Question: PROGRAMMING LOGIC AND DESIGN PLEASE HELP ME!! The equation to compute for the width of the trapezoid: portaal Therefore, proving this equation was derived from
PROGRAMMING LOGIC AND DESIGN
PLEASE HELP ME!!

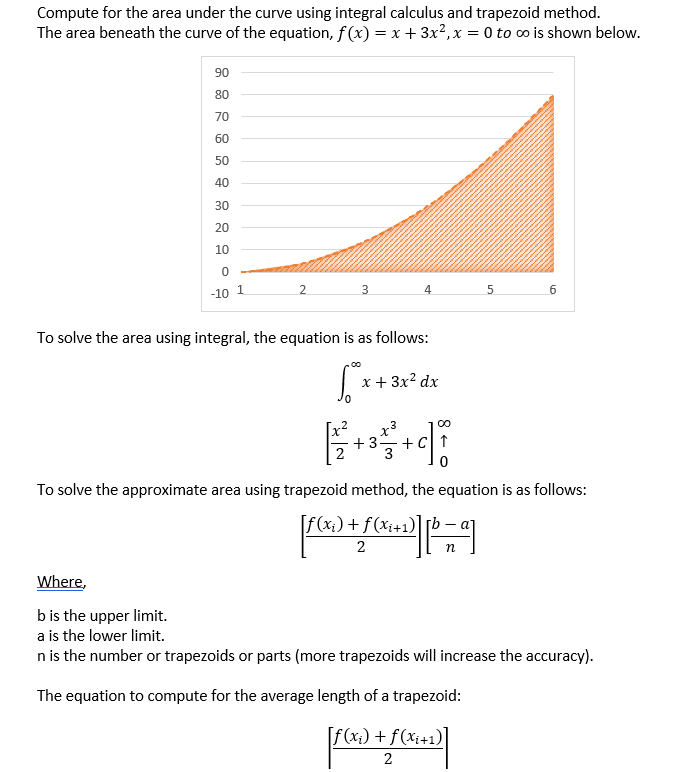

The equation to compute for the width of the trapezoid: portaal Therefore, proving this equation was derived from the area of the trapezoid: a + b h ch 2. Task Draw the flowchart and write the pseudocode that will compute for the area under the curve of the equation, f(x) = x + 3x2 Input: The lower limit a. The upper limit b. The number of trapezoids. Guide to compute for the area using trapezoids: Declare an array whose size will be equal to the number of trapezoids. Use a looping structure. Pass arguments to a module that will compute for the area of the trapezoid and return the area back to the calling method. Each element in the array will be assigned the returned area for every trapezoid. Use an accumulator to compound the sum of each element in the array. Guide to compute for the area using integral: Pass arguments to a module that will compute for the area under the curve and return the area back to the calling method. Assign the returned area to a variable. Output: The area of each trapezoid. The area using the trapezoid method. The area using integral calculus. Percentage error (absolute). True value - Experimental value %Error = x100 True value Compute for the area under the curve using integral calculus and trapezoid method. The area beneath the curve of the equation, f(x) = x + 3x2, x = 0 to co is shown below. 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 -10 1 2 3 4 5 6 To solve the area using integral, the equation is as follows: ** x + 3x2 dx 00 +3 +C1 3 0 To solve the approximate area using trapezoid method, the equation is as follows: f(xi) + f(Xi+1)][b 2 Where, b is the upper limit. a is the lower limit. n is the number or trapezoids or parts (more trapezoids will increase the accuracy). The equation to compute for the average length of a trapezoid: f%) [f(x) + f(xi+1) 2 Use the screenshot below to guide you in completing the rest of your logic. Trapezoid area are. CWINDOWSystemvonden Enter the value for a: Enter the value for b: Specify the number of trapezoids: Trapezoid area 1 units squared. Trapezoid area 2 units squared Traperoid area units squared. Traperoid area units squared. Trapezoid areas units squared. Traperold area 6 units squared units squared Trapezoid area & units squared units squared area 10 units squared area 11 - units squared area 12 - units squared area 13 - units squared. area 14 - units squared. Trapezoid area 15 - units squared Trapezoid area 16 - units squared. Trapezoid area 17 - units squared Trapezoid area 18 - units squared. Trapezoid area 19 - units squared. Trapezoid area 20 = units squared The area using trapezoid method = units squared. The area using integral calculus = units squared. percent error = Press any key to continue 7.5 3. Flowchart Grading Criteria Called a module and passed arguments to compute for the area of the trapezoid. The module returned the area back to the calling method. Called a module and passed arguments to compute for the area under the curve using 7.5 integral. The module returned the area back to the calling method. 7.5 An array was used to store the area of each trapezoid. Used an accumulator variable to compound the areas stored in each array element. 2.5 All needed variables were declared. 2.5 Used prompts whenever necessary. Correct looping structure. Correct sequence. 5 Correct statements. 50 5 7.5 5 4. Pseudocode Grading Criteria 7.5 Called a module and passed arguments to compute for the area of the trapezoid. The module returned the area back to the calling method. 7.5 Called a module and passed arguments to compute for the area under the curve using integral. The module returned the area back to the calling method. 7.5 An array was used to store the area of each trapezoid. 5 Used an accumulator variable to compound the areas stored in each array element. All needed variables were declared. Used prompts whenever necessary. Correct looping structure. 5 Correct sequence. Correct statements. 2.5 2.5 7.5 5 50 The equation to compute for the width of the trapezoid: portaal Therefore, proving this equation was derived from the area of the trapezoid: a + b h ch 2. Task Draw the flowchart and write the pseudocode that will compute for the area under the curve of the equation, f(x) = x + 3x2 Input: The lower limit a. The upper limit b. The number of trapezoids. Guide to compute for the area using trapezoids: Declare an array whose size will be equal to the number of trapezoids. Use a looping structure. Pass arguments to a module that will compute for the area of the trapezoid and return the area back to the calling method. Each element in the array will be assigned the returned area for every trapezoid. Use an accumulator to compound the sum of each element in the array. Guide to compute for the area using integral: Pass arguments to a module that will compute for the area under the curve and return the area back to the calling method. Assign the returned area to a variable. Output: The area of each trapezoid. The area using the trapezoid method. The area using integral calculus. Percentage error (absolute). True value - Experimental value %Error = x100 True value Compute for the area under the curve using integral calculus and trapezoid method. The area beneath the curve of the equation, f(x) = x + 3x2, x = 0 to co is shown below. 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 -10 1 2 3 4 5 6 To solve the area using integral, the equation is as follows: ** x + 3x2 dx 00 +3 +C1 3 0 To solve the approximate area using trapezoid method, the equation is as follows: f(xi) + f(Xi+1)][b 2 Where, b is the upper limit. a is the lower limit. n is the number or trapezoids or parts (more trapezoids will increase the accuracy). The equation to compute for the average length of a trapezoid: f%) [f(x) + f(xi+1) 2 Use the screenshot below to guide you in completing the rest of your logic. Trapezoid area are. CWINDOWSystemvonden Enter the value for a: Enter the value for b: Specify the number of trapezoids: Trapezoid area 1 units squared. Trapezoid area 2 units squared Traperoid area units squared. Traperoid area units squared. Trapezoid areas units squared. Traperold area 6 units squared units squared Trapezoid area & units squared units squared area 10 units squared area 11 - units squared area 12 - units squared area 13 - units squared. area 14 - units squared. Trapezoid area 15 - units squared Trapezoid area 16 - units squared. Trapezoid area 17 - units squared Trapezoid area 18 - units squared. Trapezoid area 19 - units squared. Trapezoid area 20 = units squared The area using trapezoid method = units squared. The area using integral calculus = units squared. percent error = Press any key to continue 7.5 3. Flowchart Grading Criteria Called a module and passed arguments to compute for the area of the trapezoid. The module returned the area back to the calling method. Called a module and passed arguments to compute for the area under the curve using 7.5 integral. The module returned the area back to the calling method. 7.5 An array was used to store the area of each trapezoid. Used an accumulator variable to compound the areas stored in each array element. 2.5 All needed variables were declared. 2.5 Used prompts whenever necessary. Correct looping structure. Correct sequence. 5 Correct statements. 50 5 7.5 5 4. Pseudocode Grading Criteria 7.5 Called a module and passed arguments to compute for the area of the trapezoid. The module returned the area back to the calling method. 7.5 Called a module and passed arguments to compute for the area under the curve using integral. The module returned the area back to the calling method. 7.5 An array was used to store the area of each trapezoid. 5 Used an accumulator variable to compound the areas stored in each array element. All needed variables were declared. Used prompts whenever necessary. Correct looping structure. 5 Correct sequence. Correct statements. 2.5 2.5 7.5 5 50
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


