Question: Program Description: You are being asked to write a program that will draw a scalable dumbbell whose size is determined by user input. Obviously, one
Program Description: You are being asked to write a program that will draw a scalable dumbbell whose size is determined by user input.
Obviously, one way to write such a program to draw this figure would be to write a series of System.out.println statements that prints each line of the figure as you did with the Guitar. However, by this point in class, you probably now realize that such a solution not only contains redundancy of statements, but also would not scale easily to draw different size dumbbells. Two important parts of this exercise are using methods to find an appropriate decomposition of the program and incorporating FOR loops for the repeated patterns of characters that vary in number from line to line. It may help to write pseudocode and tables to understand the patterns, as described in the textbook and lecture


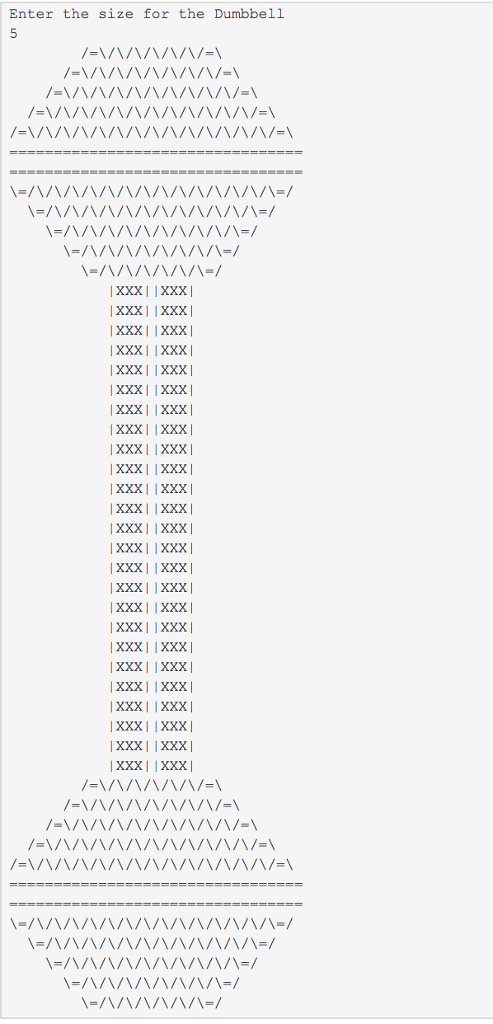
Program Requirements (what we're looking for when grading):
Correctness - You should test your Dumbbell program on the following input sizes: 3, 4, 5 and ensure it works. We have set up tests in this Zylabs that will compare your program against those sizes to make sure that your Dumbbell scales properly.
Use of for-loops (nested as appropriate) - This program is intended to test your knowledge through Chapter 2, especially nested for-loops. If you like, you will also use the Java features from Chapter 4 in Zybooks (chapter 3 in Reges) such as parameters. You may not use any Java constructs beyond what has been covered in lecture or Zybooks through Chapter 4.
Use of methods for structure and elimination of redundancy - Incorporate methods in your solution in such a way that the methods match the structure of the output itself (see TIPS below). Avoid significant redundancy; use methods so that no substantial groups of identical statements appear in your code. You should have no println() statements that draw the figure in your main() method.Your main method should only contain the prompt for the user input followed by calls to the methods to draw the Dumbbell.
Main() location - your main method should be placed above any other methods (i.e., it should be first).
Source code aesthetics (commenting, indentation, spacing, identifier names) - Your program should look nice and read easily. This means
Indent - You are required to properly indent your code and will lose points if you make significant indentation mistakes. See the textbook for examples of proper indentation.
Line length - No line of your code, including comments should be over 100 characters long (even better is limiting lines to 80 characters).
Method Decomposition - No method should have more than 20 statements. Remember that a statement is defined as line in Java ending in a semi-colon. Do not count comment lines, blank lines or lines that simply have a brace on it in your official count.
Comment block at top - Include comments at the top of all your programs giving your name, email address, etc. This includes stating what you program does beside the "Description" label.
Meaningful method/variable names - Choose names that are meaningful for your methods. In other words, you will lose points if you name your methods doFirst(); doNext(); doLast().
Method comments - Include a short description (as a comment) before each method describing its purpose.
Readable - Use "white-space" and blank lines within your code and between your methods to make it more readable.
Prompt for figure's size - Your figure must be based on the value that the user inputs specifying the size for Dumbbell. You should pass this value to your other methods as needed throughout your code. The idea is by the user simply inputting a different value, your program would produce a figure of a different size.
TIPS: Development Strategy: This program is best completed in stages. We strongly recommend the following development strategy:
Tables: Examine the output and write tables to discover the patterns of repeated characters on each line like we did in lecture.
Methods/Decomposition: Decide how you want to break down the program into methods. We suggest the following methods: drawTopHalfSphere(), drawBottomHalfSphere(), drawHandle(). You can re-use the two halves of the sphere to draw both sides of dumbbell.
Code some pieces - Code w/o worrying about size varying: Write the Java code to draw the top half of the Dumbbell at size 3. Make sure that's correct. Then code the bottom half of the Dumbbell. Then the handle and so on.
Code w/ varying input - Once you have all the pieces working, go ahead and try different inputs to see if it scales properly to different sizes. When you have that looking good in intelliJ, go ahead and copy the code to Zylabs and see if you pass the tests.
To summarize, you should not worry about the size at first. Use loop tables to help you deduce the patterns in the output. After your figure looks correct at the size of 3, begin varying the size.
Enter the size for the Dumbbell 3 1x1 1x1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


