Question: Project 1: We can store k stacks in a single array if we use the data structure suggested in Figure 1 shown below, for the
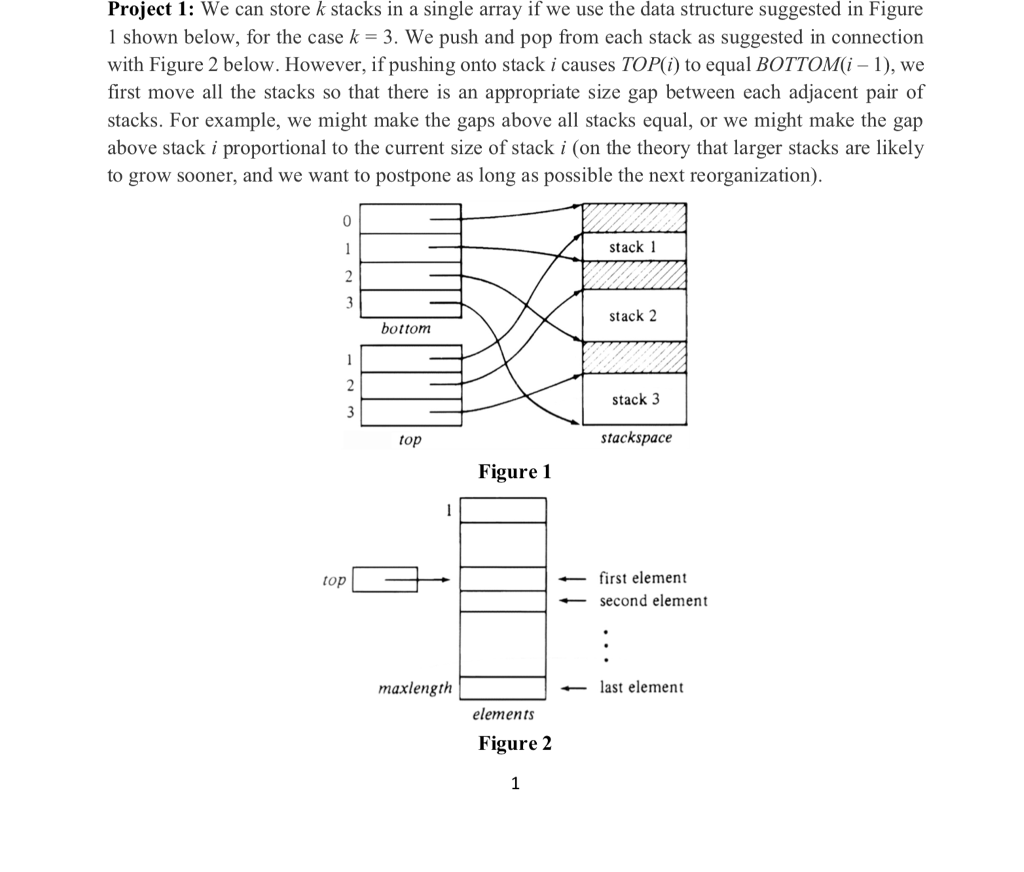

Project 1: We can store k stacks in a single array if we use the data structure suggested in Figure 1 shown below, for the case k- 3. We push and pop from each stack as suggested in connection with Figure 2 below. However, if pushing onto stack i causes TOP(i) to equal BOTTOM(i -1), we first move all the stacks so that there is an appropriate size gap between each adjacent pair of stacks. For example, we might make the gaps above all stacks equal, or we might make the gap above stack i proportional to the current size of stack i (on the theory that larger stacks are likely to grow sooner, and we want to postpone as long as possible the next reorganization) stack 1 stack 2 bottom tack 3 top stackspace Figure 1 first element second element top maxlength -last element elements Figure 2 Project 1: We can store k stacks in a single array if we use the data structure suggested in Figure 1 shown below, for the case k- 3. We push and pop from each stack as suggested in connection with Figure 2 below. However, if pushing onto stack i causes TOP(i) to equal BOTTOM(i -1), we first move all the stacks so that there is an appropriate size gap between each adjacent pair of stacks. For example, we might make the gaps above all stacks equal, or we might make the gap above stack i proportional to the current size of stack i (on the theory that larger stacks are likely to grow sooner, and we want to postpone as long as possible the next reorganization) stack 1 stack 2 bottom tack 3 top stackspace Figure 1 first element second element top maxlength -last element elements Figure 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


