Question: Project Description: Implement the A * search algorithm with graph search ( no repeated states ) for the robot path planning problem as described below.
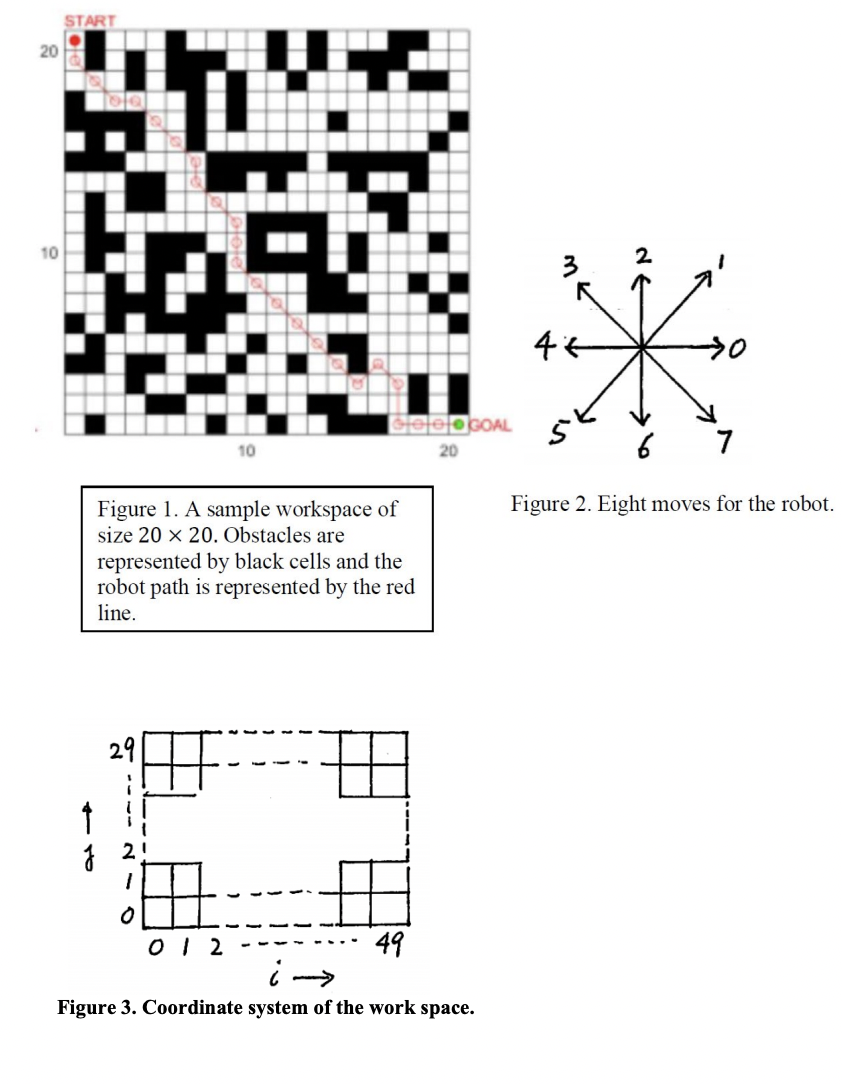
Project Description: Implement the A search algorithm with graph search no repeated states for the robot path planning problem as described below. The inputs to your program are the start and goal positions of a point robot, and a D integer array that represents the robot workspace. The robot can move from cell to cell in any of the eight directions as shown in Figure The goal is to find the lowestcost path between the start position and the goal position, and avoiding obstacles along the path. The workspace is represented as an occupancy grid as shown in Figure where the black cells represent obstacles. The red line in the figure depicts a path from the start position to the goal position. Note: the path in the figure is not the lowestcost path as required in our project. Formulation: The problem can be formulated in the following way. Each cell in the workspace is a state. The white cells are legal states and the black cells are illegal states. The actions are the eight moves as defined in Figure The step cost for the actions is the sum of the angle cost and the distance cost; ie where ; let if s is the initial state start position; if let equals for horizontal and vertical moves and for diagonal moves In the above, s is the current state, a is the action and s is the next state. The angle cost is to penalize any change in the direction of the robot between two consecutive moves. k is a constant that we can set to control the amount of penalty we want to impose for angle change. For the initial state start position we let the angle cost between the initial state s and next state s equals to The distance cost is for the distance travelled in an action. Let be the Euclidian distance between the current position and the goal position. thus defined is admissible in this problem. During the search, only legal states cells without obstacles will be added to the tree. Input and output formats: The workspace in the test input files is of size rows x columns. We will use the coordinate system as shown in Figure below. The coordinates of the lowerleft corner cell are The input file contains lines of integers as shown in Figure below. Line contains the coordinates of the start and goal positions of the point robot. Lines to contain the cell values of the robot workspace, with s representing white cells, s representing black cells, representing the start position and representing the goal position. Line contains values for with to Line contains values for with to etc. The integers in each line are separated by blank spaces. Your program will produce an output text file that contains lines of text as shown in Figure below. Line contains the depth level d of the goal node as found by the A algorithm assume that the root node is at level Line contains the total number of nodes N generated in your tree including the root node. Line contains the solution a sequence of moves from the root node to the goal node represented by as The as are separated by blanks. Each a is a move from the set Line contains the fn values of the nodes separated by blanks, from the root node to the goal node, along the solution path. There should be d number of a values in line and d number of f values in line Lines to contain values for the robot workspace, with s representing white cells, s representing black cells, representing the start position, representing the goal position, and s representing cells along the solution path excluding the start position and the goal position. Figure A sample workspace of size times Obstacles are represented by black cells and the robot path is represented by the red line.
Figure Eight moves for the robot.
Figure Coordinate system of the work space.
nnnn
m m m m m m m
m m m m m m m
m m m m m m m
Figure Input file format lines. ns and m s are integers separated by blanks.
d
N
a a a a
ffff
m m m m m m m
m m m m m mm
m m m m m m m
Figure Output file format lines. d N as and ms are integers. fs are floating point numbers. The as fs and ms are separated by blanks.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


