Question: public class Animalbriver { public static void main(String[] args) { Dog dog = new Dog(woof); Cat cat = new Cat (meow); Pig pig = new
![public class Animalbriver { public static void main(String[] args) { Dog](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f2e8f30d416_37866f2e8f2a5a9c.jpg)
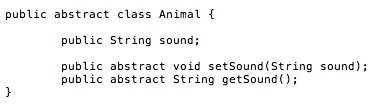

public class Animalbriver { public static void main(String[] args) { Dog dog = new Dog("woof"); Cat cat = new Cat ("meow"); Pig pig = new Pig("oink"); System.out.println(dog); System.out.println(cat); System.out.println(pig); public abstract class Animal { public String sound; public abstract void set Sound (String sound); public abstract String get Sound(); Given the parent abstract class Animal , create child classes Dog, Cat and Pig that implement the methods defined in the abstract class. In addition, create a constructor that takes a string parameter that represents the sound the animal makes and a toString method to provide a string representation of the object in each of the child classes. Your program should run with this diver without modification
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


