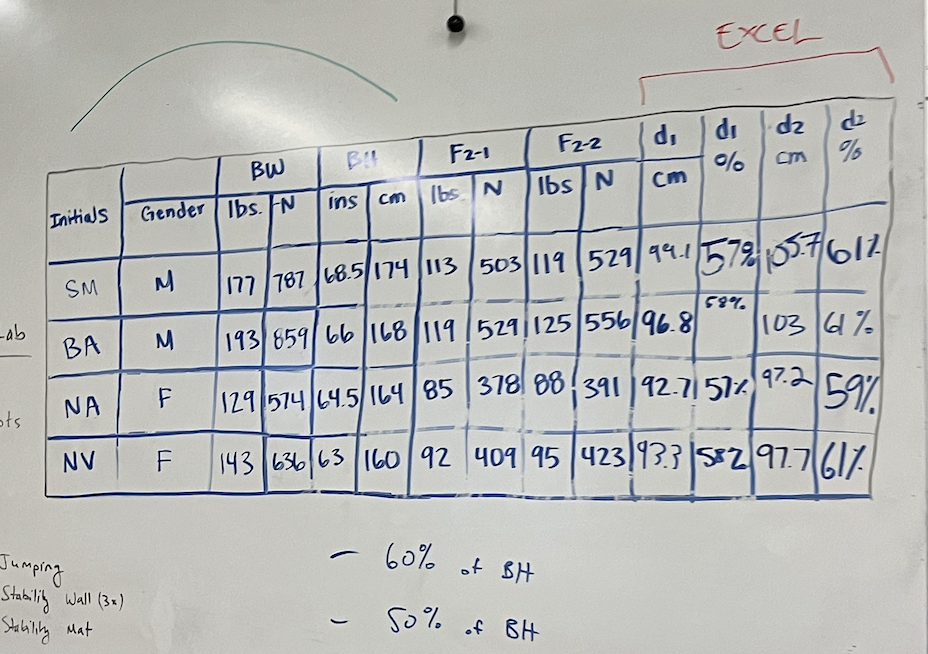
Question: Procedures To calculate the CG using this method, a person would lie on the reaction board under two separate conditions: one with their arms at


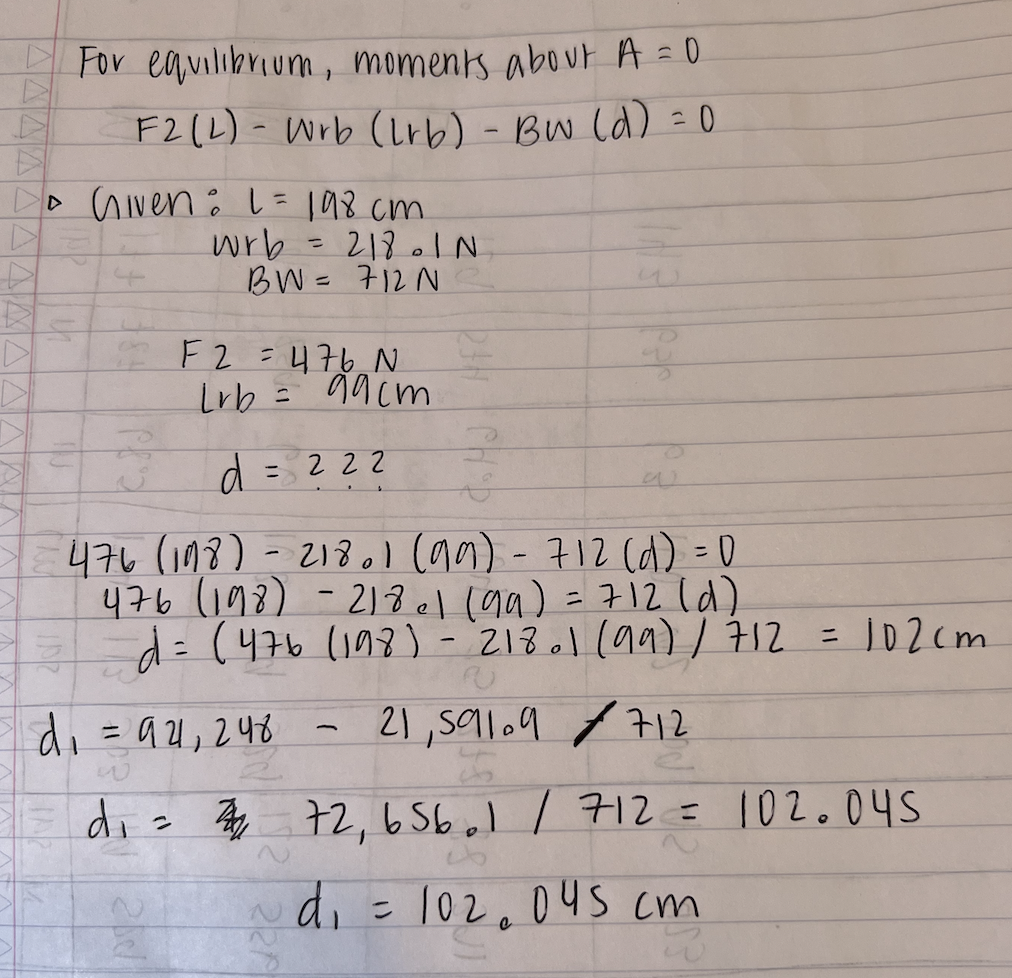
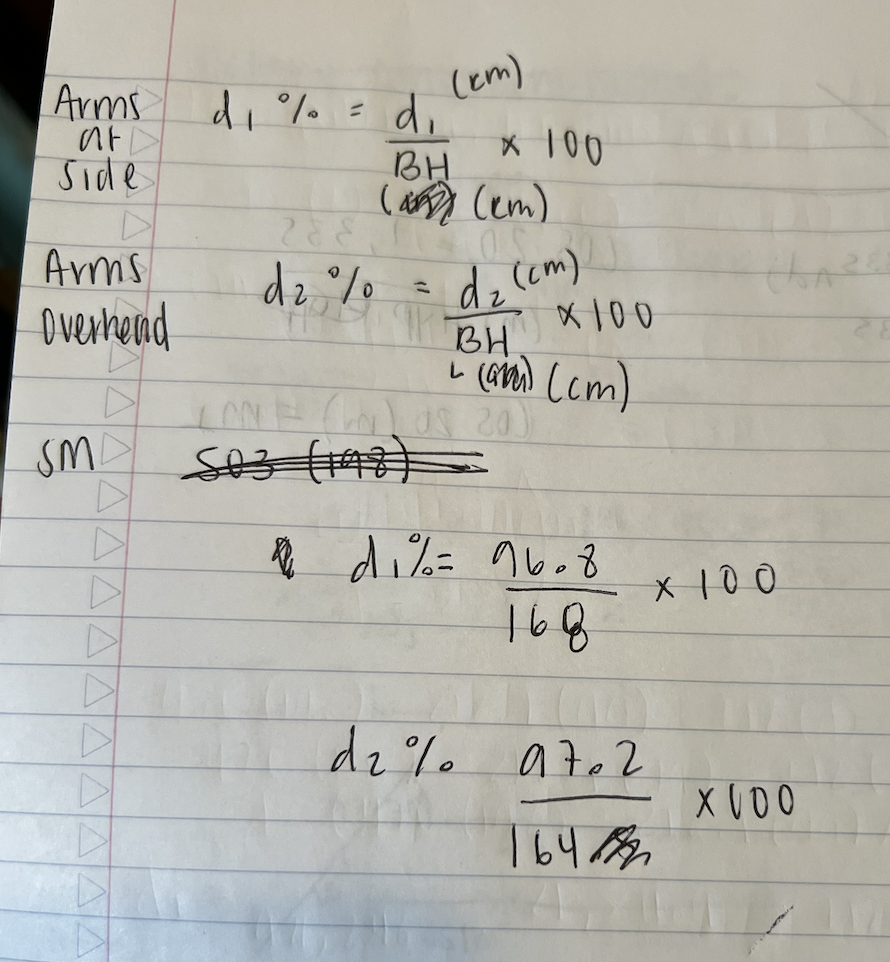
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


