Question: Provide complete answer with clear working, show all units & box final answer Thanks 5. Figure 2 shows a schematic of a continuous stirred tank
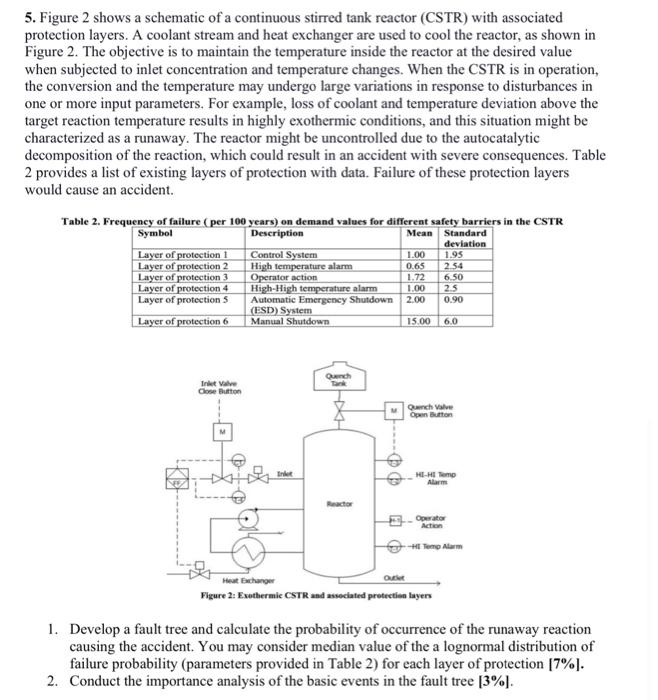
5. Figure 2 shows a schematic of a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) with associated protection layers. A coolant stream and heat exchanger are used to cool the reactor, as shown in Figure 2. The objective is to maintain the temperature inside the reactor at the desired value when subjected to inlet concentration and temperature changes. When the CSTR is in operation, the conversion and the temperature may undergo large variations in response to disturbances in one or more input parameters. For example, loss of coolant and temperature deviation above the target reaction temperature results in highly exothermic conditions, and this situation might be characterized as a runaway. The reactor might be uncontrolled due to the autocatalytic decomposition of the reaction, which could result in an accident with severe consequences. Table 2 provides a list of existing layers of protection with data. Failure of these protection layers would cause an accident. Table 2. Frequenev of failure ( ner 100 vearsi an demand values for different safetv harriers in the CSTR 1. Develop a fault tree and calculate the probability of occurrence of the runaway reaction causing the accident. You may consider median value of the a lognormal distribution of failure probability (parameters provided in Table 2) for each layer of protection [7\%]. 2. Conduct the importance analysis of the basic events in the fault tree [3\%]. 5. Figure 2 shows a schematic of a continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR) with associated protection layers. A coolant stream and heat exchanger are used to cool the reactor, as shown in Figure 2. The objective is to maintain the temperature inside the reactor at the desired value when subjected to inlet concentration and temperature changes. When the CSTR is in operation, the conversion and the temperature may undergo large variations in response to disturbances in one or more input parameters. For example, loss of coolant and temperature deviation above the target reaction temperature results in highly exothermic conditions, and this situation might be characterized as a runaway. The reactor might be uncontrolled due to the autocatalytic decomposition of the reaction, which could result in an accident with severe consequences. Table 2 provides a list of existing layers of protection with data. Failure of these protection layers would cause an accident. Table 2. Frequenev of failure ( ner 100 vearsi an demand values for different safetv harriers in the CSTR 1. Develop a fault tree and calculate the probability of occurrence of the runaway reaction causing the accident. You may consider median value of the a lognormal distribution of failure probability (parameters provided in Table 2) for each layer of protection [7\%]. 2. Conduct the importance analysis of the basic events in the fault tree [3\%]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


