Question: Problem 6. (10 points) Here's the minimization algorithm. Since we would never merge accepting and non-accepting states, it starts (in Step 2) by dividing the
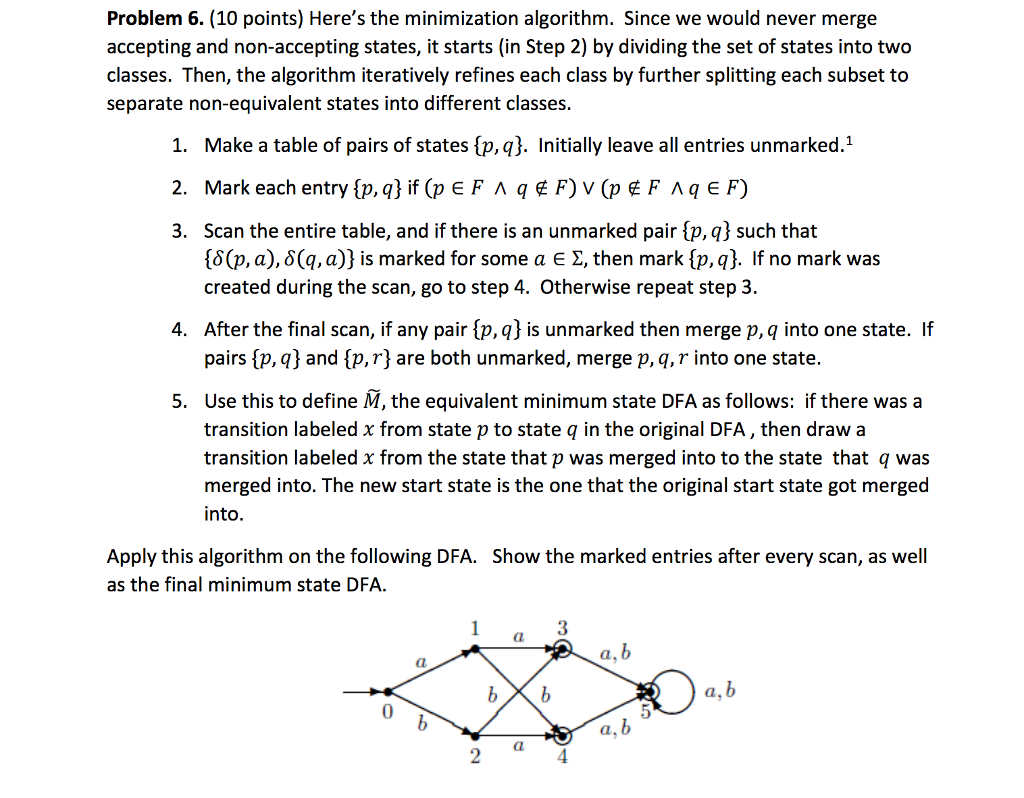
Problem 6. (10 points) Here's the minimization algorithm. Since we would never merge accepting and non-accepting states, it starts (in Step 2) by dividing the set of states into two classes. Then, the algorithm iteratively refines each class by further splitting each subset to separate non-equivalent states into different classes 1. Make a table of pairs of states aj. Initially leave all entries unmarked." 2. Mark each entry {p, q} if (p E F q E F) v (PE F q E F) 3. Scan the entire table, and if there is an unmarked pair 93 such that {6(P. a), (q, a)) is marked for some a E , then mark {p,q). If no mark was created during the scan, go to step 4. Otherwise repeat step 3 After the final scan, if any pair(p, q} is unmarked then merge p, q into one state. If pairs sp,q) and sp,r) are both unmarked, merge p, q,r into one state. 4. 5. Use this to define M, the equivalent minimum state DFA as follows: if there was a transition labeled x from state p to state q in the original DFA, then draw a transition labeled from the state that p was merged into to the state that q was merged into. The new start state is the one that the original start state got merged into Apply this algorithm on the following DFA. Show the marked entries after every scan, as well as the final minimum state DFA 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


