Question: Problems: find_all_years (db) : This function accepts an existing database db, finds all years included in it anywhere. Return the list of years sorted in


Problems:
find_all_years (db) : This function accepts an existing database db, finds all years included in it anywhere. Return the list of years sorted in ascending order.
total_count_for_name (db, name, gender) : This function accepts an existing database db, a name and a gender, adds all counts for that name/gender from different years and returns the total.
names_by_year(db, year): accepts a database db, and a year. It builds/returns a new database with only names (of either gender) with a count in the specified year and only information for that year. The original database must not be modified.
largest_count_for_year(db, year): accepts a database db, and a year. It finds the name/gender pair(s) with the highest count in that year and returns as a list of tuples (name, gender, count). Since multiple name/gender pairs might tie with the highest count, sort the list alphabetically with .sort() or sorted().
add_name (db, name, gender, year, count, rank=None): This function accepts an existing database db, name, gender, year, count, and rank then it updates the database to include that information.
Return None.
The resulting database is considered unranked, as the addition means the rankings aren't up-to-date. It's acceptable that there are some None ranks and some numeric ranks, so some calls to add_name may intentionally use None as the rank argument.
If there is already an entry for that name/gender/year, you must replace it.
Hint: This function can be helpful to implement read_file(), as well as any functions that must create a new database dictionary.


Data Files:
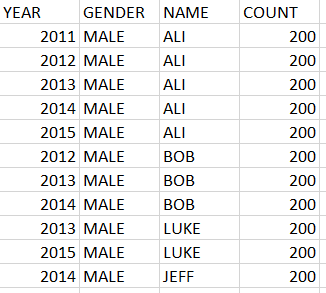
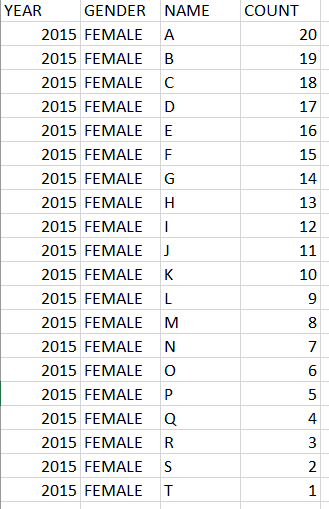
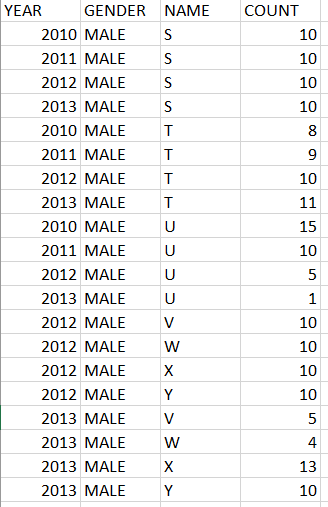
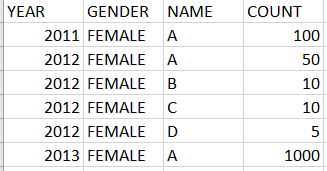
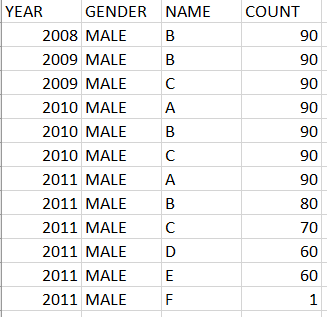
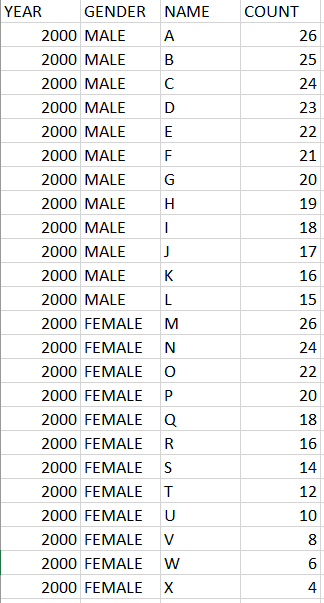
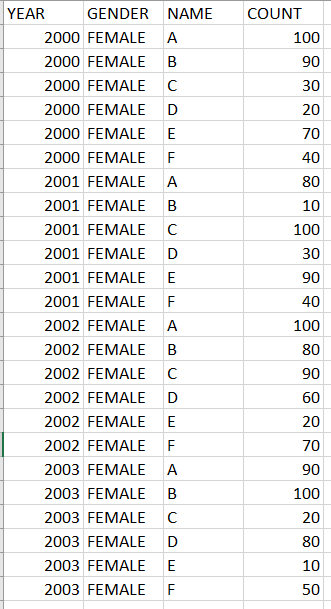
Test cases : https://repl.it/N7up/1
Thank you!
Restrictions no modules may be imported. (this definitely includes the csv module - do the work directly!) Allowed * all basic expressions and statements file reading: open(), close(), read(), readline), readlines (), with syntax dictionaries: len, get, clear, copy, keys, values, items, pop, popitem, update all sets and set operations; all exception handling blocks/raises. functions: len(), range(), min), max), enumerate(), int), and any functions you write list methods: remove(), insert(), append(), extend), pop(), index() string methods: split), endswith), startswith), join(), insert, index) more: sorted(), sort(), reversed(), reverse() calling other functions of the project (and your own defined helper functions). Please do this! ) Hint In our solution, we only used range, len, int, open, close, readlines, .get(), .items, .remove)., .append), .split(), .sort()
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


