Question: Provide the name and formula for the two reactants in this experiment. a) Do Calculations 1 and 2 explained on page 8 . Record the
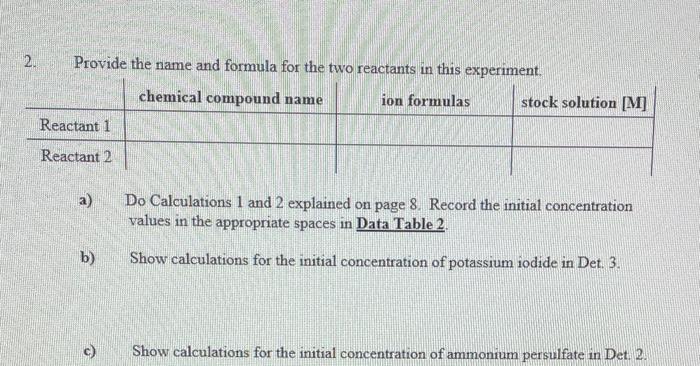

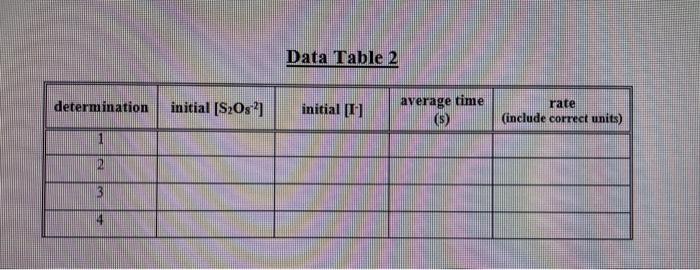
Provide the name and formula for the two reactants in this experiment. a) Do Calculations 1 and 2 explained on page 8 . Record the initial concentration values in the appropriate spaces in Data Table 2. b) Show calculations for the initial concentration of potassium iodide in Det. 3. 1. Calculate the initial concentration of iodide ions for each determination, and record them on Data Table 2. "Initial" here means at the moment the solutions are mixed but before any reaction has taken place. So this is, in effect, a dilution calculation. For example, in determination 1, you have taken 4.00mL of 0.20MKI and diluted it to a total volume of 19.00mL. (Note that the total volume for all six determinations is 19.00 mL.) You can use the dilution formula M1V1=M2V2 to calculate the initial concentration M2 at the moment of mixing, where M1 and M2 are the undiluted and diluted molarities, and V1 and V2 are the undiluted and diluted volumes, respectively. 2. Calculate the initial concentration of persulfate ions for each determination using volumes and concentrations of (NH4)2S2O8 along with equation 18 . Record these initial concentrations on Data Table 2. 3. Calculate the average reaction time for each of the four determinations, and record on both Data Table 1 and Data Table 2. 4. Calculate the reaction rate for each determination using equation 9 . Use your average reaction times for t in equation 9. Record the rates on Data Table 2, including correct units with your rates. 5. Using your data for determinations 1 and 2 , calculate the reaction order with respect to persulfate ion by solving for x in equation 15 . Calculate x to two digits to the right of the decimal point by taking the logarithm of both sides (see mathematical note on page 13. Record the results on Data Table 3. 6. Using your data for determinations 3 and 4 , calculate the reaction order with respect to iodide ion by solving for y in equation 16. Calculate y to two digits to the right of the decimal point. Record the results on Data Table 3 , 7. Using equation 17, calculate the rate constant, k, for each of the four determinations. Record your results on Data Table 4. Be sure to include correct units with your rate constants. 8. On the bottom line of Data Table 4, write the complete rate law for the reaction you studied in this experiment. Include the average of your calculated values for the rate constant, k, and your reaction orders rounded off to an integer. Data Table 2 Provide the name and formula for the two reactants in this experiment. a) Do Calculations 1 and 2 explained on page 8 . Record the initial concentration values in the appropriate spaces in Data Table 2. b) Show calculations for the initial concentration of potassium iodide in Det. 3. 1. Calculate the initial concentration of iodide ions for each determination, and record them on Data Table 2. "Initial" here means at the moment the solutions are mixed but before any reaction has taken place. So this is, in effect, a dilution calculation. For example, in determination 1, you have taken 4.00mL of 0.20MKI and diluted it to a total volume of 19.00mL. (Note that the total volume for all six determinations is 19.00 mL.) You can use the dilution formula M1V1=M2V2 to calculate the initial concentration M2 at the moment of mixing, where M1 and M2 are the undiluted and diluted molarities, and V1 and V2 are the undiluted and diluted volumes, respectively. 2. Calculate the initial concentration of persulfate ions for each determination using volumes and concentrations of (NH4)2S2O8 along with equation 18 . Record these initial concentrations on Data Table 2. 3. Calculate the average reaction time for each of the four determinations, and record on both Data Table 1 and Data Table 2. 4. Calculate the reaction rate for each determination using equation 9 . Use your average reaction times for t in equation 9. Record the rates on Data Table 2, including correct units with your rates. 5. Using your data for determinations 1 and 2 , calculate the reaction order with respect to persulfate ion by solving for x in equation 15 . Calculate x to two digits to the right of the decimal point by taking the logarithm of both sides (see mathematical note on page 13. Record the results on Data Table 3. 6. Using your data for determinations 3 and 4 , calculate the reaction order with respect to iodide ion by solving for y in equation 16. Calculate y to two digits to the right of the decimal point. Record the results on Data Table 3 , 7. Using equation 17, calculate the rate constant, k, for each of the four determinations. Record your results on Data Table 4. Be sure to include correct units with your rate constants. 8. On the bottom line of Data Table 4, write the complete rate law for the reaction you studied in this experiment. Include the average of your calculated values for the rate constant, k, and your reaction orders rounded off to an integer. Data Table 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


