Question: Problem#1 :In computational fluid dynamics (CFD), the energy equation can be solved in four different forms. They are (1) the transport equation for total energy
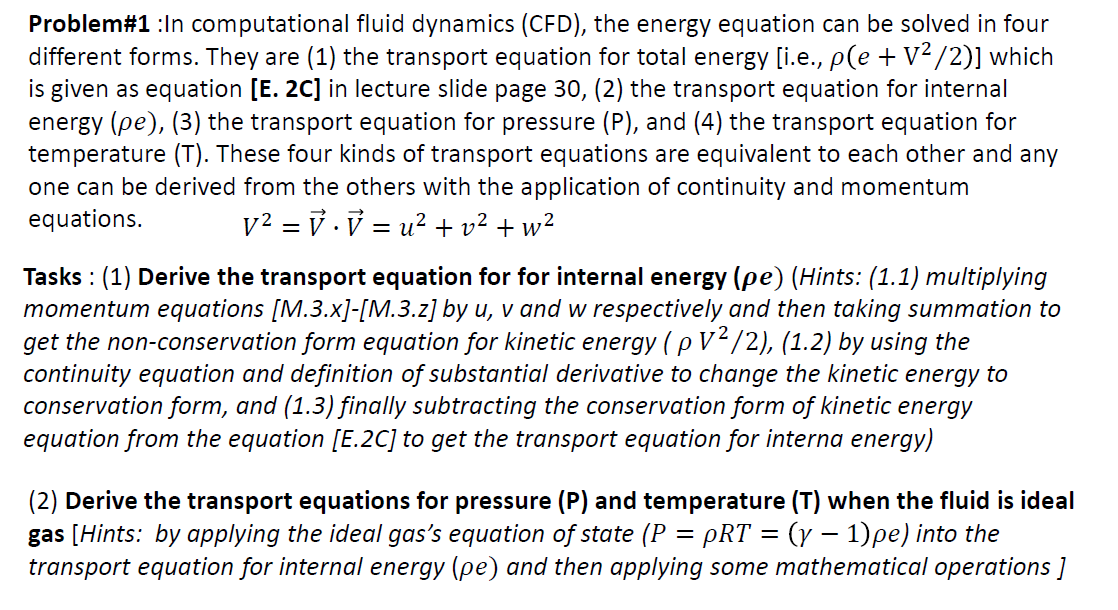
Problem#1 :In computational fluid dynamics (CFD), the energy equation can be solved in four different forms. They are (1) the transport equation for total energy [i.e., ple + V2/2)] which is given as equation [E. 2C) in lecture slide page 30, (2) the transport equation for internal energy (pe), (3) the transport equation for pressure (P), and (4) the transport equation for temperature (T). These four kinds of transport equations are equivalent to each other and any one can be derived from the others with the application of continuity and momentum equations. v2 = V V = u2 + v2 + w2 Tasks : (1) Derive the transport equation for for internal energy (pe) (Hints: (1.1) multiplying momentum equations [M.3.x]-[M.3.z] by u, v and w respectively and then taking summation to get the non-conservation form equation for kinetic energy (P V2/2), (1.2) by using the continuity equation and definition of substantial derivative to change the kinetic energy to conservation form, and (1.3) finally subtracting the conservation form of kinetic energy equation from the equation [E.2C] to get the transport equation for interna energy) (2) Derive the transport equations for pressure (P) and temperature (T) when the fluid is ideal gas [Hints: by applying the ideal gas's equation of state (P = PRT = (y 1)pe) into the transport equation for internal energy (pe) and then applying some mathematical operations ] Problem#1 :In computational fluid dynamics (CFD), the energy equation can be solved in four different forms. They are (1) the transport equation for total energy [i.e., ple + V2/2)] which is given as equation [E. 2C) in lecture slide page 30, (2) the transport equation for internal energy (pe), (3) the transport equation for pressure (P), and (4) the transport equation for temperature (T). These four kinds of transport equations are equivalent to each other and any one can be derived from the others with the application of continuity and momentum equations. v2 = V V = u2 + v2 + w2 Tasks : (1) Derive the transport equation for for internal energy (pe) (Hints: (1.1) multiplying momentum equations [M.3.x]-[M.3.z] by u, v and w respectively and then taking summation to get the non-conservation form equation for kinetic energy (P V2/2), (1.2) by using the continuity equation and definition of substantial derivative to change the kinetic energy to conservation form, and (1.3) finally subtracting the conservation form of kinetic energy equation from the equation [E.2C] to get the transport equation for interna energy) (2) Derive the transport equations for pressure (P) and temperature (T) when the fluid is ideal gas [Hints: by applying the ideal gas's equation of state (P = PRT = (y 1)pe) into the transport equation for internal energy (pe) and then applying some mathematical operations ]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


