Question: Programming assignment 3: Doubly-linked lists Bonus 5% for a correct implementation that has no unnecessary repetition of code Make the class DLL which uses a


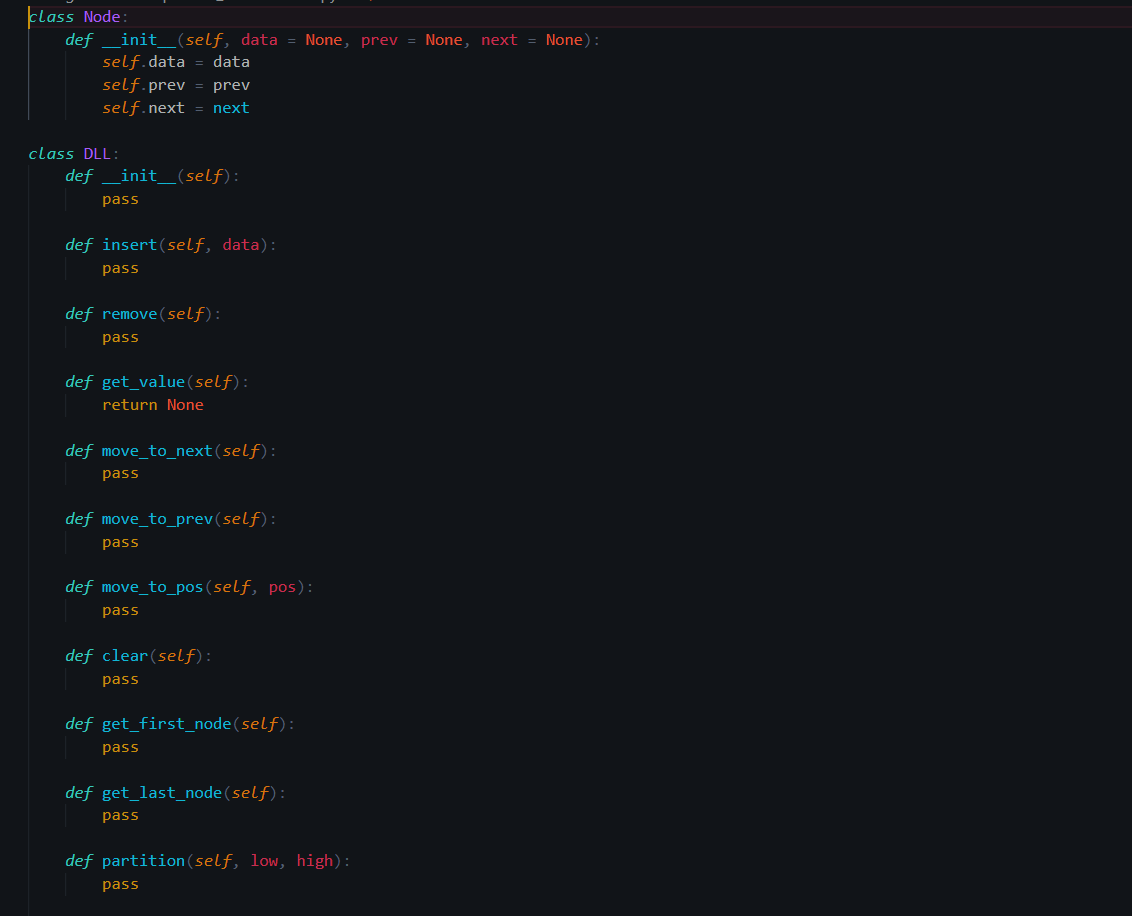
Programming assignment 3: Doubly-linked lists Bonus 5% for a correct implementation that has no unnecessary repetition of code Make the class DLL which uses a doubly-linked list to implement the following operations: _str_(self) - (5%) o Returns string with all the items in the list with a single space between them _len_(self) - (5%) o Returns the number of items in the list insert(value) - (5%) o Inserts an item with that value in front of the node at the current position The new node is now in the current position remove() - (5%) o Removes the node at the current position if there is one (otherwise does nothing) The node behind the removed node is now in the current position get_value() - (5%) o Returns the value of the item at the current position in the list (None if not item) move_to_next() - (5%) o Moves the current position one item closer to the tail/trailer Do nothing if at end move_to_prev() - (5%) o Moves the current position one item closer to the head/header Do nothing if at beginning move_to_pos(position) - (5%) o Moves the current position to item #position in the list The first actual data item is #0 Do nothing if position not between beginning and end (including both) clear() - (10%) o Clears all nodes from the list get_first_node() - (5%) o Returns the first Node of the list The headers next pointer should be pointing to this node Returns the node, not the value inside it o If list is empty, return None get_last_node() - (5%) o Returns the last Node of the list The tailers prev pointer should be pointing to this node Returns the node, not the value inside it If list is empty, return None partition(low, high) - (20%) o Takes in two nodes from the list as a parameter You can fetch these nodes with get_first_node and get_last_node o Uses low as a pivot Loops from low to high and moves all nodes smaller than low so they are ahead(left side) of the low node. Example: List before partition: 10 7 7 14 10 15 18 24 13 7 11 8 8 13 Low is 10 which is also a pivot High is 13 List after partition: 7718 24 7 8 8 10 14 10 15 13 11 13 Note: The list is not sorted but all elements left of 10 are smaller then 10 and all elements right of 10 are bigger(or equal) The order of elements above and below pivot doesn't matter, only that they are on the correct side of the pivot After partitioning current position should point towards the pivot o Partition will only be tested with valid low and high nodes sort() - (20%) o Order the items in the list with any method that uses only your DLL structure No moving everything to another structure, sorting and then moving back! After sorting reset the current position to the beginning of the list 5% Bonus for implementing sort using quicksort Partition comes in handy when implementing quicksort None, prev = None, next None): class Node: def _init__(self, data self data data self.prev prev self.next next class DLL: def _init__(self): pass def insert (self, data): pass def remove(self): pass def get_value(self): return None def move_to_next(self): pass def move_to_prev(self): pass def move_to_pos(self, pos): pass def clear(self): pass def get_first_node (self): pass def get_last_node (self): pass def partition(self, low, high): pass
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


