b) to determine the linear acceleration vector a of point A located on the rim of the disk. 1.5 ft w=6 rad/s 0.5 ft wp 8 rad/s wp = 3 rad/s Figure 5: A spinning disk attached to an arm that is attached to a rotating shaft and measurements.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


