Question: problem 6-4A periodic ps xyMMHE Reader c 0 I secure | https//player.mt /epub/sn80t0#epubcfi(%2f6%2F31 6%5Bitem . 1 5 Problem 6-3A Perpetual: Alternative cost flows P1 Montoure
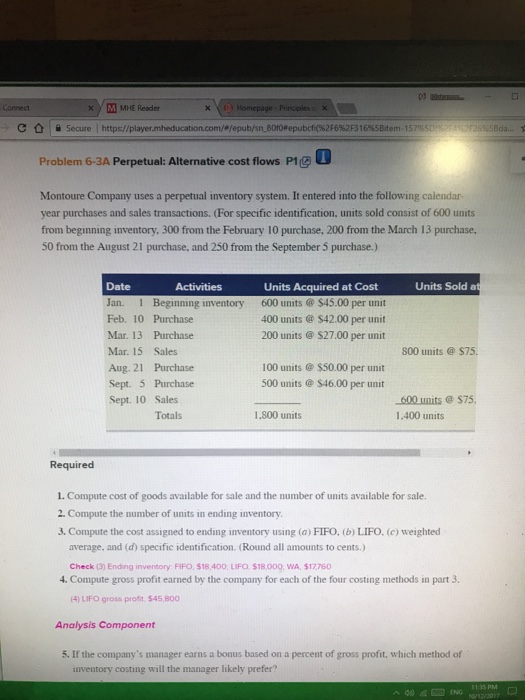
ps xyMMHE Reader c 0 I secure | https//player.mt /epub/sn80t0#epubcfi(%2f6%2F31 6%5Bitem . 1 5 Problem 6-3A Perpetual: Alternative cost flows P1 Montoure Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following calendar- year purchases and sales transactions. (For specific identification, units sold consist of 600 units from beginning inventory, 300 from the February 10 purchase, 200 from the March 13 purchase, 50 from the August 21 purchase, and 250 from the September 5 purchase.) Activities Units Sold a Date Jan. 1 Beginning inventory 600 units @ $45.00 per unit Feb. 10 Purchase Mar. 13 Purchase Mar. 15 Sales Aug. 21 Purchase Sept. 5 Purchase Sept. 10 Sales Units Acquired at Cost 400 units@ $42.00 per unit 200 units @ $27.00 per unit 800 units @$75. 100 units @ S50.00 per unit 500 units @ $46.00 per unit 600 units@ $75, 1-400 units Totals 1,800 units Required 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale. 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO. (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification. (Round all amounts to cents.) Check (3) Ending inventory FIFO, $18.400, LIFO $18.000, WA, $17760 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3 (4) LIFO gross protit, $45,800 Analysis Component 5. If the company's manager earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit, which method of inventory costing will the manager likely prefer
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


