Question: Problem Formulation (4 points) Setting of Objectives and Overall Project Plan (2 points) Model Conceptualization (4 points) Model Translation (15 points) Explain about your choice
Problem Formulation (4 points)
Setting of Objectives and Overall Project Plan (2 points)
Model Conceptualization (4 points)
Model Translation (15 points)
Explain about your choice of simulation language. Describe your model implementation with software architecture and functions of each module at high level as well as source code of each module at detail level.
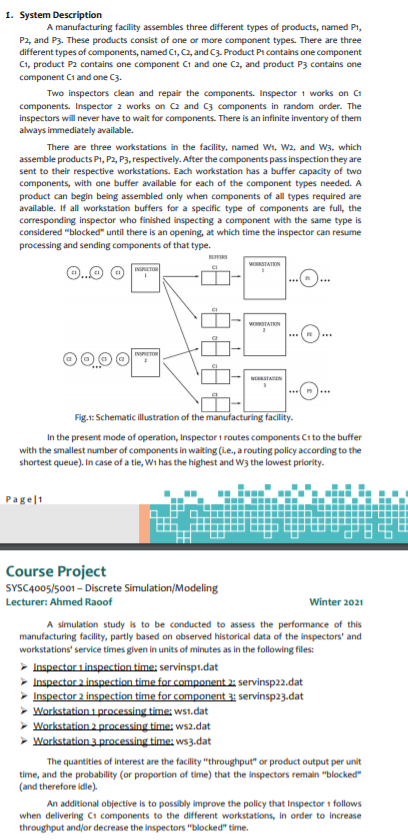
1. System Description A manufacturing facility assembles three different types of products, named P1, P2, and Ps. These products consist of one or more component types. There are three different types of components, named C1,C2, and C3. Product Pa contains one component C1, product contains one component C1 and one C2, and product P3 contains one component C1 and one C3. Two inspectors clean and repair the components. Inspector 1 works on Cu components. Inspector 2 works on Q and 3 components in random order. The inspectors will never have to wait for components. There is an infinite inventory of them always immediately available. There are three workstations in the facility, named W1, W2, and W3. which assemble products P1, P2, P3, respectively. After the components pass inspection they are sent to their respective workstations. Each workstation has a buffer capacity of two components, with one buffer available for each of the component types needed. A product can begin being assembled only when components of all types required are available. If all workstation buffers for a specific type of components are full, the corresponding inspector who finished inspecting a component with the same type is considered "blocked" until there is an opening, at which time the inspector can resume processing and sending components of that type. TAN OSTATIN - Fig.1: Schematic illustration of the manufacturing facility. e present mode of operation, Inspector 1 routes components Cu to the buffer with the smallest number of components in waiting (.e., a routing policy according to the shortest queue). In case of a tie, Wi has the highest and W3 the lowest priority. Page 1 Course Project SYSC4005/5001 - Discrete Simulation/Modeling Lecturer: Ahmed Raoof Winter 2021 A simulation study is to be conducted to assess the performance of this manufacturing facility, partly based on observed historical data of the inspectors' and workstations service times given in units of minutes as in the following files: Inspector 1 inspection time: servinspi.dat Inspector 2 inspection time for component 2: servinsp22.dat Inspector 2 inspection time for component 3: servinsp23.dat Workstation 1 processing time: wsi.dat Workstation 2 processing time:ws2.dat Workstation 3 processing time: ws3.dat The quantities of interest are the facility "throughput" or product output per unit time, and the probability (or proportion of time) that the inspectors remain "blocked" (and therefore idle) An additional objective is to possibly improve the policy that Inspector 1 follows when delivering C1 components to the different workstations, in order to increase throughput and/or decrease the inspectors "blocked" time. 1. System Description A manufacturing facility assembles three different types of products, named P1, P2, and Ps. These products consist of one or more component types. There are three different types of components, named C1,C2, and C3. Product Pa contains one component C1, product contains one component C1 and one C2, and product P3 contains one component C1 and one C3. Two inspectors clean and repair the components. Inspector 1 works on Cu components. Inspector 2 works on Q and 3 components in random order. The inspectors will never have to wait for components. There is an infinite inventory of them always immediately available. There are three workstations in the facility, named W1, W2, and W3. which assemble products P1, P2, P3, respectively. After the components pass inspection they are sent to their respective workstations. Each workstation has a buffer capacity of two components, with one buffer available for each of the component types needed. A product can begin being assembled only when components of all types required are available. If all workstation buffers for a specific type of components are full, the corresponding inspector who finished inspecting a component with the same type is considered "blocked" until there is an opening, at which time the inspector can resume processing and sending components of that type. TAN OSTATIN - Fig.1: Schematic illustration of the manufacturing facility. e present mode of operation, Inspector 1 routes components Cu to the buffer with the smallest number of components in waiting (.e., a routing policy according to the shortest queue). In case of a tie, Wi has the highest and W3 the lowest priority. Page 1 Course Project SYSC4005/5001 - Discrete Simulation/Modeling Lecturer: Ahmed Raoof Winter 2021 A simulation study is to be conducted to assess the performance of this manufacturing facility, partly based on observed historical data of the inspectors' and workstations service times given in units of minutes as in the following files: Inspector 1 inspection time: servinspi.dat Inspector 2 inspection time for component 2: servinsp22.dat Inspector 2 inspection time for component 3: servinsp23.dat Workstation 1 processing time: wsi.dat Workstation 2 processing time:ws2.dat Workstation 3 processing time: ws3.dat The quantities of interest are the facility "throughput" or product output per unit time, and the probability (or proportion of time) that the inspectors remain "blocked" (and therefore idle) An additional objective is to possibly improve the policy that Inspector 1 follows when delivering C1 components to the different workstations, in order to increase throughput and/or decrease the inspectors "blocked" time
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


