Question: Problem 8. (4 points) Car Hinges ~ Motor General uses a series of machines to manufacture hinges for automobile doors. Historically, this process has
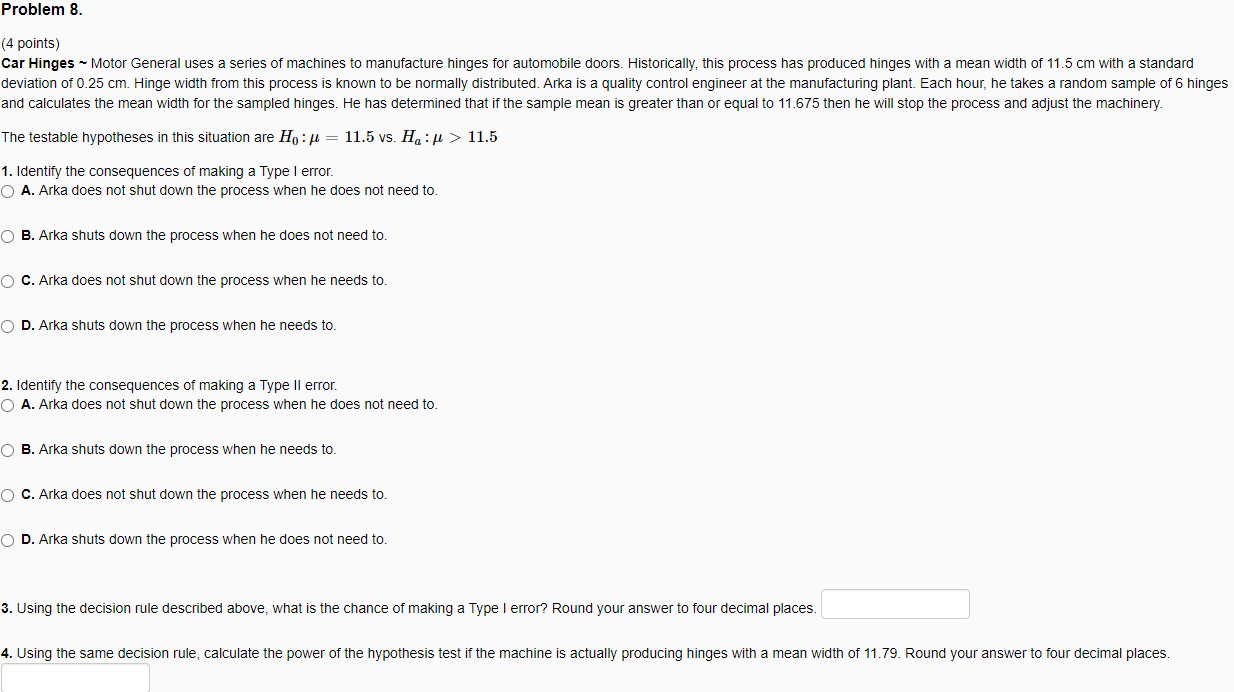
Problem 8. (4 points) Car Hinges ~ Motor General uses a series of machines to manufacture hinges for automobile doors. Historically, this process has produced hinges with a mean width of 11.5 cm with a standard deviation of 0.25 cm. Hinge width from this process is known to be normally distributed. Arka is a quality control engineer at the manufacturing plant. Each hour, he takes a random sample of 6 hinges and calculates the mean width for the sampled hinges. He has determined that if the sample mean is greater than or equal to 11.675 then he will stop the process and adjust the machinery. The testable hypotheses in this situation are Ho: = 1. Identify the consequences of making a Type I error. O A. Arka does not shut down the process when he does not need to. 11.5 vs. Ha:> 11.5 O B. Arka shuts down the process when he does not need to. O C. Arka does not shut down the process when he needs to. O D. Arka shuts down the process when he needs to. 2. Identify the consequences of making a Type Il error. O A. Arka does not shut down the process when he does not need to. O B. Arka shuts down the process when he needs to. O C. Arka does not shut down the process when he needs to. O D. Arka shuts down the process when he does not need to. 3. Using the decision rule described above, what is the chance of making a Type I error? Round your answer to four decimal places. 4. Using the same decision rule, calculate the power of the hypothesis test the machine is actually producing hinges with mean width of 11.79. Round your answer to four decimal places.
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The detailed answer for the above question is provided below 1 Identify the consequences of making a Type I error A Type I error is also known as a fa... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


