Question: Problem: 9 For the given Schedule S transactions ( T 1 , T 2 , T 3 , T 4 ) : a ) What
Problem:
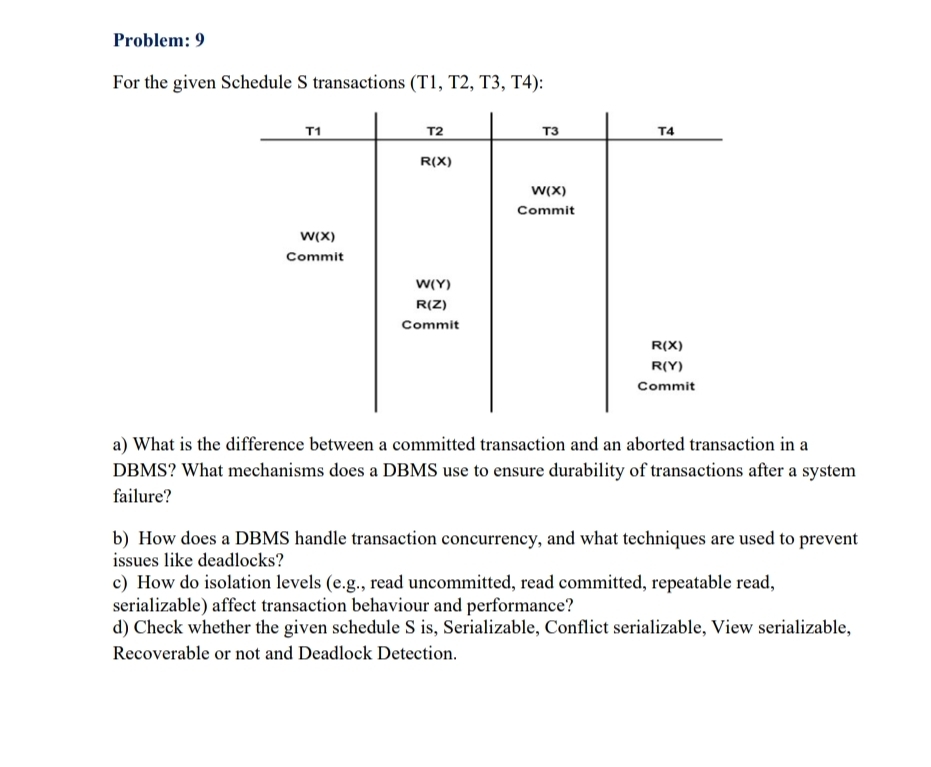
For the given Schedule S transactions T T T T:
a What is the difference between a committed transaction and an aborted transaction in a
DBMS What mechanisms does a DBMS use to ensure durability of transactions after a system
failure?
b How does a DBMS handle transaction concurrency, and what techniques are used to prevent
issues like deadlocks?
c How do isolation levels eg read uncommitted, read committed, repeatable read,
serializable affect transaction behaviour and performance?
d Check whether the given schedule S is Serializable, Conflict serializable, View serializable,
Recoverable or not and Deadlock Detection.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


