Question: Project Description Conduction within relatively complex geometries can sometimes be evaluated easily by using the finite - difference methods that are applied to subdomains and
Project Description
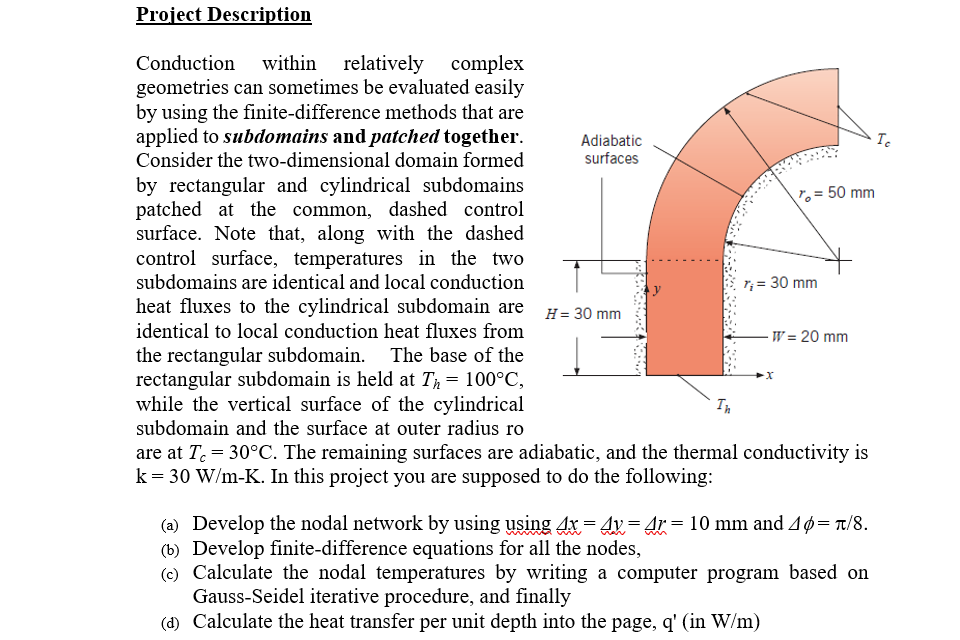
Conduction within relatively complex
geometries can sometimes be evaluated easily
by using the finitedifference methods that are
applied to subdomains and patched together.
Consider the twodimensional domain formed
by rectangular and cylindrical subdomains
patched at the common, dashed control
surface. Note that, along with the dashed
control surface, temperatures in the two
subdomains are identical and local conduction
heat fluxes to the cylindrical subdomain are
identical to local conduction heat fluxes from
the rectangular subdomain. The base of the
rectangular subdomain is held at Thdeg C
while the vertical surface of the cylindrical
subdomain and the surface at outer radius ro
are at Tcdeg C The remaining surfaces are adiabatic, and the thermal conductivity is
kWmK In this project you are supposed to do the following:
a Develop the nodal network by using using Delta xDelta
u Delta rmm and Delta phi pi
b Develop finitedifference equations for all the nodes,
c Calculate the nodal temperatures by writing a computer program based on
GaussSeidel iterative procedure, and finally
d Calculate the heat transfer per unit depth into the page, qWm
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


