Question: Problem 6: Using the Cayley Hamilton Theorem, compute the state transition matrix e for the characteristic matrix, 0 1 0 A = 0 -4

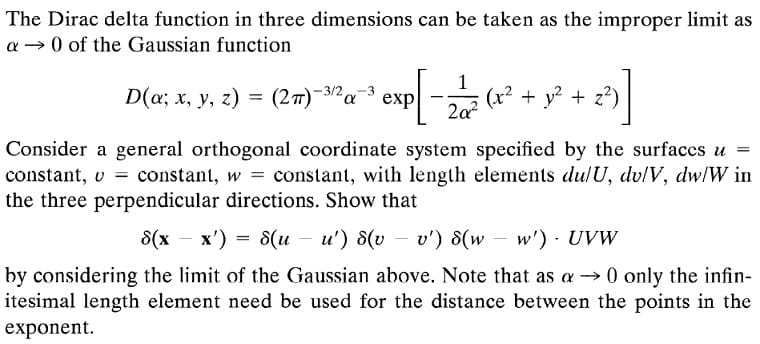
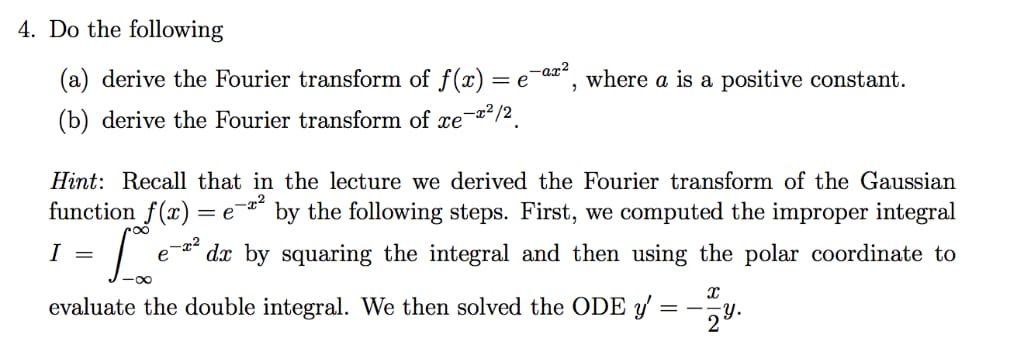
Problem 6: Using the Cayley Hamilton Theorem, compute the state transition matrix e for the characteristic matrix, 0 1 0 A = 0 -4 3 -1 -2 The Dirac delta function in three dimensions can be taken as the improper limit as a0 of the Gaussian function constant, D(a; x, y, z) = (2)-3/2- exp 1 exp 2a2 (x + y2 2 + 23)] Consider a general orthogonal coordinate system specified by the surfaces u = constant, w = constant, with length elements du/U, dv/V, dw/W in the three perpendicular directions. Show that 8(x x') = d(u u') (v v') (w w') UVW - -> by considering the limit of the Gaussian above. Note that as a 0 only the infin- itesimal length element need be used for the distance between the points in the exponent. 4. Do the following (a) derive the Fourier transform of f(x) = = e e-ax2, where a is a positive constant. (b) derive the Fourier transform of xe-x/2. Hint: Recall that in the lecture we derived the Fourier transform of the Gaussian function f(x) -22 = e by the following steps. First, we computed the improper integral e-x I = 0- dx by squaring the integral and then using the polar coordinate to evaluate the double integral. We then solved the ODE y' ===Y. 29.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


