Question: Programming code: Matlab A. Create a program that estimates pi (Tt) by simulation. This is accomplished by drawing random points in a unit square (1x1),
Programming code: Matlab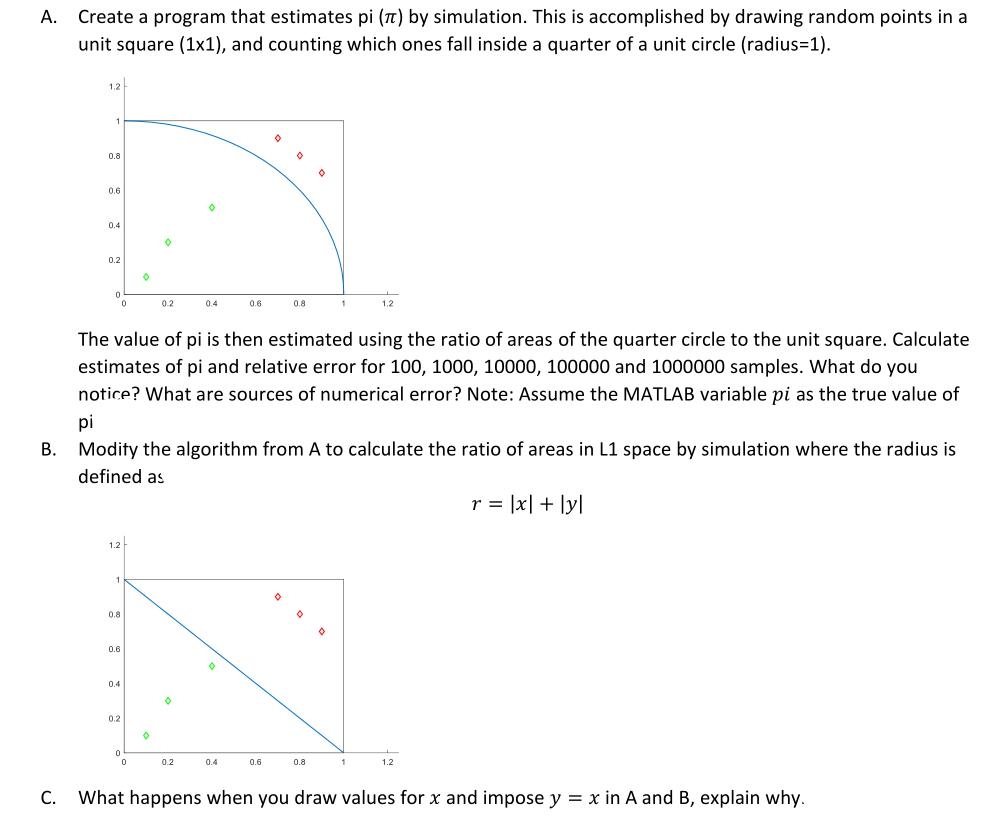
A. Create a program that estimates pi (Tt) by simulation. This is accomplished by drawing random points in a unit square (1x1), and counting which ones fall inside a quarter of a unit circle (radius=1). 1.2 1 0.8 o 0.6 0.4 0.2 o 0 02 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 The value of pi is then estimated using the ratio of areas of the quarter circle to the unit square. Calculate estimates of pi and relative error for 100, 1000, 10000, 100000 and 1000000 samples. What do you notice? What are sources of numerical error? Note: Assume the MATLAB variable pi as the true value of pi B. Modify the algorithm from A to calculate the ratio of areas in L1 space by simulation where the radius is defined as r = [x] + [y] 1.2 1 0 0.8 0 0.6 0 0.4 0.2 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.2 C. What happens when you draw values for x and impose y = x in A and B, explain why. A. Create a program that estimates pi (Tt) by simulation. This is accomplished by drawing random points in a unit square (1x1), and counting which ones fall inside a quarter of a unit circle (radius=1). 1.2 1 0.8 o 0.6 0.4 0.2 o 0 02 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 The value of pi is then estimated using the ratio of areas of the quarter circle to the unit square. Calculate estimates of pi and relative error for 100, 1000, 10000, 100000 and 1000000 samples. What do you notice? What are sources of numerical error? Note: Assume the MATLAB variable pi as the true value of pi B. Modify the algorithm from A to calculate the ratio of areas in L1 space by simulation where the radius is defined as r = [x] + [y] 1.2 1 0 0.8 0 0.6 0 0.4 0.2 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.2 C. What happens when you draw values for x and impose y = x in A and B, explain why
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


