Question: Problem 8-23A Computing materials, labor, and cost variances d. Labor price variance: $11,592 F g. Fixed cost volume variance: $2,820 F The following data were
Problem 8-23A Computing materials, labor, and cost variances
d. Labor price variance: $11,592 F
g. Fixed cost volume variance: $2,820 F
The following data were drawn from the records of Quentin Corporation.
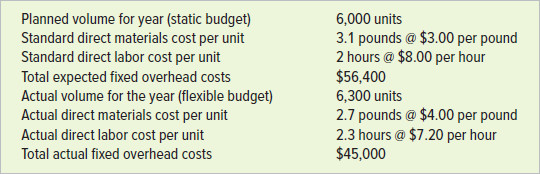
Required
-
Prepare a materials variance information table showing the standard price, the actual price, the standard quantity, and the actual quantity.
-
Calculate the materials price and usage variances. Indicate whether the variances are favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
-
Prepare a labor variance information table showing the standard price, the actual price, the standard hours, and the actual hours.
-
Calculate the labor price and usage variances. Indicate whether the variances are favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
-
Calculate the predetermined overhead rate, assuming that Quentin uses the number of units as the allocation base.
-
Calculate the fixed cost spending variance. Indicate whether the variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
-
Calculate the fixed cost volume variance. Indicate whether the variance is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
Problem 8-23B Computing materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead cost variances
Martin Hickey was a new cost accountant at Freeport Plastics Corporation. He was assigned to analyze the following data that his predecessor left him.
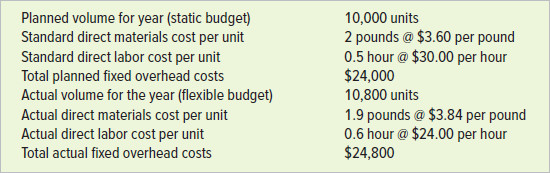
Required
-
Prepare a materials variance information table showing the standard price, the actual price, the standard quantity, and the actual quantity.
-
Calculate the materials price and usage variances and indicate whether they are favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
-
Prepare a labor variance information table showing the standard price, the actual price, the standard hours, and the actual hours.
-
Calculate the labor price and usage variances and indicate whether they are favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
-
Calculate the predetermined overhead rate, assuming that Freeport Plastics uses the number of units as the allocation base.
-
Calculate the fixed manufacturing overhead cost spending variance and indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
-
Calculate the fixed manufacturing overhead cost volume variance and indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
Problem 8-25A Determining labor price and usage variances
Bonnies Doll Company produces handmade dolls. The standard amount of time spent on each doll is 2.0 hours. The standard cost of labor is $20 per hour. The company planned to make 8,000 dolls during the year but actually used 17,500 hours of labor to make 9,000 dolls. The payroll amounted to $344,750.
Required
-
Should labor variances be based on the planned volume of 8,000 dolls or the actual volume of 9,000 dolls?
-
Prepare a table that shows the standard labor price, the actual labor price, the standard labor hours, and the actual labor hours.
-
Compute the labor price variance and indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
-
Compute the labor usage variance and indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U). Problem 8-25B Determining labor price and usage variances
-
As noted in Problem 8-24B, Watonga Swimsuit makes swimsuits. In Year 2, Watonga produced its most popular swimsuit, the Sarong, for a standard labor price of $33.60 per hour. The standard amount of labor was 1.0 hour per swimsuit. The company had planned to produce 100,000 Sarong swimsuits. At the end of Year 2, the companys cost accountant reported that Watonga had used 107,000 hours of labor to make 102,000 swimsuits. The total labor cost was $3,723,600.
-
Required
-
Should the labor variances be based on the planned volume of 100,000 swimsuits or on the actual volume of 102,000 swimsuits?
-
Prepare a table that shows the standard labor price, the actual labor price, the standard labor hours, and the actual labor hours.
-
Compute the labor price variance and indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
-
Compute the labor usage variance and indicate whether it is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U).
Planned volume for year (static budget) Standard direct materials cost per unit Standard direct labor cost per unit Total expected fixed overhead costs Actual volume for the year (flexible budget) Actual direct materials cost per unit Actual direct labor cost per unit Total actual fixed overhead costs 6,000 units 3.1 pounds @ $3.00 per pound 2 hours @ $8.00 per hour $56,400 6,300 units 2.7 pounds @ $4.00 per pound 2.3 hours @ $7.20 per hour $45,000 Planned volume for year (static budget) Standard direct materials cost per unit Standard direct labor cost per unit Total planned fixed overhead costs Actual volume for the year (flexible budget) Actual direct materials cost per unit Actual direct labor cost per unit Total actual fixed overhead costs 10,000 units 2 pounds @ $3.60 per pound 0.5 hour @ $30.00 per hour $24,000 10,800 units 1.9 pounds @ $3.84 per pound 0.6 hour @ $24.00 per hour $24,800
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


