Question: public class TreePrinter { private static final int MAX_LEVELS = 6; private BinarySearchTree tree; // the tree private int height; // its height // Powers
public class TreePrinter { private static final int MAX_LEVELS = 6; private BinarySearchTree
// Queue of nodes at this level. BinaryNode 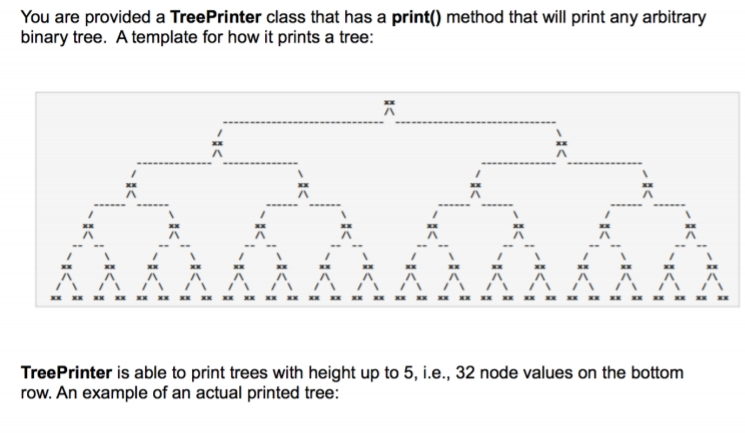

![Powers of 2 private static int POWERS_OF_2[] = new int[MAX_LEVELS+2]; static {](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f3be88cc863_05666f3be884b22f.jpg)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


