Question: Provide Simple Python Code for the following function with comments and a screenshot of the code: Challenge Write a function called partition_modulo_n that accepts an
Provide Simple Python Code for the following function with comments and a screenshot of the code:
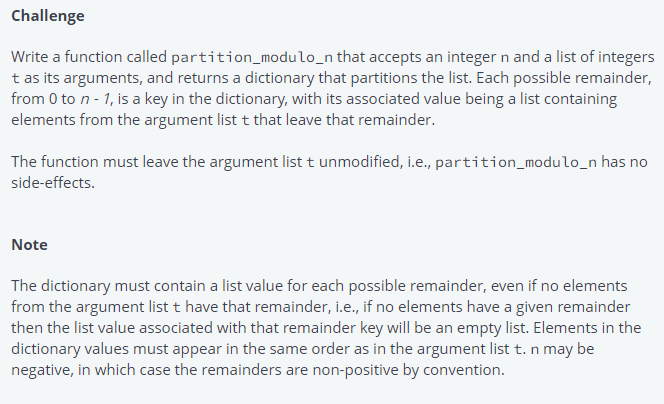
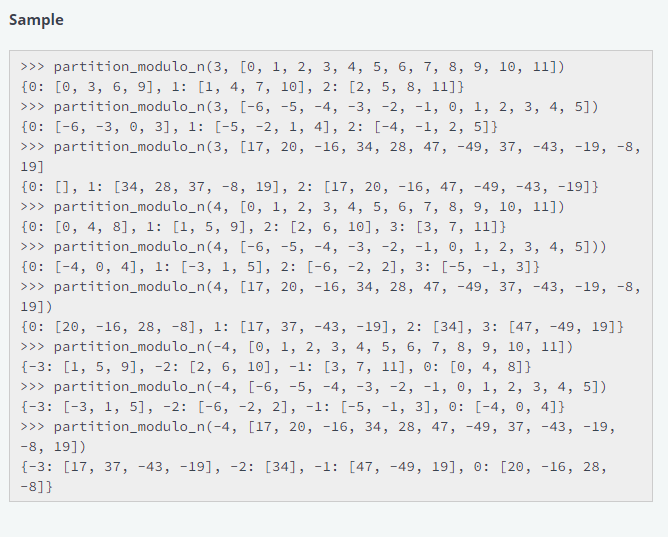

Challenge Write a function called partition_modulo_n that accepts an integer n and a list of integers tas its arguments, and returns a dictionary that partitions the list. Each possible remainder, from 0 to n-1, is a key in the dictionary, with its associated value being a list containing elements from the argument list t that leave that remainder. The function must leave the argument list t unmodified, i.e., partition_modulo_n has no side-effects. Note The dictionary must contain a list value for each possible remainder, even if no elements from the argument list t have that remainder, i.e., if no elements have a given remainder then the list value associated with that remainder key will be an empty list. Elements in the dictionary values must appear in the same order as in the argument list t. n may be negative, in which case the remainders are non-positive by convention. Sample >>> partition_modulo_n(3, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]) {0: [0, 3, 6, 9], 1: [1, 4, 7, 10], 2: [2, 5, 8, 11]} >>> partition_modulo_n(3, [-6, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) {0: [-6, -3, 0, 3], 1: [-5, -2, 1, 4], 2: [-4, -1, 2, 5]} >>> partition_modulo_n(3, [17, 20, -16, 34, 28, 47, -49, 37, -43, -19, -8, 19] {0: [], 1: [34, 28, 37, -8, 19], 2: (17, 20, -16, 47, -49, -43, -19]} >>> partition_modulo_n(4, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]) {0: [0, 4, 8], 1: [1, 5, 9], 2: [2, 6, 10], 3: [3, 7, 11]} >>> partition_modulo_n(4, [-6, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])) {0: [-4, 0, 4], 1: [-3, 1, 5], 2: [-6, -2, 2], 3: [-5, -1, 3]} >>> partition_modulo_n(4, [17, 20, -16, 34, 28, 47, -49, 37, -43, -19, -8, 19]) {0: [20, -16, 28, -8], 1: [17, 37, -43, -19], 2: [34], 3: [47, -49, 19]} >>> partition_modulo_n(-4, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]) {-3: [1, 5, 9], -2: [2, 6, 10], -1: [3, 7, 11], 0: [0, 4, 8]} >>> partition_modulo_n(-4, [-6, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) {-3: [-3, 1, 5], -2: [-6, -2, 2], -1: [-5, -1, 3], 0: [-4, 0, 4]} >>> partition_modulo_n(-4, [17, 20, -16, 34, 28, 47, -49, 37, -43, -19, -8, 19]) {-3: [17, 37, -43, -19], -2: [34], -1: [47, -49, 19], 0: [20, -16, 28, -8]] Input/Output Input consists of a single integer by itself on the first line to represent n, and zero or more space-separated integers on the second line to represent integers in list t. HackerRank will read in the integers and pass the arguments to your function, and then output the dictionary, with the keys sorted in a natural order. Dictionary values, however, will not be sorted. Constraints isinstance(n, int) and all(isinstance(i, int) for i in t) and n != O is True
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


