Question: Problem A Oldman Inc. has been manufacturing its own lamp shades for its table lamps. The company is currently operating at 100% capacity. The direct

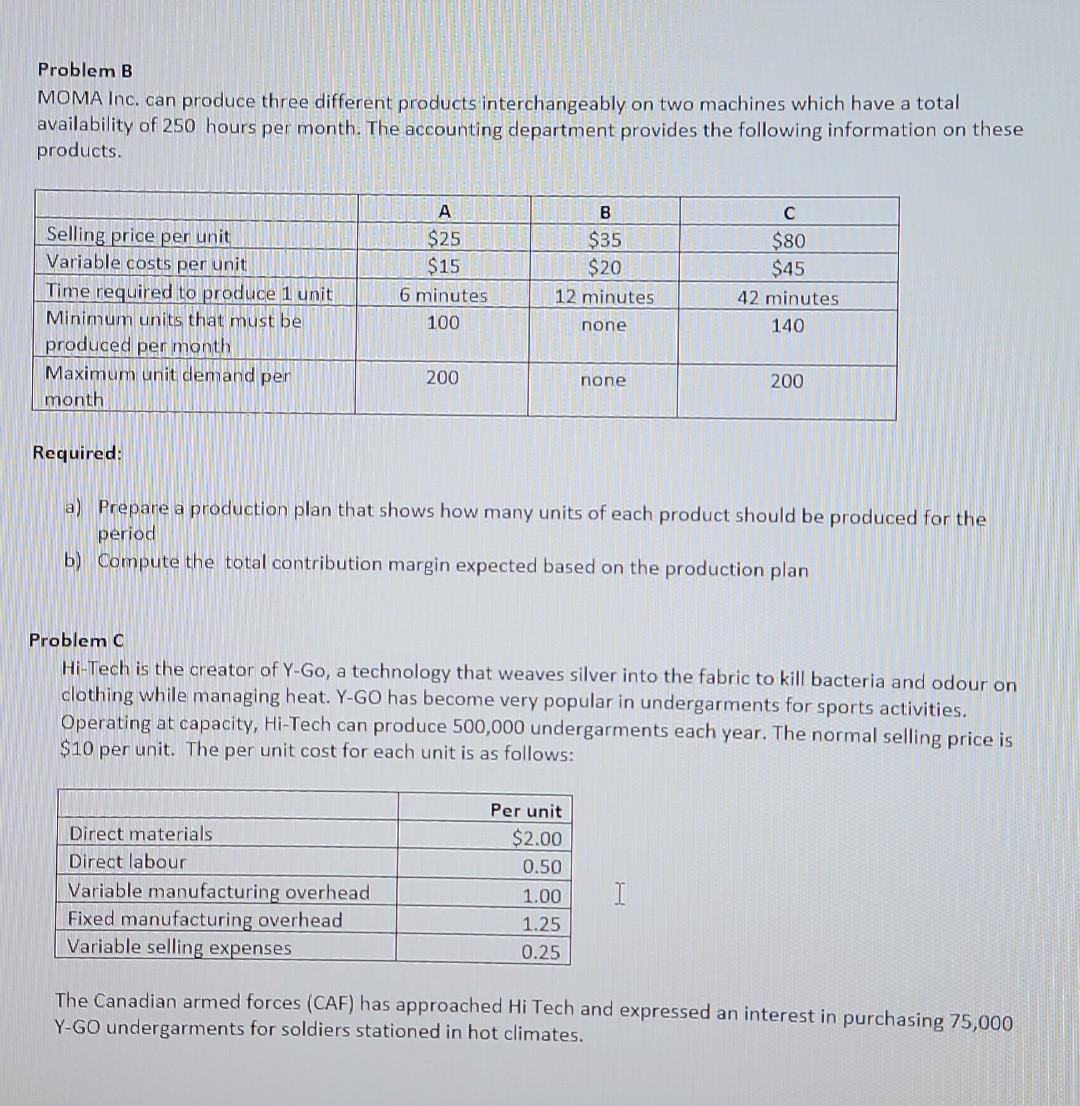
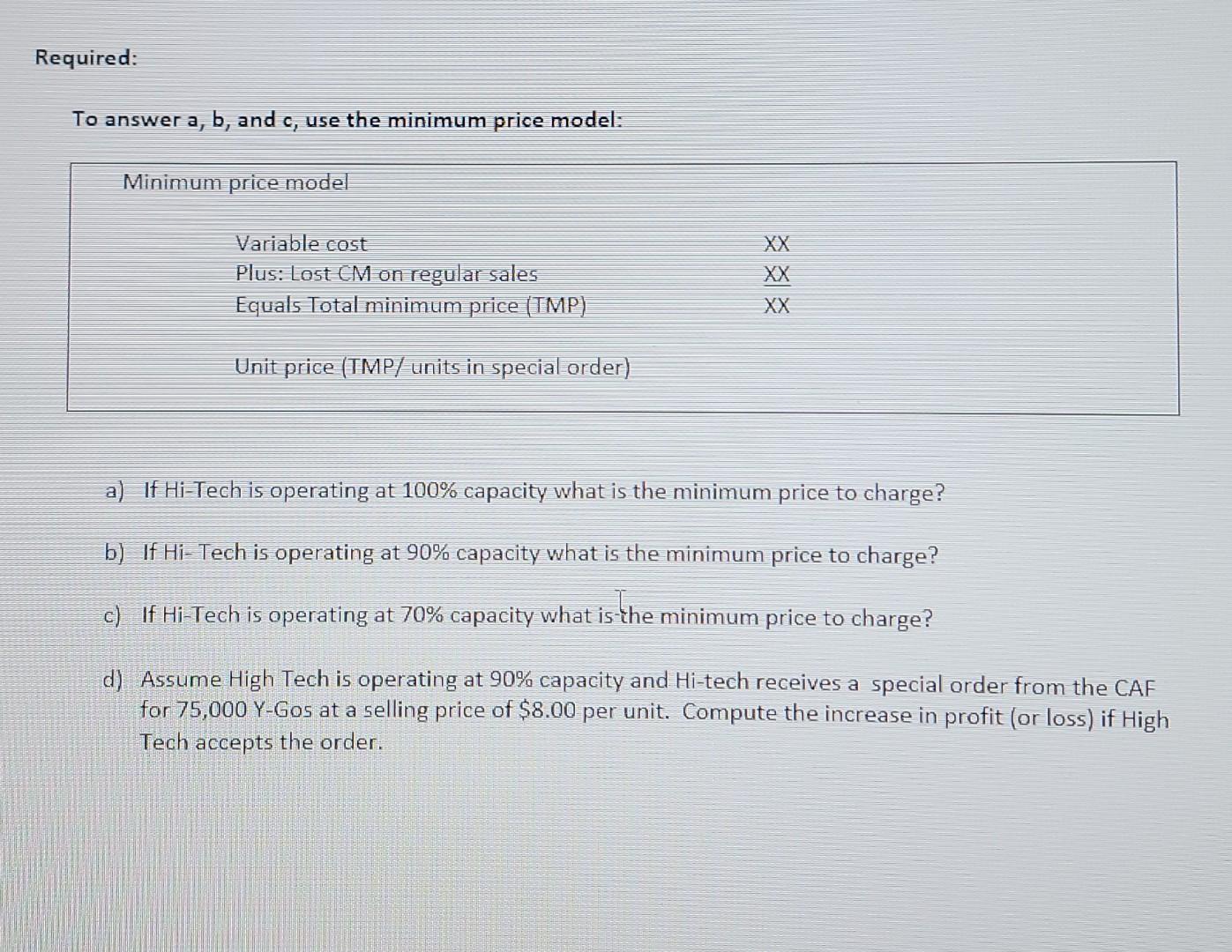
Problem A Oldman Inc. has been manufacturing its own lamp shades for its table lamps. The company is currently operating at 100% capacity. The direct materials cost is $5 per unit, the direct labour cost is $6 per unit and variable manufacturing costs are 40% of direct labour costs. Total fixed manufacturing costs are $500,000 per year. Normal production is 50,000 lampshades per year. A supplier offers to make the lampshades at a price of $20 per unit. If Oldman Inc. accepts the offer all variable manufacturing costs would be 100% avoidable and $200,000 of the total fixed manufacturing costs would be unavoidable. a) Prepare an incremental analysis for the decision to make or buy the lampshades. b) Should Oldman make or buy the lampshades? What is the $ advantage? c) Assume that if Oldman decides to buy the lampshades part of the factory space could be used to produce 10,000 other lighting products that would generate a contribution margin $15 per unit. Should Oldman make or buy the lampshades? Show your calculations. I Problem B MOMA Inc. can produce three different products interchangeably on two machines which have a total availability of 250 hours per month. The accounting department provides the following information on these products. A $25 $15 6 minutes 100 B $35 $20 12 minutes Selling price per unit Variable costs per unit Time required to produce 1 unit Minimum units that must be produced per month Maximum unit demand per month $80 $45 42 minutes 140 none 200 none 200 Required: a) Prepare a production plan that shows how many units of each product should be produced for the period b) Compute the total contribution margin expected based on the production plan Problem C Hi-Tech is the creator of Y-Go, a technology that weaves silver into the fabric to kill bacteria and odour on clothing while managing heat. Y-GO has become very popular in undergarments for sports activities. Operating at capacity, Hi-Tech can produce 500,000 undergarments each year. The normal selling price is $10 per unit. The per unit cost for each unit is as follows: Direct materials Direct labour Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Variable selling expenses Per unit $2.00 0.50 1.00 1.25 0.25 1 The Canadian armed forces (CAF) has approached Hi Tech and expressed an interest in purchasing 75,000 Y-GO undergarments for soldiers stationed in hot climates. Required: To answer a, b, and c, use the minimum price model: Minimum price model Variable cost Plus: Lost CM on regular sales Equals Total minimum price (TMP) XX Unit price (TMP/ units in special order) a) If Hi-Tech is operating at 100% capacity what is the minimum price to charge? b) If Hi-Tech is operating at 90% capacity what is the minimum price to charge? c) If Hi-Tech is operating at 70% capacity what is the minimum price to charge? d) Assume High Tech is operating at 90% capacity and Hi-tech receives a special order from the CAF for 75,000 Y-Gos at a selling price of $8.00 per unit. Compute the increase in profit (or loss) if High Tech accepts the order
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


