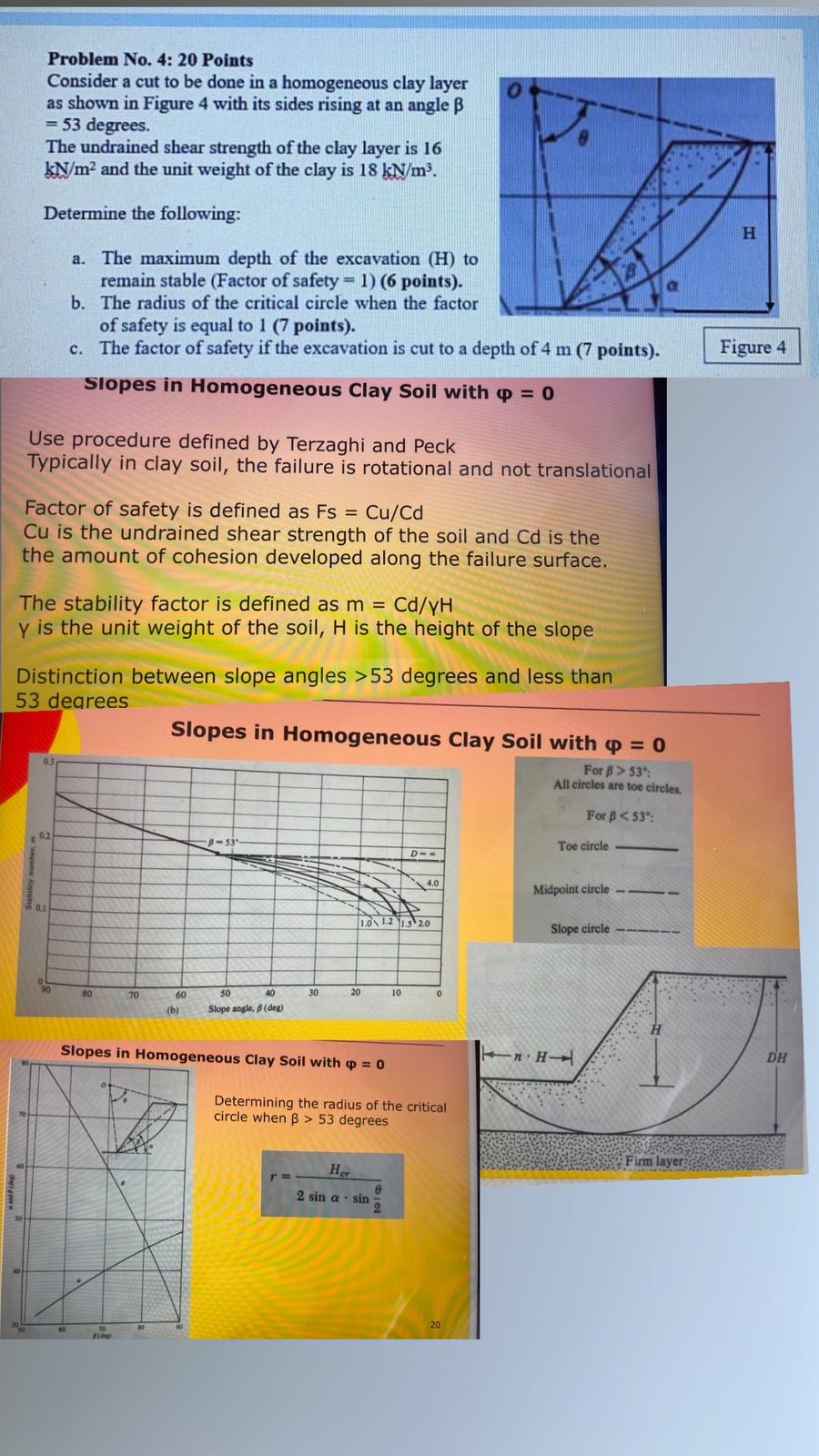
Question: Problem No . 4 : 2 0 Points Consider a cut to be done in a homogeneous clay layer as shown in Figure 4 with
Problem No: Points
Consider a cut to be done in a homogeneous clay layer as shown in Figure with its sides rising at an angle degrees.
The undrained shear strength of the clay layer is and the unit weight of the clay is
Determine the following:
a The maximum depth of the excavation to remain stable Factor of safety points
b The radius of the critical circle when the factor of safety is equal to points
c The factor of safety if the excavation is cut to a depth of points
Slopes in Homogeneous Clay Soil with
Use procedure defined by Terzaghi and Peck
Typically in clay soil, the failure is rotational and not translational
Factor of safety is defined as Fs is the undrained shear strength of the soil and is the the amount of cohesion developed along the failure surface.
The stability factor is defined as is the unit weight of the soil, is the height of the slope
Distinction between slope angles degrees and less than dearees
Slopes in Homogeneous Clay Soil with
For :
All circles are toe circles.
For ;
Toe circle
Midpoint circle
Slope circle
Slopes in Homoaeneous Clay Soil with
Determining the radius of the critical circle when degrees
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


