Question: Problem A Reading and manipulating character arrays (20 pts) Specification Write an ANSI-C program that reads from standard input a word (string with no spaces)




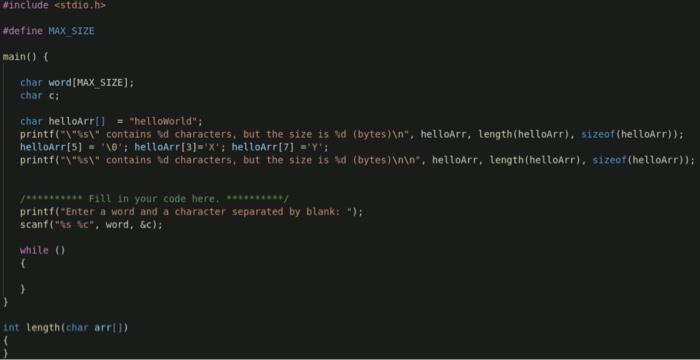
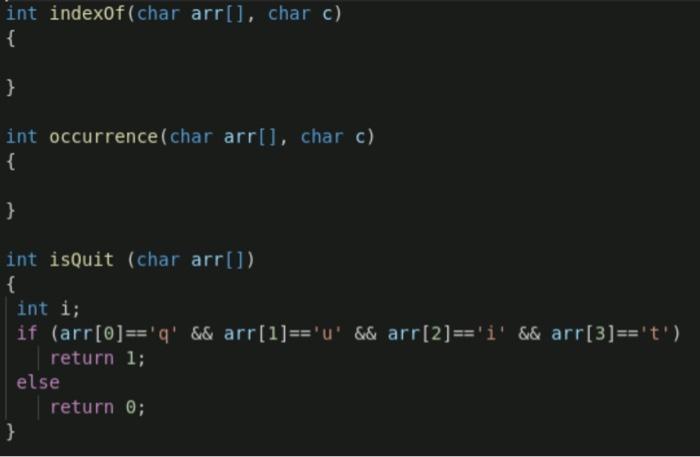
Problem A Reading and manipulating character arrays (20 pts) Specification Write an ANSI-C program that reads from standard input a word (string with no spaces) followed by a character, and then outputs the word, the number of characters in the word, and the index of the character in the word. . . Implementation download program lab3occur.c and start from there. Observe how the string" "helloWorld" is modified and shortened at the char level. define a char array to hold the input word. Assume each input word contains no more than 20 characters (so what is the minimum capacity the array should be declared to have?). use scanf ("%s %c", ..) to read the word and char. define a function int length (char word []) which returns the number of characters in word (excluding the trailing character '\0'). This function is similar to strlen(s) C library function shown earlier, and s.length() method in Java. You should NOT call strlen() library function in your function. Write your own version of strlen. define a function int indexOf(char word(), char c) which returns the index (position of the first occurrence) of c in word. Return -1 if c does not occur in word. This function is similar to s.indexof() method in Java. define a function int occurrence (char word(), char c) which returns the number of occurrences of c in word. Return 0 if c does not appear in word. keep on reading until a word "quit" is read in, followed by any character. In checking the terminating condition, as shown earlier, word == "quit" will not work as this will not compare array contents (both in C and Java). One approach is to check the contents char by char. You are provided with a "boolean" function int isQuit (char word []) which intends to check whether argument word is "quit", but this function has a flaw. Try to discover the flaw, and fix the bug. Don't use C library function here. . Sample Inputs/Outputs: red 308 $ gcc -Wall lab3occur.c -o lab3occur red 309 % lab3occur "helloWorld" contains 10 characters, but the size is 11 (bytes) "helo" contains 5 characters, but the size is 11 (bytes) Enter a word and a character separated by blank: hello x Input word is "hello". Contains 5 characters 'x' appears 0 times in the word Index of 'x' in the word is -1 Enter a word and a character separated by blank: hello 1 Input word is "hello". Contains 5 characters 'l' appears 2 times in the word Index of 'l' in the word is 2 Enter a word and a character separated by blank: beautifulworld b Input word is "beautifulworld". Contains 14 characters 'b' appears 1 times in the word Index of 'b' in the word is o Enter a word and a character separated by blank: beautifulworld u Input word is "beautifulworld". Contains 14 characters 'u' appears 2 times in the word Index of 'u' in the word is 3 Enter a word and a character separated by blank: beautifulworld U Input word is "beautifulworld". Contains 14 characters 'U' appears 0 times in the word Index of 'U' in the word is -1 Enter a word and a character separated by blank: quit x red 310 % #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


